Future COVID-19 Tests Could Be Based on Biomarkers and Molecular Profiles of Individuals
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 23 Oct 2020 |
Illustration
A new study has shown how variations in SARS-CoV-2 host gene expression can be linked to variations in COVID-19 susceptibility and symptom severity. This could pave the way for better medical tests based on biomarkers and molecular profiles of individuals, to accommodate these variations in monitoring virus transmission and disease pathology, which helps guide mitigation and treatment options.
People have different susceptibilities to the SARS-CoV-2 virus and develop varying degrees of fever, fatigue, and breathing problems - common symptoms of the illness. Scientists at the University of California, Riverside (Riverside, CA, USA) and University of Southern California (Los Angeles, CA, USA) may have an answer to explain this variation. The scientists have shown for the first time that the observed COVID-19 variability may have underlying molecular sources. The finding could help in the development of effective prophylactic and therapeutic strategies against the disease.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus hijacks human host molecules for fusion and virus replication, attacking human cellular functions. These human host molecules are collectively called SARS-CoV-2 host genes. The scientists systematically analyzed SARS-CoV-2 host gene expression, their variations, and age- and sex-dependency in the human population using large-scale genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. They first found similarity of host gene expression is generally correlated with tissue vulnerability to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Among the six most variably expressed genes in the population they identified ACE2, CLEC4G, and CLEC4M, which are known to interact with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
Higher expression of these genes likely increases the possibility of being infected and of developing severe symptoms. Other variable genes include SLC27A2 and PKP2, both known to inhibit virus replication; and PTGS2, which mediates fever response. The scientists also identified genetic variants linked to variable expression of these genes. According to them, the expression profiles of these marker genes may help better categorize risk groups. In addition to identifying the most variable SARS-CoV-2 host genes, results from the study suggest genetic and multiple biological factors underlie the population variation in SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptom severity. Next, the researchers plan to further analyze large scale genotypes and transcriptome data of COVID-19 patients when made available and to refine the results for higher association and accuracy.
“Based on biomarkers and molecular profiles of individuals, one would hope to develop better medical tests to accommodate these variations in monitoring virus transmission and disease pathology, which helps guide mitigation and treatment options,” said Sika Zheng, an associate professor of biomedical sciences at the UC Riverside School of Medicine, who led the study.
“More comprehensive risk assessment can better guide the early stage of vaccine distribution,” added Zheng. “Tests can also be developed to include these molecular markers to better monitor disease progression. They can also be used to stratify patients to assess and ultimately enhance treatment effectiveness.”
Related Links:
University of California
People have different susceptibilities to the SARS-CoV-2 virus and develop varying degrees of fever, fatigue, and breathing problems - common symptoms of the illness. Scientists at the University of California, Riverside (Riverside, CA, USA) and University of Southern California (Los Angeles, CA, USA) may have an answer to explain this variation. The scientists have shown for the first time that the observed COVID-19 variability may have underlying molecular sources. The finding could help in the development of effective prophylactic and therapeutic strategies against the disease.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus hijacks human host molecules for fusion and virus replication, attacking human cellular functions. These human host molecules are collectively called SARS-CoV-2 host genes. The scientists systematically analyzed SARS-CoV-2 host gene expression, their variations, and age- and sex-dependency in the human population using large-scale genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. They first found similarity of host gene expression is generally correlated with tissue vulnerability to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Among the six most variably expressed genes in the population they identified ACE2, CLEC4G, and CLEC4M, which are known to interact with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2.
Higher expression of these genes likely increases the possibility of being infected and of developing severe symptoms. Other variable genes include SLC27A2 and PKP2, both known to inhibit virus replication; and PTGS2, which mediates fever response. The scientists also identified genetic variants linked to variable expression of these genes. According to them, the expression profiles of these marker genes may help better categorize risk groups. In addition to identifying the most variable SARS-CoV-2 host genes, results from the study suggest genetic and multiple biological factors underlie the population variation in SARS-CoV-2 infection and symptom severity. Next, the researchers plan to further analyze large scale genotypes and transcriptome data of COVID-19 patients when made available and to refine the results for higher association and accuracy.
“Based on biomarkers and molecular profiles of individuals, one would hope to develop better medical tests to accommodate these variations in monitoring virus transmission and disease pathology, which helps guide mitigation and treatment options,” said Sika Zheng, an associate professor of biomedical sciences at the UC Riverside School of Medicine, who led the study.
“More comprehensive risk assessment can better guide the early stage of vaccine distribution,” added Zheng. “Tests can also be developed to include these molecular markers to better monitor disease progression. They can also be used to stratify patients to assess and ultimately enhance treatment effectiveness.”
