Cutting Edge Technology Used to Grade Cancer Tumors
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 28 Mar 2018 |
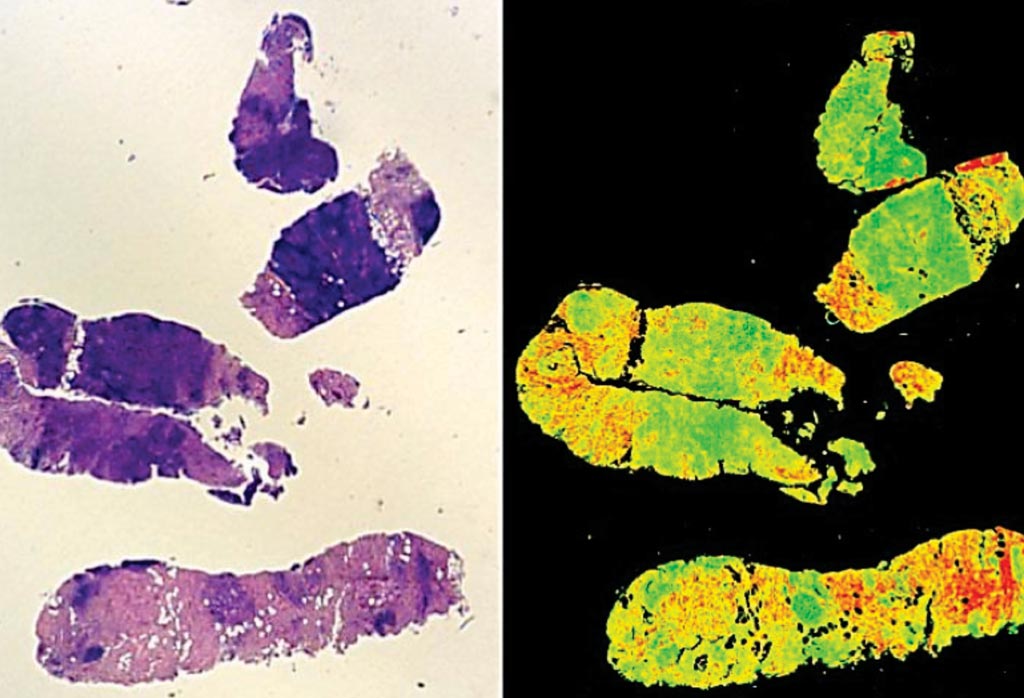
Image: New cutting edge technology can be used to grade cancer tumors, eradicating human subjectivity. A traditional stained H+E biopsy (L) and a Digistain view (R) (Photo courtesy of Imperial College London).
Biopsy specimens are processed into formalin-fixed-paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks and currently, hematoxylin and eosin (H + E) stained sections are widely used for the histopathological diagnosis of cancer and other pathologies.
Typically the sections are graded subjectively by eye, using disease-specific grading protocols. Histological grading of breast cancer currently varies widely across multiple institutions and practitioners, because it relies on subjective criteria. However an analysis of more than 24, 000 biopsies, graded by 732 breast cancer graders, found that they only agreed ~73% of the time on average.
A team of scientists from Imperial College London (London, UK) carried out a double-blind clinical pilot trial using two adjacent slices taken from 75 breast cancer biopsies. The patients were all female with ages ranging from 30.4 to 83.7, mean age 58.7 at diagnosis. More than half of the samples were grade 2 tumors (54.3%). The majority were HER2 negative (90.0%). The first slice was graded by clinicians as usual, using the standard H+E protocol. It was also used to identify the so-called 'region of interest' (RoI), i.e. the part of the slice containing the tumor.
The team used their new 'Digistain' technology addresses the problem of consensus among pathologists by using invisible mid-infrared light to photograph the tissue slices in a way that maps out the chemical changes that signal the onset of cancer. In particular, they measure the 'nuclear-to-cytoplasmic-ratio' (NCR): a recognized biological marker for a wide range of cancers. The team then used the Digistain imager to get a 'Digistain index' (DI) value averaged over the corresponding RoI on the other, unstained slice, and ran a statistical analysis on the results.
The DI measures the concentration ratios of phosphodiester to amide moieties, and because these are dominantly related to the amounts of nuclear and cytoplasmic material, respectively, The DI images can be regarded as 2D maps of the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, (NCR). The NCR factor that ‘Digistain’ measures is known to be common to a wide range of cancers, as it occurs when the reproductive cell cycle gets disrupted in the tumor and cell nuclei get distorted with rogue DNA. It is likely that in the long run, Digistain could help with the diagnosis of all different types of cancer. At a practical level, the team reported that the Digistain imaging technology can easily and cheaply be incorporated into existing hospital laboratories, and be used by their staff.
