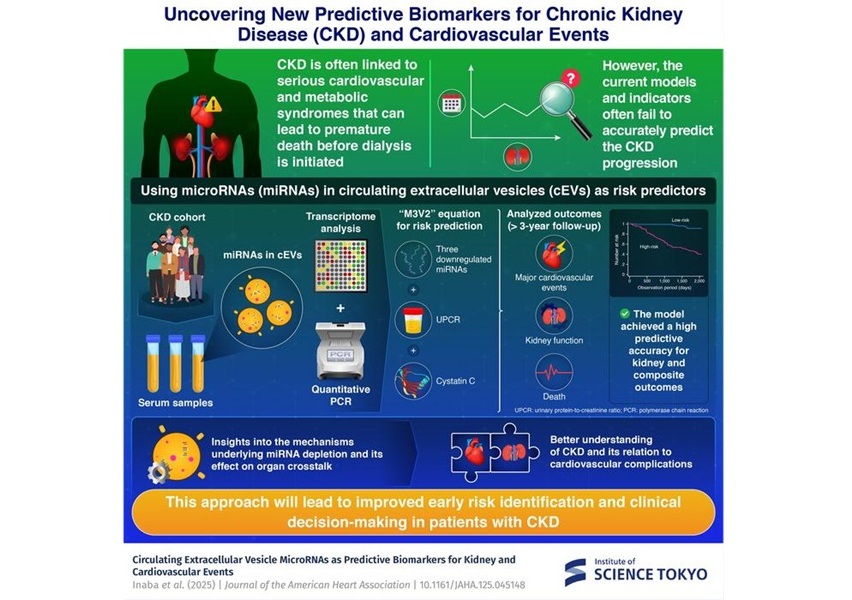
Phosphorylation of Tau Protein Inhibits Amyloid-beta Toxicity in Alzheimer’s Model
|
By Gerald M. Slutzky, PhD Posted on 29 Nov 2016 |
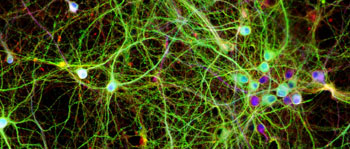
Image: A photomicrograph of neurons growing in culture. The colors highlight the human tau protein in green, a structural component in red, and the DNA inside the cell nucleus in blue (Photo courtesy of Dr. Lars Ittner, University of New South Wales).
A team of Australian Alzheimer's disease (AD) researchers have presented evidence suggesting that phosphorylation of tau protein in the early stages of the disease acts to protect against the toxicity of amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaques, and that this protective effect disappears as the disease progresses.
The prevailing idea among AD researchers has been that Abeta induced phosphorylation of tau, which in turn triggered the neuronal dysfunction that characterized the disease.
Investigators at the University of New South Wales (Sydney, Australia) worked with Alzheimer's disease mouse models and samples of brain tissue obtained from AD patients. They reported in the November 18, 2016, issue of the journal Science that at least in early stages of the disease, site-specific phosphorylation of tau inhibited Abeta toxicity. This specific tau phosphorylation was mediated by the neuronal enzyme p38gamma (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase) and interfered with postsynaptic toxic signaling complexes engaged by Abeta.
Depletion of p38gamma increased the severity of neuronal circuit aberrations, cognitive deficits, and premature lethality in a mouse model of AD, whereas increasing the activity of p38gamma abolished these deficits. Furthermore, mimicking site-specific tau phosphorylation alleviated Abeta-induced neuronal death and offered protection from its toxicity.
"This study has completely changed our understanding of what happens in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease," said senior author Dr. Lars Ittner, professor of medicine at the University of New South Wales. "Amyloid-beta induces toxicity in the neurons but the first step in tau phosphorylation is actually to decrease this toxicity. This is a completely new mindset; that the reason tau becomes modified is actually to protect from damage. We found that p38gamma, which initially offers protection, fades away early in the brains of people with AD, suggesting a loss of protection."
"We set out to find mediators of this progression, which led us quickly to our surprising finding. It was the opposite of what we expected. It was only when we changed our view of the process involved in the development of AD that these results started to make sense," said Dr. Ittner. "We used mice to screen for a very specific toxicity that we knew from previous work is involved in the progression of the disease. Part of our study involved reintroducing p38gamma and increasing its activity. We saw that, in mice, it could prevent memory deficits from happening, so it has true therapeutic potential. If we can stimulate that activity, we may be able to delay or even halt the progression of Alzheimer's disease."
Related Links:
University of New South Wales
The prevailing idea among AD researchers has been that Abeta induced phosphorylation of tau, which in turn triggered the neuronal dysfunction that characterized the disease.
Investigators at the University of New South Wales (Sydney, Australia) worked with Alzheimer's disease mouse models and samples of brain tissue obtained from AD patients. They reported in the November 18, 2016, issue of the journal Science that at least in early stages of the disease, site-specific phosphorylation of tau inhibited Abeta toxicity. This specific tau phosphorylation was mediated by the neuronal enzyme p38gamma (p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase) and interfered with postsynaptic toxic signaling complexes engaged by Abeta.
Depletion of p38gamma increased the severity of neuronal circuit aberrations, cognitive deficits, and premature lethality in a mouse model of AD, whereas increasing the activity of p38gamma abolished these deficits. Furthermore, mimicking site-specific tau phosphorylation alleviated Abeta-induced neuronal death and offered protection from its toxicity.
"This study has completely changed our understanding of what happens in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease," said senior author Dr. Lars Ittner, professor of medicine at the University of New South Wales. "Amyloid-beta induces toxicity in the neurons but the first step in tau phosphorylation is actually to decrease this toxicity. This is a completely new mindset; that the reason tau becomes modified is actually to protect from damage. We found that p38gamma, which initially offers protection, fades away early in the brains of people with AD, suggesting a loss of protection."
"We set out to find mediators of this progression, which led us quickly to our surprising finding. It was the opposite of what we expected. It was only when we changed our view of the process involved in the development of AD that these results started to make sense," said Dr. Ittner. "We used mice to screen for a very specific toxicity that we knew from previous work is involved in the progression of the disease. Part of our study involved reintroducing p38gamma and increasing its activity. We saw that, in mice, it could prevent memory deficits from happening, so it has true therapeutic potential. If we can stimulate that activity, we may be able to delay or even halt the progression of Alzheimer's disease."
Related Links:
University of New South Wales
Latest BioResearch News
- Barcoded DNA Sheds Light on Hidden Complexities in Breast Cancer Detection
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read more
Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
Bloodstream infections are a major threat to children undergoing intensive leukemia treatment. Chemotherapy weakens the immune system, allowing bacteria and fungi to trigger sepsis, prolonged hospital... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read more
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more