Novel Fluorescent Probe Shows Potential in Precision Cancer Diagnostics and Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
Posted on 08 Jul 2025
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common type of liver cancer, is difficult to diagnose early and accurately due to the limitations of current diagnostic methods. Glycans, carbohydrate structures present on the surface of cells, are critical to various biological processes and are often altered in cancer cells. In particular, sialylated glycans, such as sialyl Lewis x (sLex) and sialyl Lewis a (sLea), are overexpressed in liver cancer, positioning them as potential biomarkers. However, conventional techniques for detecting these glycans are complex and unsuitable for real-time imaging. This gap underscores the need for a more accessible and precise diagnostic tool to identify liver cancer and improve surgical precision. Now, researchers have successfully developed a novel fluorescent probe that is capable of precisely identifying HCC tissue.
This novel fluorescent probe, SLY (Sialyl Lewis Yellow) was developed by a research team from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH, Pohang, South Korea\) by incorporating oxaborole as a recognition moiety into a library of fluorescent probes. SLY was found to selectively target sialylated glycans on the surface of liver cancer cells, specifically sLex and sLea, which are overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells. Once bound, SLY enters the cells via caveolae-mediated endocytosis and accumulates in the mitochondria, providing a fluorescent signal to aid in cancer detection.
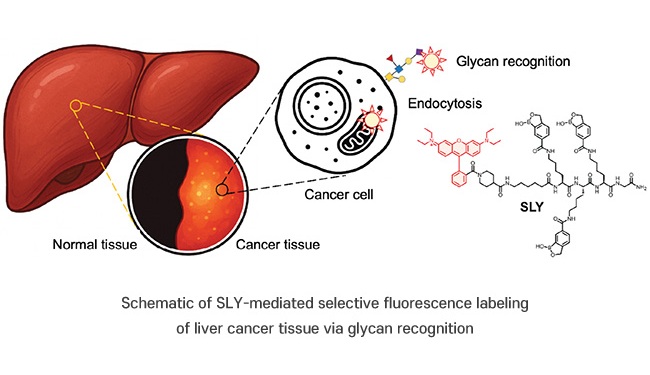
SLY was tested in both in vivo and ex vivo experiments using cryo-sectioned liver cancer tissues, which confirmed its ability to specifically label cancerous regions with high fluorescence contrast. The results, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, demonstrated that SLY outperforms conventional probes by clearly distinguishing tumor margins in liver tissues. This innovative probe holds strong potential for precision diagnostics and fluorescence-guided surgery, making it an important tool for the early detection of liver cancer. The researchers plan to continue exploring the application of SLY in clinical settings, potentially advancing glycan-based cancer diagnostics and precision medicine.
“SLY represents the first fluorescent probe capable of selectively identifying sialylated glycans on the cell surface with such precision, enabling the identification of liver cancer at the cellular level,” said POSTECH Professor Young-Tae Chang, who led the study. “This work opens new possibilities in glycan-based cancer diagnostics and may lay the groundwork for future applications in fluorescence-guided surgery and precision medicine.”
Related Links:
POSTECH









 (3) (1).png)