Chris Phillips, PhD, a Professor of Experimental Solid State Physics and lead investigator of the study, said, “Our machine gives a quantitative 'Digistain index' (DI) score, corresponding to the NCR, and this study shows that it is an extremely reliable indicator of the degree of progression of the disease. Because it is based on a physical measurement, rather than a human judgement, it promises to remove the element of chance in cancer diagnosis.” The study was published on March 13, 2018, in the journal Convergent Science Physical Oncology.
Related Links:
Imperial College London
Typically the sections are graded subjectively by eye, using disease-specific grading protocols. Histological grading of breast cancer currently varies widely across multiple institutions and practitioners, because it relies on subjective criteria. However an analysis of more than 24, 000 biopsies, graded by 732 breast cancer graders, found that they only agreed ~73% of the time on average.
A team of scientists from Imperial College London (London, UK) carried out a double-blind clinical pilot trial using two adjacent slices taken from 75 breast cancer biopsies. The patients were all female with ages ranging from 30.4 to 83.7, mean age 58.7 at diagnosis. More than half of the samples were grade 2 tumors (54.3%). The majority were HER2 negative (90.0%). The first slice was graded by clinicians as usual, using the standard H+E protocol. It was also used to identify the so-called 'region of interest' (RoI), i.e. the part of the slice containing the tumor.
The team used their new 'Digistain' technology addresses the problem of consensus among pathologists by using invisible mid-infrared light to photograph the tissue slices in a way that maps out the chemical changes that signal the onset of cancer. In particular, they measure the 'nuclear-to-cytoplasmic-ratio' (NCR): a recognized biological marker for a wide range of cancers. The team then used the Digistain imager to get a 'Digistain index' (DI) value averaged over the corresponding RoI on the other, unstained slice, and ran a statistical analysis on the results.
The DI measures the concentration ratios of phosphodiester to amide moieties, and because these are dominantly related to the amounts of nuclear and cytoplasmic material, respectively, The DI images can be regarded as 2D maps of the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, (NCR). The NCR factor that ‘Digistain’ measures is known to be common to a wide range of cancers, as it occurs when the reproductive cell cycle gets disrupted in the tumor and cell nuclei get distorted with rogue DNA. It is likely that in the long run, Digistain could help with the diagnosis of all different types of cancer. At a practical level, the team reported that the Digistain imaging technology can easily and cheaply be incorporated into existing hospital laboratories, and be used by their staff.
Chris Phillips, PhD, a Professor of Experimental Solid State Physics and lead investigator of the study, said, “Our machine gives a quantitative 'Digistain index' (DI) score, corresponding to the NCR, and this study shows that it is an extremely reliable indicator of the degree of progression of the disease. Because it is based on a physical measurement, rather than a human judgement, it promises to remove the element of chance in cancer diagnosis.” The study was published on March 13, 2018, in the journal Convergent Science Physical Oncology.
Related Links:
Imperial College London
Latest Technology News
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
- AI Predicts Colorectal Cancer Survival Using Clinical and Molecular Features
- Diagnostic Chip Monitors Chemotherapy Effectiveness for Brain Cancer
- Machine Learning Models Diagnose ALS Earlier Through Blood Biomarkers
- Artificial Intelligence Model Could Accelerate Rare Disease Diagnosis
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more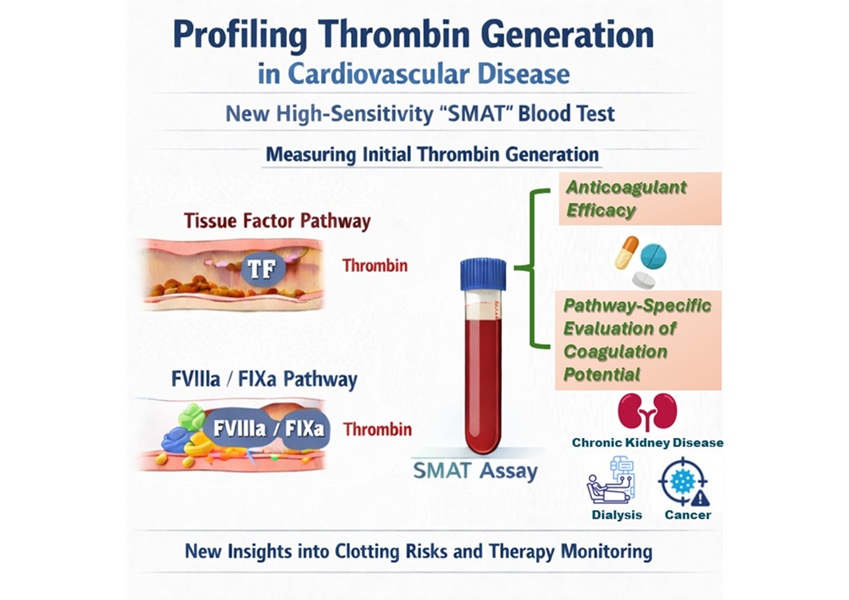
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more









 Analyzer.jpg)