FDA-Cleared Automated Cell Counter for CSF Launched at AACC 2016
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 04 Aug 2016 |
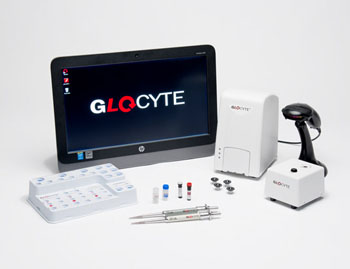
Image: The GloCyte system delivers highly accurate and precise total nucleated cell and red blood cell counts using a novel combination of technologies (Photo courtesy of Advanced Instruments).
The system provides superior accuracy of low cell counts in cerebrospinal fluid samples. It is being introduced at the AACC Annual Scientific Meeting & Clinical Lab Expo (July 31 - August 4; Philadelphia, PA, USA). Linda Sandhaus, MD, University Hospitals Case Medical Center, presented a poster (#A-290) on August 2 titled GloCyte: A New Automated Technology for Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Cell Counts.
Advanced Instruments, Inc. (Norwood, MA, USA) has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) to market its GloCyte Automated Cell Counter System and GloCyte Low and High Level Controls. The patented GloCyte System is intended to provide a quantitative determination of red blood cells (RBCs) and total nucleated cells (TNCs) in CSF collected from adult and pediatric patients. Currently, low cell counts often present a challenge to standard methods.
“To date, there has not been a way to provide dependable, low cell counts,” said John Coughlin, president and CEO, Advanced Instruments, “We use a novel combination of fluorescence, microscopy with digital image analysis principles, highly specific reagents, and an intelligent counting algorithm to provide accurate and precise cell counts. We are very excited as this marks a major achievement in giving laboratories a new way to obtain reliable and timely CSF results.”
Additional benefits of the GloCyte System are that the test requires only 30 microliters of sample per test, it uses disposable test cartridges ensuring no sample carryover and easy disposal, and it includes built-in quality control of Levey-Jennings charts and an audit table. The company expects to begin GloCyte shipments in September 2016.
Related Links:
Advanced Instruments
Advanced Instruments, Inc. (Norwood, MA, USA) has received 510(k) clearance from the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA) to market its GloCyte Automated Cell Counter System and GloCyte Low and High Level Controls. The patented GloCyte System is intended to provide a quantitative determination of red blood cells (RBCs) and total nucleated cells (TNCs) in CSF collected from adult and pediatric patients. Currently, low cell counts often present a challenge to standard methods.
“To date, there has not been a way to provide dependable, low cell counts,” said John Coughlin, president and CEO, Advanced Instruments, “We use a novel combination of fluorescence, microscopy with digital image analysis principles, highly specific reagents, and an intelligent counting algorithm to provide accurate and precise cell counts. We are very excited as this marks a major achievement in giving laboratories a new way to obtain reliable and timely CSF results.”
Additional benefits of the GloCyte System are that the test requires only 30 microliters of sample per test, it uses disposable test cartridges ensuring no sample carryover and easy disposal, and it includes built-in quality control of Levey-Jennings charts and an audit table. The company expects to begin GloCyte shipments in September 2016.
Related Links:
Advanced Instruments
Latest AACC 2016 News
- Molecular Test Detects Three Arboviruses in Plasma Samples
- Derived Exosomal Protein Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
- New Biochip Array Developed for ApoE4 Classification
- Cell-Free DNA Identifies Liver Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection
- New Method Tested for Early Diagnosis Pediatric Diabetic Nephropathy
- Semen Analysis Portfolio with Two New Products Featured at AACC 2016
- Automation Solutions for Clinical Diagnostic Equipment Showcased at AACC 2016
- New Tubes Designed for Medium Sample Volumes
- Multi Sample Osmometer Improves Testing Efficiency
- Innovative Information System Optimizes Laboratory Processes
- Innovative eLearning Interface Seamlessly Connects Competency Data
- Cloud-Based Connectivity Platform Advances Decentralized Healthcare
- Adhesives Research to Present Hydrophilic Adhesive Technologies
- Point-of-Care Immunoassay Analyzer on Display at AACC Annual Meeting
- Assay for Determination of 17-OH Progesterone to Be Featured at AACC Annual Meeting
- Fully Automated HbA1c Analyzer Available for Inspection at AACC Annual Meeting
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more























