Sensitive Detection Method Identifies Protein Clumps in Parkinson’s Disease Skin Samples
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 02 Nov 2020 |
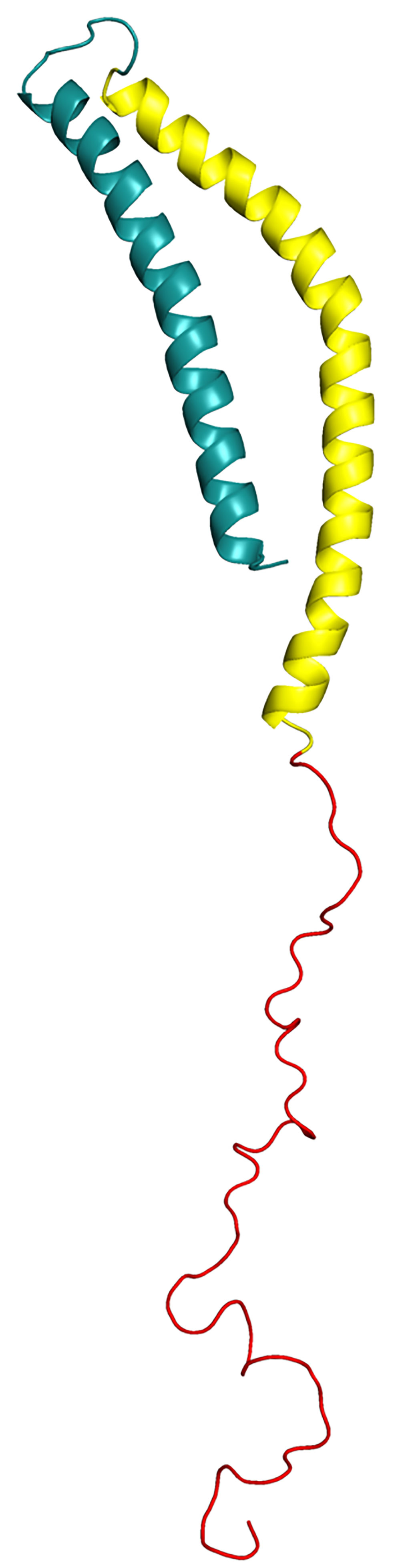
Image: A structural model of human alpha-synuclein protein (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
A sensitive detection method usually used to identify aggregated prion proteins has been adapted for the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease in skin samples.
An unmet clinical need in Parkinson's disease (PD) has been the identification of biomarkers for diagnosis, preferably in easily accessible tissues such as skin. In this regard previous immunohistochemical studies have detected pathological clumping of alpha‐synuclein (aSyn) protein in skin biopsies from PD patients.
To identify aSyn aggregates in skin samples, investigators at Iowa State University (Ames, USA) used a real‐time quaking‐induced conversion assay. Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) is a highly sensitive assay generally used for prion detection. The "quaking" in the name of the technique refers to the fact that samples in the RT-QuIC assay are literally subjected to shaking. This action breaks apart aggregates of prion protein (PrP) that are then further incubated, amplifying the amount of misfolded PrP to detectable levels.
The investigators adapted the RT-QuIC assay to determine the seeding kinetics of the aSyn present in the skin from autopsied subjects consisting of frozen skin tissues from 25 PD and 25 controls and formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded skin sections from 12 PD and 12 controls.
Results of the analysis revealed that the assay had correctly identified 24/25 PD and 24/25 controls using frozen skin tissues (96% sensitivity and 96% specificity) compared to 9/12 PD and 10/12 controls using formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded skin sections (75% sensitivity and 83% specificity). These results clearly demonstrated the feasibility of using skin tissues for clinical diagnosis of PD by detecting pathological aSyn.
"Since there is no easy and reliable test available for the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease at present, we think there will be a lot interest in the potential use of skin samples for diagnosis," said senior author Dr. Anumantha Kanthasamy, professor of biomedical sciences at Iowa State University. "Testing skin samples could lead to earlier detection of Parkinson's disease. Earlier diagnosis could allow physicians to test therapeutic strategies designed to slow or prevent the development of advanced symptoms."
The skin test paper was published in the September 22, 2020, online edition of the journal Movement Disorders.
Related Links:
Iowa State University
An unmet clinical need in Parkinson's disease (PD) has been the identification of biomarkers for diagnosis, preferably in easily accessible tissues such as skin. In this regard previous immunohistochemical studies have detected pathological clumping of alpha‐synuclein (aSyn) protein in skin biopsies from PD patients.
To identify aSyn aggregates in skin samples, investigators at Iowa State University (Ames, USA) used a real‐time quaking‐induced conversion assay. Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) is a highly sensitive assay generally used for prion detection. The "quaking" in the name of the technique refers to the fact that samples in the RT-QuIC assay are literally subjected to shaking. This action breaks apart aggregates of prion protein (PrP) that are then further incubated, amplifying the amount of misfolded PrP to detectable levels.
The investigators adapted the RT-QuIC assay to determine the seeding kinetics of the aSyn present in the skin from autopsied subjects consisting of frozen skin tissues from 25 PD and 25 controls and formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded skin sections from 12 PD and 12 controls.
Results of the analysis revealed that the assay had correctly identified 24/25 PD and 24/25 controls using frozen skin tissues (96% sensitivity and 96% specificity) compared to 9/12 PD and 10/12 controls using formalin‐fixed paraffin‐embedded skin sections (75% sensitivity and 83% specificity). These results clearly demonstrated the feasibility of using skin tissues for clinical diagnosis of PD by detecting pathological aSyn.
"Since there is no easy and reliable test available for the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease at present, we think there will be a lot interest in the potential use of skin samples for diagnosis," said senior author Dr. Anumantha Kanthasamy, professor of biomedical sciences at Iowa State University. "Testing skin samples could lead to earlier detection of Parkinson's disease. Earlier diagnosis could allow physicians to test therapeutic strategies designed to slow or prevent the development of advanced symptoms."
The skin test paper was published in the September 22, 2020, online edition of the journal Movement Disorders.
Related Links:
Iowa State University
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
- Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
- Two-in-One DNA Analysis Improves Diagnostic Accuracy While Saving Time and Costs
- “Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
- New Tool Maps Chromosome Shifts in Cancer Cells to Predict Tumor Evolution
- Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
- Newly-Identified Parkinson’s Biomarkers to Enable Early Diagnosis Via Blood Tests
- New Blood Test Could Detect Pancreatic Cancer at More Treatable Stage
- Liquid Biopsy Could Replace Surgical Biopsy for Diagnosing Primary Central Nervous Lymphoma
- New Tool Reveals Hidden Metabolic Weakness in Blood Cancers
- World's First Blood Test Distinguishes Between Benign and Cancerous Lung Nodules
- Rapid Test Uses Mobile Phone to Identify Severe Imported Malaria Within Minutes
- Gut Microbiome Signatures Predict Long-Term Outcomes in Acute Pancreatitis
- Blood Test Promises Faster Answers for Deadly Fungal Infections
- Blood Test Could Detect Infection Exposure History
- Urine-Based MRD Test Tracks Response to Bladder Cancer Surgery
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more