Microfluidic Chip Enables Simultaneous Diagnosis of COVID-19 and Influenza Diseases
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 06 Jan 2022 |
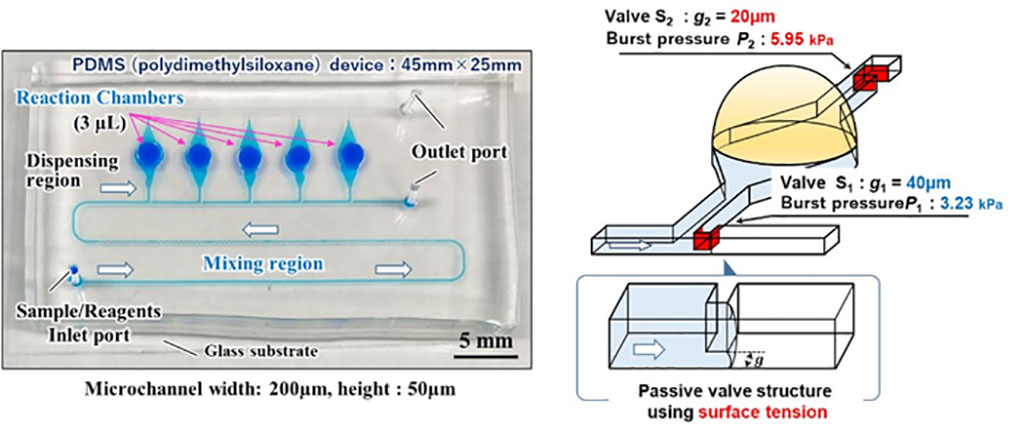
A research team has developed a microfluidic chip that is capable of simultaneous diagnosis of COVID-19 and influenza diseases, by applying the microfluidic chip technologies.
Researchers from the Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi, Japan) and Jikei University School of Medicine (Tokyo, Japan) built a theoretical model that manipulates microfluidic flow with an extremely simple microchannel design and has established an optimal design theory for microfluidic chips. Further, by using the diagnostic device they developed, they performed genetic amplification experiments on four types of infectious diseases, including COVID-19, and demonstrated that multiplexed rapid and simultaneous diagnosis was possible within 30 minutes. The device can be utilized for genetic diagnoses in a range of fields (e.g. agriculture, farming, and fisheries industries, food industry, and health and medical care), not only human infectious diseases. The diagnostic technology can enable anyone, anywhere, any time to detect viral diseases in a rapid, simple, and low-cost way.
The LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) method is a genetic test technology. This simple test method does not require an expensive accurate temperature control equipment, etc., in contrast to the widespread PCR test, and can be conducted on site because it allows genetic amplification at a constant temperature for a constant length of time (60 to 65℃, 30 minutes to an hour or so). However, to diagnose multiple types of viruses, the conventional LAMP method entails considerable effort to perform as many preparations of samples and reagents and genetic amplification reactions as the number of analytes, requiring expert knowledge and skills.
Therefore, the research team developed a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based multiplexed genetic diagnostic device (size: 45mm x 25mm, reaction chamber: 3µL x 5 pieces) by applying the microfluidic chip technology. It autonomously, equally, and accurately dispenses samples and reagent into an array of reaction chambers simply by introducing the liquid, a mixture of an extremely small amount of sample extracted from the analytes and a reagent, into the diagnostic device. By heating the device in warm water (at 60 to 65℃, for 30 minutes to an hour or so), it is capable of simultaneous diagnosis of multiple types of viruses with only one operation (one work process per sample).
The genetic diagnosis result showed that four types of infectious diseases including the COVID-19 (seasonal influenza A, SARS, and influenza H1N1 pdm09) were successfully detected with this diagnosis device. Only the reaction chamber that reacted when a sample containing the gene of each virus was introduced turned sky blue (denoting a positive reaction) after 30 minutes, which means that visual detection is possible.
In addition, to support on-site diagnoses, the team has developed a smartphone app, which automatically diagnoses the reaction as positive or negative based on photographs taken with a smartphone camera. The diagnosis device is capable of easy automatic test result diagnosis (positive or negative), by placing the device after LAMP reaction in a simple LED illumination device and taking photographs with a smartphone. As a result, it is expected that anyone will be able to easily perform the test, anywhere and anytime. In the future, aiming to commercialize the diagnosis device, the research team will develop devices capable of multiplexed rapid diagnosis of variants of the COVID-19 and human infectious diseases for a safe life during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Related Links:
Toyohashi University of Technology
Jikei University School of Medicine
Latest COVID-19 News
- New Immunosensor Paves Way to Rapid POC Testing for COVID-19 and Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Long COVID Etiologies Found in Acute Infection Blood Samples
- Novel Device Detects COVID-19 Antibodies in Five Minutes
- CRISPR-Powered COVID-19 Test Detects SARS-CoV-2 in 30 Minutes Using Gene Scissors
- Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis Linked to COVID-19
- Novel SARS CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Test Validated for Diagnostic Accuracy
- New COVID + Flu + R.S.V. Test to Help Prepare for `Tripledemic`
- AI Takes Guesswork Out Of Lateral Flow Testing
- Fastest Ever SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Test Designed for Non-Invasive COVID-19 Testing in Any Setting
- Rapid Antigen Tests Detect Omicron, Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- Health Care Professionals Showed Increased Interest in POC Technologies During Pandemic, Finds Study
- Set Up Reserve Lab Capacity Now for Faster Response to Next Pandemic, Say Researchers
- Blood Test Performed During Initial Infection Predicts Long COVID Risk
- Low-Cost COVID-19 Testing Platform Combines Sensitivity of PCR and Speed of Antigen Tests
- Finger-Prick Blood Test Identifies Immunity to COVID-19
- Quick Test Kit Determines Immunity Against COVID-19 and Its Variants
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
DNA Aptamers Offer New Tool for Easy Alzheimer's Blood Test
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia and is marked by progressive loss of nerve cells that begins many years before symptoms become noticeable. Detecting early signs of neurodegeneration... Read more
AI-Based Liquid Biopsy Detects Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis and Chronic Disease Signals
Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis often develop silently for years before symptoms appear, making early diagnosis difficult. Detecting these conditions earlier could allow treatment before irreversible damage... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Study Highlights Accuracy Gaps in Consumer Gut Microbiome Kits
Direct-to-consumer gut microbiome kits promise personalized insights by profiling fecal bacteria and generating health readouts, but their analytical accuracy remains uncertain. A new study shows that... Read more
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more






