Related Links:
University of California
Latest COVID-19 News
- New Immunosensor Paves Way to Rapid POC Testing for COVID-19 and Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Long COVID Etiologies Found in Acute Infection Blood Samples
- Novel Device Detects COVID-19 Antibodies in Five Minutes
- CRISPR-Powered COVID-19 Test Detects SARS-CoV-2 in 30 Minutes Using Gene Scissors
- Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis Linked to COVID-19
- Novel SARS CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test Validated for Diagnostic Accuracy
- New COVID + Flu + R.S.V. Test to Help Prepare for `Tripledemic`
- AI Takes Guesswork Out Of Lateral Flow Testing
- Fastest Ever SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test Designed for Non-Invasive COVID-19 Testing in Any Setting
- Rapid Antigen Tests Detect Omicron, Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- Health Care Professionals Showed Increased Interest in POC Technologies During Pandemic, Finds Study
- Set Up Reserve Lab Capacity Now for Faster Response to Next Pandemic, Say Researchers
- Blood Test Performed During Initial Infection Predicts Long COVID Risk
- Low-Cost COVID-19 Testing Platform Combines Sensitivity of PCR and Speed of Antigen Tests
- Finger-Prick Blood Test Identifies Immunity to COVID-19
- Quick Test Kit Determines Immunity Against COVID-19 and Its Variants
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more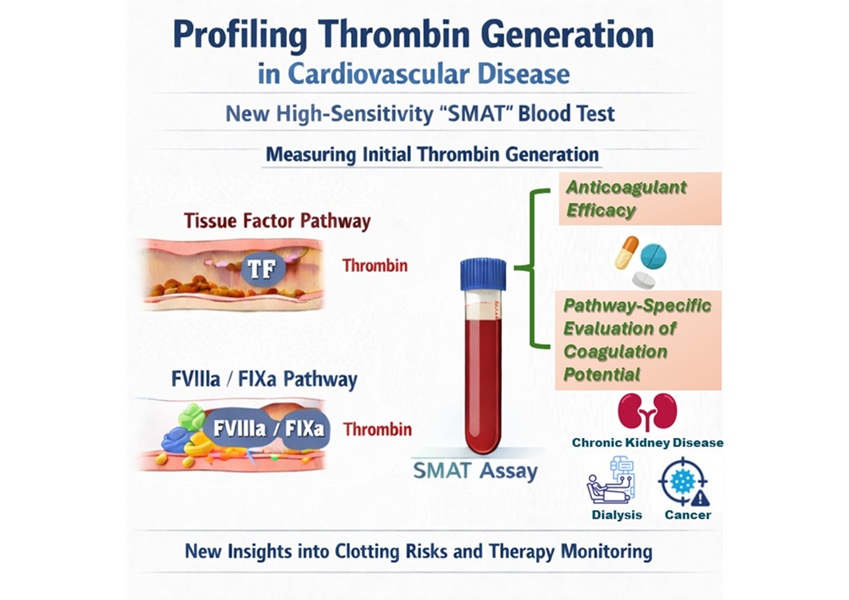
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel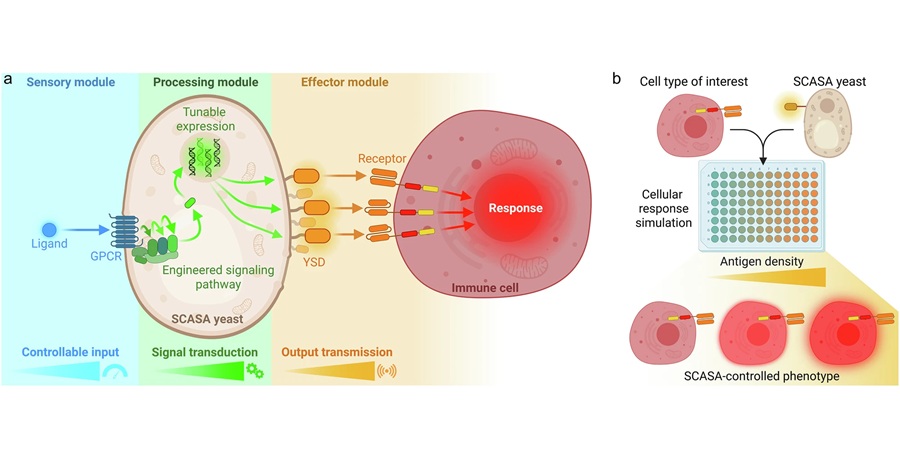
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more








 Analyzer.jpg)