Loss of MicroRNA Induces Pro-Metastatic Changes in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 14 Jun 2016 |
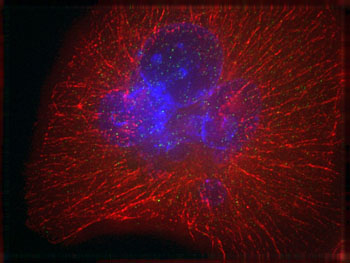
Image: A pancreatic cancer cell. The nucleus is stained blue, while the fibers of the cytoskeleton are labelled with a red fluorescent dye (Photo courtesy of Dr. Nathalie Giese, Chirurgische Universitätsklinik Heidelberg, Germany).
Reduced activity of a specific microRNA (miRNA) is apparent in chronically inflamed pancreatic tissue and in early stages of pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma or PDAC) even before tumor formation.
PDAC is characterized by very early metastasis, which has led some researchers to postulate that metastasis-associated changes may occur prior to actual tumor formation. To confirm this hypothesis investigators at the German Cancer Research Center (Heidelberg, Germany) analyzed levels of miRNAs known to be linked to PDAC.
MicroRNAs are a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
The investigators reported in the May 23, 2016, online edition of the journal Cancer Research that they had identified the microRNA miR-192 as an epigenetically regulated suppressor gene with predictive value in PDAC. Levels of miR-192 were downregulated by promoter methylation in both PDAC and chronic pancreatitis (CP), a risk factor that leads to a 15-fold increase in the likelihood of contracting pancreatic cancer.
Functional studies in vitro and in mouse models of PDAC showed that overexpression of miR-192 was sufficient to reduce cell proliferation and invasion. Mechanistic analyses correlated changes in miR-192 promoter methylation and expression with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Cell proliferation and invasion were linked to altered expression of the miR-192 target gene SERPINE1, which encodes the protein plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), an established regulator of these properties in PDAC cells. These results suggested that miR-192 downregulation established an invasive capacity in these pancreatic cells even before they transformed into cancer cells.
"We think that the cells often already have metastatic capacity before even transforming into cancer cells," said senior author Dr. Jörg Hoheisel, head of the division of functional genome analysis at the German Cancer Research Center. "To check this hypothesis, we searched the tumor cells for molecular changes that are indicative of the tendency to spread early. Our interpretation of these results is that epigenetic changes that occur already in inflamed pancreatic tissue lead to reduced production of miR-192. This means that the cells acquire the capacity of invasion and metastasis, which initially has no consequences. The actual transformation into cancer cells is caused by other, unrelated factors and can occur later. The result is cancer cells that are capable, from the very start, to invade surrounding tissue and spread metastases."
Related Links:
German Cancer Research Center
PDAC is characterized by very early metastasis, which has led some researchers to postulate that metastasis-associated changes may occur prior to actual tumor formation. To confirm this hypothesis investigators at the German Cancer Research Center (Heidelberg, Germany) analyzed levels of miRNAs known to be linked to PDAC.
MicroRNAs are a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
The investigators reported in the May 23, 2016, online edition of the journal Cancer Research that they had identified the microRNA miR-192 as an epigenetically regulated suppressor gene with predictive value in PDAC. Levels of miR-192 were downregulated by promoter methylation in both PDAC and chronic pancreatitis (CP), a risk factor that leads to a 15-fold increase in the likelihood of contracting pancreatic cancer.
Functional studies in vitro and in mouse models of PDAC showed that overexpression of miR-192 was sufficient to reduce cell proliferation and invasion. Mechanistic analyses correlated changes in miR-192 promoter methylation and expression with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
Cell proliferation and invasion were linked to altered expression of the miR-192 target gene SERPINE1, which encodes the protein plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), an established regulator of these properties in PDAC cells. These results suggested that miR-192 downregulation established an invasive capacity in these pancreatic cells even before they transformed into cancer cells.
"We think that the cells often already have metastatic capacity before even transforming into cancer cells," said senior author Dr. Jörg Hoheisel, head of the division of functional genome analysis at the German Cancer Research Center. "To check this hypothesis, we searched the tumor cells for molecular changes that are indicative of the tendency to spread early. Our interpretation of these results is that epigenetic changes that occur already in inflamed pancreatic tissue lead to reduced production of miR-192. This means that the cells acquire the capacity of invasion and metastasis, which initially has no consequences. The actual transformation into cancer cells is caused by other, unrelated factors and can occur later. The result is cancer cells that are capable, from the very start, to invade surrounding tissue and spread metastases."
Related Links:
German Cancer Research Center
Latest BioResearch News
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
- Liquid Biopsy More Effective for Analyzing Tumor Drug Resistance Mutations
- New Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Host-Pathogen Interactions
- Method Developed for Enriching Trophoblast Population in Samples
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read more
Existing Hospital Analyzers Can Identify Fake Liquid Medical Products
Counterfeit and substandard medicines remain a serious global health threat, with World Health Organization estimates suggesting that 10.5% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries are either fake... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infects up to 95% of adults worldwide and remains in the body for life. While usually kept under control, the virus is linked to cancers such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma and autoimmune... Read more
Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
Brain and central nervous system (CNS) tumors are often diagnosed at an advanced stage, when treatment options are limited, and survival rates remain low. Around 300,000 new cases are diagnosed each year... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
Parasitic liver fluke infections remain endemic in parts of Asia, where transmission commonly occurs through consumption of raw freshwater fish or aquatic plants. Chronic infection is a well-established... Read more
Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
Drug-resistant pathogens continue to pose a growing threat in healthcare facilities, where delayed detection can impede outbreak control and increase mortality. Candida auris is notoriously difficult to... Read more
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the deadliest cancers, in part because of its dense tumor microenvironment that influences how tumors grow and respond to treatment.... Read more
New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
Sputum smear microscopy remains central to tuberculosis treatment monitoring and follow-up, particularly in high‑burden settings where serial testing is routine. Yet consistent, repeatable bacillary assessment... Read more
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more