Microbiology
Immunoassays Compared to Improve Diagnosis of Chagas Disease
Chagas disease (CD), caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi, is a vector-borne infection of significant public health concern in Latin America, where nearly six million people are infected and 70 million are at risk of infection. More...26 Oct 2019

PCR Kit Developed for Detection of Q-fever Pathogen
Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular bacterium that causes Q fever in animals and humans. The infection results from inhalation of a spore-like small-cell variant, and from contact with the milk, urine, feces, vaginal mucus or semen of infected animals. More...17 Oct 2019

Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
Following careful analysis of DNA sequences collected in The Cancer Genome Atlas, researchers have proposed that CEACAM (carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule) proteins disrupt TGFB signaling, which alters the composition of the intestinal microbiome to promote development of colorectal cancer. More...14 Oct 2019
Stunted Microbiota and Opportunistic Pathogen Colonize C-Section Birth
Immediately after birth, newborn babies experience rapid colonization by microorganisms from their mothers and the surrounding environment. Infants born by Caesarean section have gut microbiomes that differ from those of infants born vaginally, carrying more hospital-associated opportunistic pathogens. More...10 Oct 2019
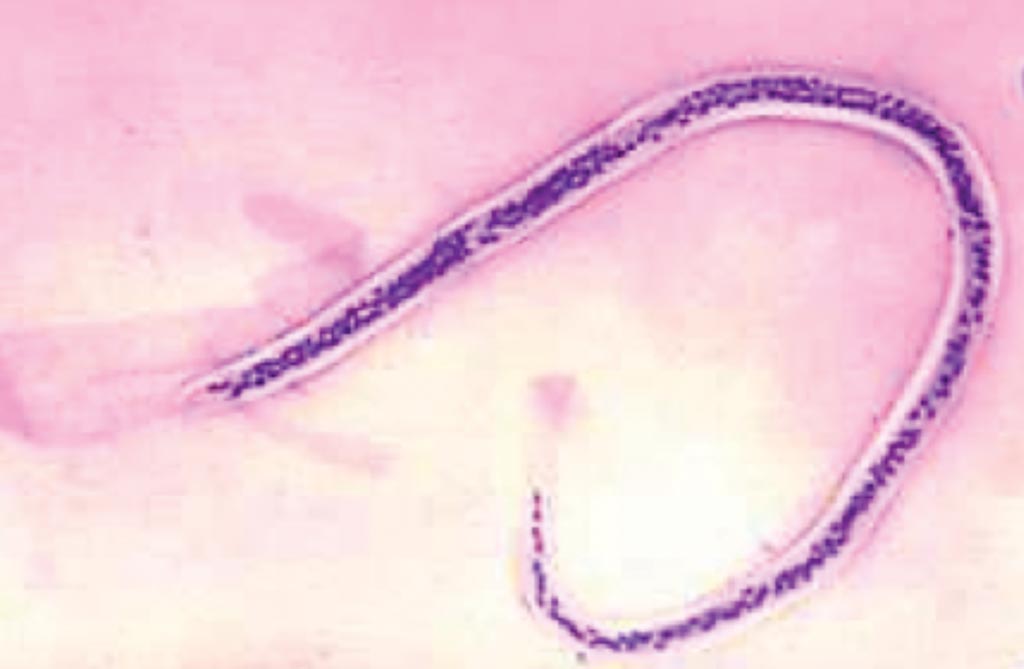
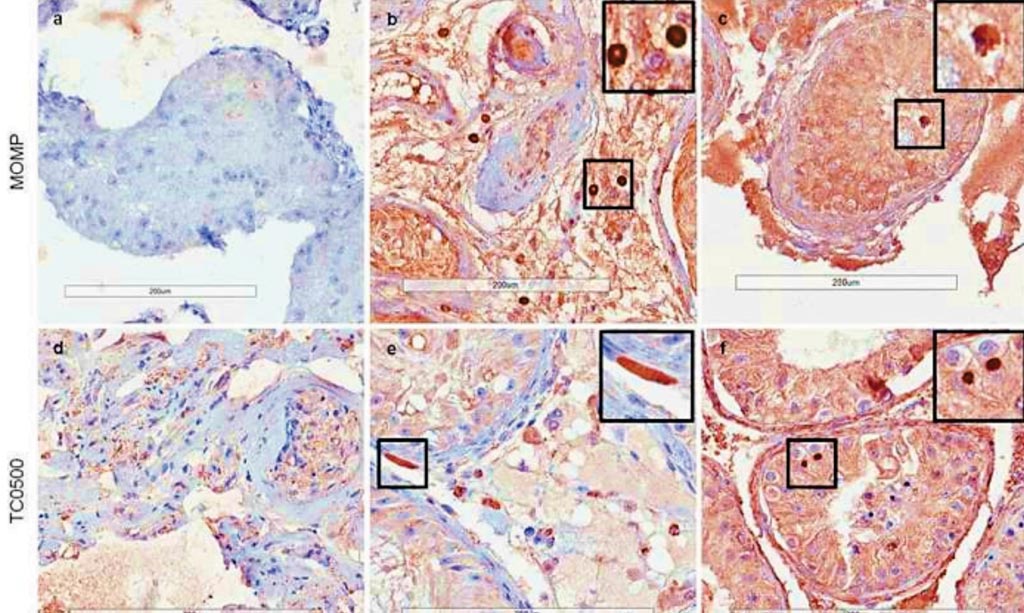
Molecular Changes Associated with Treating Lymphatic Filariasis
Lymphatic filariasis (LF) is a disabling neglected tropical disease that is caused by the mosquito-borne filarial parasites Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi and B. timori. Adult worms live in the human host’s lymphatic system and release larval parasites (microfilariae or Mf) that circulate in the blood. More...09 Oct 2019
Immunochromatographic Strip Test Developed for Rift Valley Fever
