Derived Exosomal Protein Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 04 Aug 2016
Alzheimer’s disease results in brain neuronal plaques composed of amyloid beta peptide (Aβ42) and neurofibrillary tangles composed of phosphorylated tau proteins (P-T181-tau and P-S396-tau). Exosomes are shed by brain neurons, freely cross the blood brain barrier and protect and carry proteins from their cellular origin into plasma.Posted on 04 Aug 2016
P-T181-tau and P-S396-tau are present at higher than normal concentrations and Aβ42 at lower than normal concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients. These proteins are not high in plasma samples of AD patients in part due to poor blood brain barrier transport and protease activities.
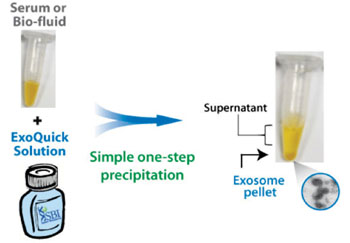
Image: The ExoQuick preparation method obtains high-quality exosomes from most biofluids using a protocol that can easily be performed on multiple samples and requires very low volumes of input sample (Photo courtesy of System Biosciences).
Scientists at Pan Laboratories (Irvine, CA, USA) and their colleagues validated enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for Aβ42, P-T181-tau and P-S396-tau, and used them to quantify these proteins in neuron-derived exosomal extracts from normal and AD plasma samples. Plasma samples were obtained from patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), as well as matched normal controls. Exosomes were precipitated from the plasma samples using the ExoQuick preparation (System Biosciences, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
The team reported that ELISA assays for Aβ42, P-T181-tau and P-S396-tau were reproducible and the Inter-assay Coefficient of Variability (CV) was less than 15%. The sensitivity of the biomarker ELISAs varied from 2 to10 pg/mL. Neuron-specific exosomes were prepared from the plasma of normal controls, MCI and AD patients. The reproducibility of the exosome preparations and biomarker levels were monitored in each ELISA. All biomarkers were elevated in MCI patients and AD patients compared to normal.
The authors concluded that they have validated a reproducible procedure to isolate specific neuron-derived exosomes for quantification of specific protein biomarkers in plasma samples. The concentrations of the biomarkers are high in patients with early dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. This procedure may be useful in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was presented at the 68th American Association of Clinical Chemistry (AACC) Annual Scientific Meeting held July 31 to August 4, 2016, in Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Related Links:
Pan Laboratories
System Biosciences
American Association of Clinical Chemistry