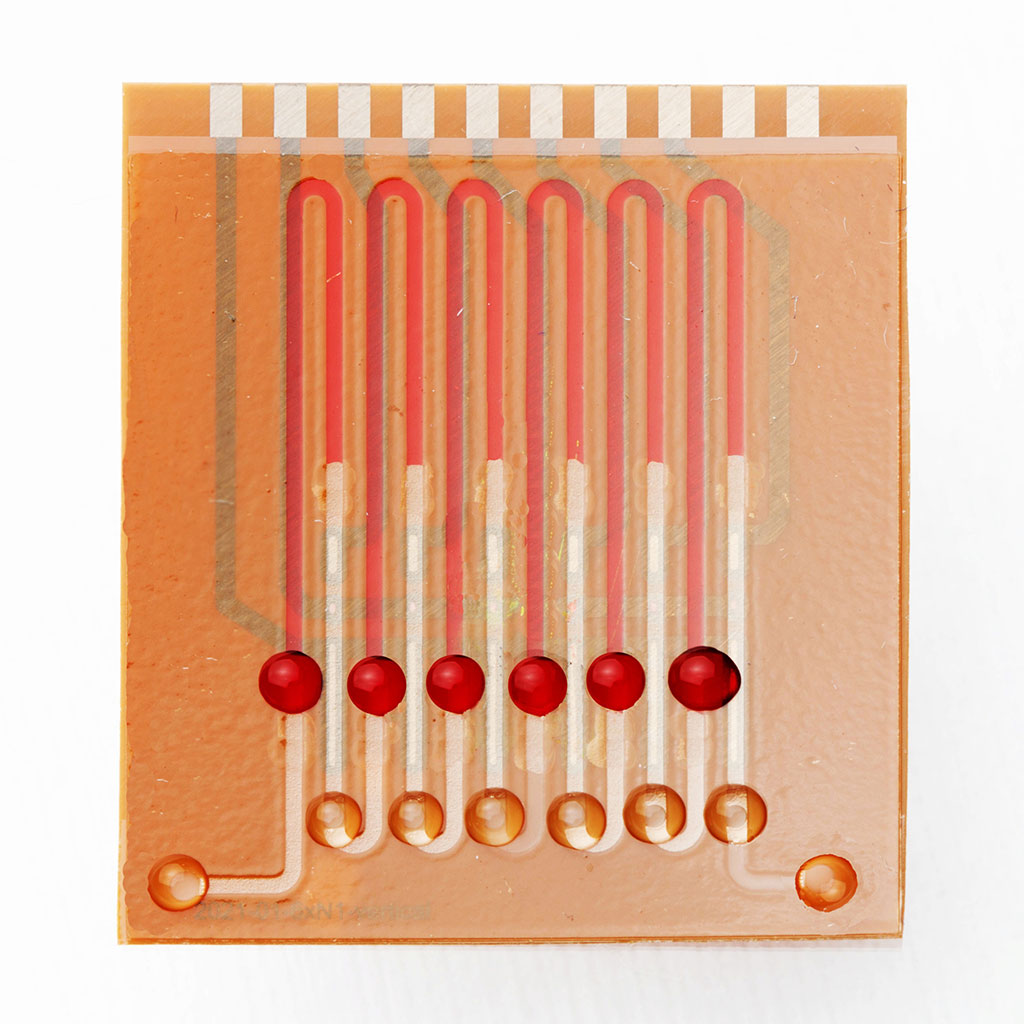
Novel Device Detects COVID-19 Antibodies in Five Minutes
Posted on 30 Nov 2022
Rapid, cheap and accurate tests continue to be essential for epidemiological surveillance and for health services to monitor and contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2. A team of scientists has now developed an electrochemical immunosensor that detects antibodies against the virus.
In search of a novel diagnostic method, a group of scientists at the Federal University of the ABC (UFABC, São Paulo, Brazil) opted for a material frequently used in metallurgy – zinc oxide – and combined it for the first time with fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass, a conductive material used in electrodes for photovoltaics and other advanced applications. The electrode fabricated by the researchers detected COVID-19 antibodies in serum in about five minutes with 88.7% sensitivity and 100% specificity, outperforming even the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test, the current gold-standard clinical diagnostic tool. One of the advantages of the electrode they developed is its flexible architecture, which means that it can easily be customized for other diagnostic and biomedical applications using different biomolecules on the zinc oxide nanorods and other target analytes.
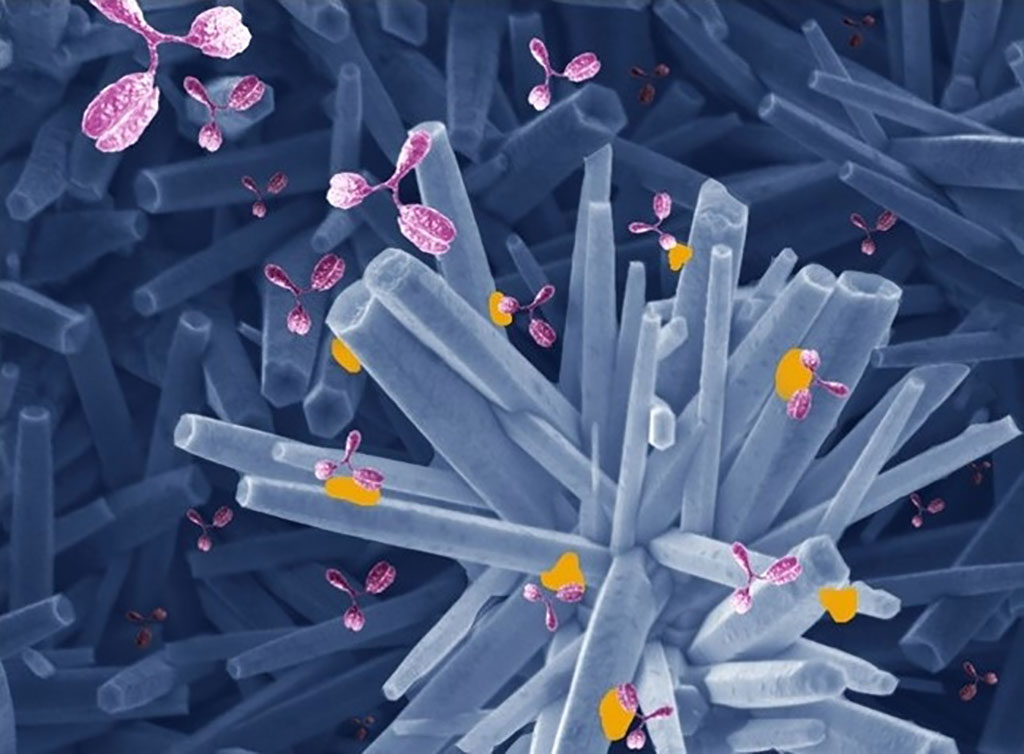
Prior knowledge of chemical properties such as the isoelectric point of the virus’s spike protein (S), enabled the group to develop a platform for S to bind electrostatically to zinc oxide nanorods. Zinc oxide is increasingly used to fabricate biosensors because of its versatility and unique chemical, optical and electrical properties. The immunosensor is easy to make and use, and its production cost is relatively low. The nanorods form a film on the FTO’s conductive surface, creating a favorable molecular microenvironment for immobilization of the S protein and making the construct a simple way to detect these antibodies. The researchers will now adapt the platform to make it portable and connectable to mobile devices for use in diagnosing COVID-19 and other infectious diseases.
“The technology is a versatile biosensing platform. As developed by us, it can be modified and customized for serological detection of other diseases of public health interest," said chemist Wendel Alves, lead author and a professor at the Center for Natural and Human Sciences, UFABC.
Related Links:
UFABC