Rift Valley fever (RVF) is an emerging mosquito-borne disease that affects a wide range of animals and human beings in Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. A rapid and specific test for RVF diagnosis at the site of a suspected outbreak is crucial for the implementation of control measures. More...03 Oct 2019
In Other News
RT-PCR Evaluated for Diagnosis of Imported Schistosomiasis
Early Diagnosis of Tularemia Accomplished by Flow Cytometry
Multiplexed Immunoassay System Differentiates Malaria Species
Drug-Resistant Strains of Salmonella Causing Bloodstream Infections
Commercial TB Test Compared to Recombinant Allergen Skin Test
New Strain of Bacteria Causes Scarlet Fever
Mutation Found Determines Nature of Host Response to MRSA Infection
Unusual Sugar Facilitates Long-Term Survival of Leishmania Parasites
Differences in Gut Bacteria May Predispose to Heart Attacks
Multiplex Microsphere Immunoassay Identifies Three Flavivirus Infections
Gut Bacteria Linked to High Blood Pressure and Depression
Zika Virus Test Kit Receives American Marketing Approval
Human Intestinal Enteroids Used to Detect Norovirus Infectivity
Detergent-Enhanced LAMP Detects African Trypanosome in CSF
Fungus-Associated Bacteriome Associated with C. difficile Infection
Immunoassays Compared for Diagnosis of Acute Murine Typhus Infections
New Official Guideline Summarizes Advances in Fungal Infections Diagnosis
New Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Host-Pathogen Interactions
Differential Immune Responses Triggered against Salmonella enterica
Type 1 Diabetes Risk Reflected in Gut Microbiome
Optimized Immunoassays Detect HBV in Oral Fluid Samples
Novel ELISA Detects Invasive Aspergillosis
Sequencing Methods for Hepatitis C Virus Genotyping Compared
The LabMedica Microbiology channel provides the latest news in the fields of epidemiology, bacteriology, virology, and parasitology, all viewed from the unique perspective of Laboratory Medicine.









 Analyzer.jpg)
