Low-Cost COVID-19 Testing Platform Combines Sensitivity of PCR and Speed of Antigen Tests
Posted on 27 Sep 2022
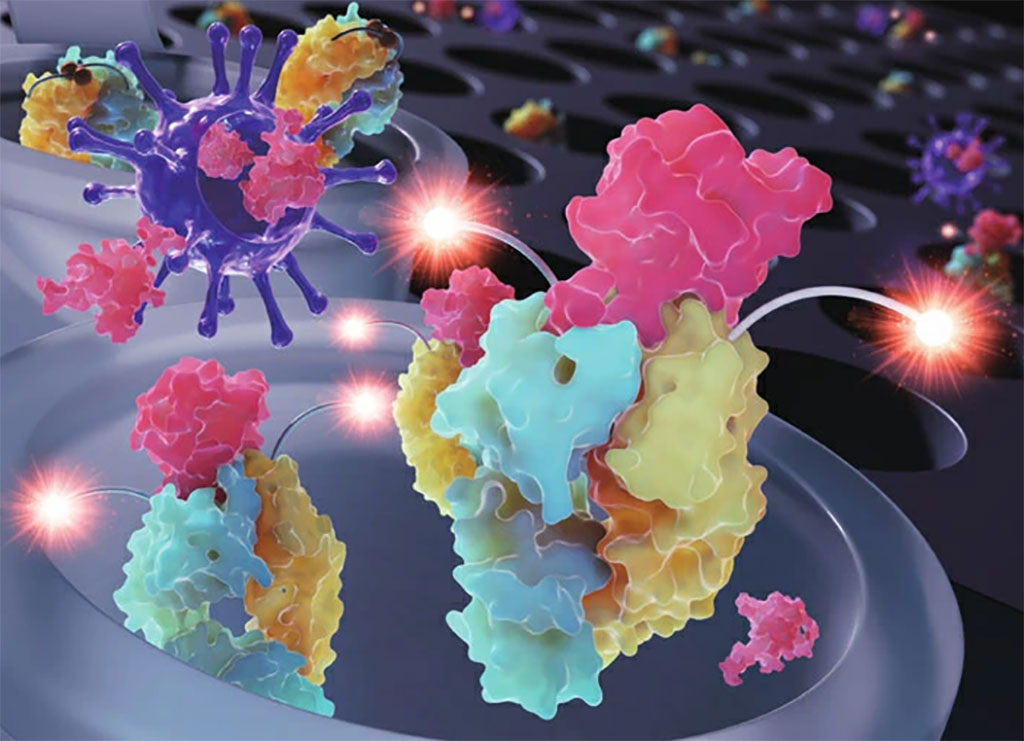
DNA is best known for its genetic properties, but it also can be folded into custom nanoscale structures that can perform functions or specifically bind to other structures much like proteins do. Now, a new study has shown that tiny nets woven from DNA strands can ensnare the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19, lighting up the virus for a fast-yet-sensitive diagnostic test – and also impeding it from infecting cells, thus opening a new possible route to antiviral treatment.
The DNA nets’ ability to detect and impede COVID-19 in human cell cultures was demonstrated by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (Champaign, IL, USA). The DNA nets were designed to bind to the coronavirus spike protein – the structure that sticks out from the surface of the virus and binds to receptors on human cells to infect them. Once bound, the nets give off a fluorescent signal that can be read by an inexpensive handheld device in about 10 minutes. The researchers demonstrated that their DNA nets effectively targeted the spike protein and were able to detect the virus at very low levels, equivalent to the sensitivity of gold-standard PCR tests that detect the virus’s genetic material but can take a day or more to return results from a clinical lab.
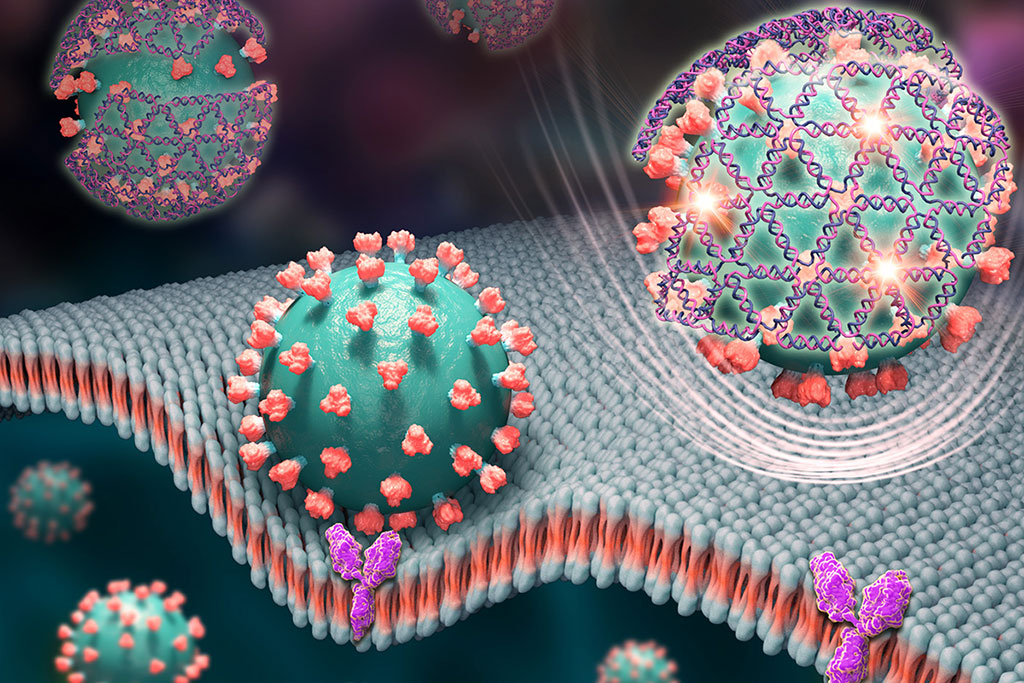
The technique holds several advantages. It does not need any special preparation or equipment, and can be performed at room temperature, so all a user would do is mix the sample with the solution and read it. The researchers estimated in their study that the method would cost USD 1.26 per test. The technique can detect the entire virus, which is still infectious, and distinguish it from fragments that may not be infectious anymore. This not only gives patients and physicians a better understanding of whether they are infectious, but it could greatly improve community-level modeling and tracking of active outbreaks, such as through wastewater. In addition, the DNA nets inhibited the virus’s spread in live cell cultures, with the antiviral activity increasing with the size of the DNA net scaffold. This points to DNA structures’ potential as therapeutic agents. The DNA net platform can be adapted to other viruses and even multiplexed so that a single test could detect multiple viruses.
“This platform combines the sensitivity of clinical PCR tests and the speed and low cost of antigen tests,” said study leader Xing Wang, a professor of bioengineering and of chemistry at Illinois. “We need tests like this for a couple of reasons. One is to prepare for the next pandemic. The other reason is to track ongoing viral epidemics – not only coronaviruses, but also other deadly and economically impactful viruses like HIV or influenza.”
Related Links:
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign