X-ray Crystallography Study May Lead to New Drugs to Block Cancer Metastasis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 28 Apr 2016 |
Cancer researchers expect that the structure of the enzyme P-Rex1 (PIP3-dependent Rac exchanger 1), which was recently established by X-ray crystallography, will lead to development of a new generation of cancer chemotherapeutic agents to block the processes leading to metastasis.
P-Rex1 is a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor synergistically activated by the lipid PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate) that plays an important role in the metastasis of breast, prostate, and skin cancer, which makes it an attractive therapeutic target. However, the molecular mechanisms behind P-Rex1 regulation have been poorly understood.
Investigators at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, USA) used X-ray crystallography to determine structures of the P-Rex1 pleckstrin homology domain (a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling) bound to the headgroup of PIP3.
They reported in the April 14, 2016, online edition of the journal Structure that PIP3 binding to the pleckstrin homology domain was required for P-Rex1 activity in cells but not for membrane localization, which pointed to an allosteric activation mechanism by PIP3.
"P-Rex1 has been an attractive drug target for some time," said senior author Dr. John J.G. Tesmer, professor of pharmacology and biological chemistry at the University of Michigan. "But development of these drugs has been hindered by a lack of understanding of its structure and regulatory mechanisms. Our data have confirmed the location of the binding site, which will greatly assist with the identification or design of small molecules that target this mechanism of activation."
Related Links:
University of Michigan
P-Rex1 is a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor synergistically activated by the lipid PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate) that plays an important role in the metastasis of breast, prostate, and skin cancer, which makes it an attractive therapeutic target. However, the molecular mechanisms behind P-Rex1 regulation have been poorly understood.
Investigators at the University of Michigan (Ann Arbor, USA) used X-ray crystallography to determine structures of the P-Rex1 pleckstrin homology domain (a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling) bound to the headgroup of PIP3.
They reported in the April 14, 2016, online edition of the journal Structure that PIP3 binding to the pleckstrin homology domain was required for P-Rex1 activity in cells but not for membrane localization, which pointed to an allosteric activation mechanism by PIP3.
"P-Rex1 has been an attractive drug target for some time," said senior author Dr. John J.G. Tesmer, professor of pharmacology and biological chemistry at the University of Michigan. "But development of these drugs has been hindered by a lack of understanding of its structure and regulatory mechanisms. Our data have confirmed the location of the binding site, which will greatly assist with the identification or design of small molecules that target this mechanism of activation."
Related Links:
University of Michigan
Latest BioResearch News
- Barcoded DNA Sheds Light on Hidden Complexities in Breast Cancer Detection
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
Chronic diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, colon cancer, and heart failure often develop silently for years before symptoms appear. By the time they are diagnosed, significant... Read more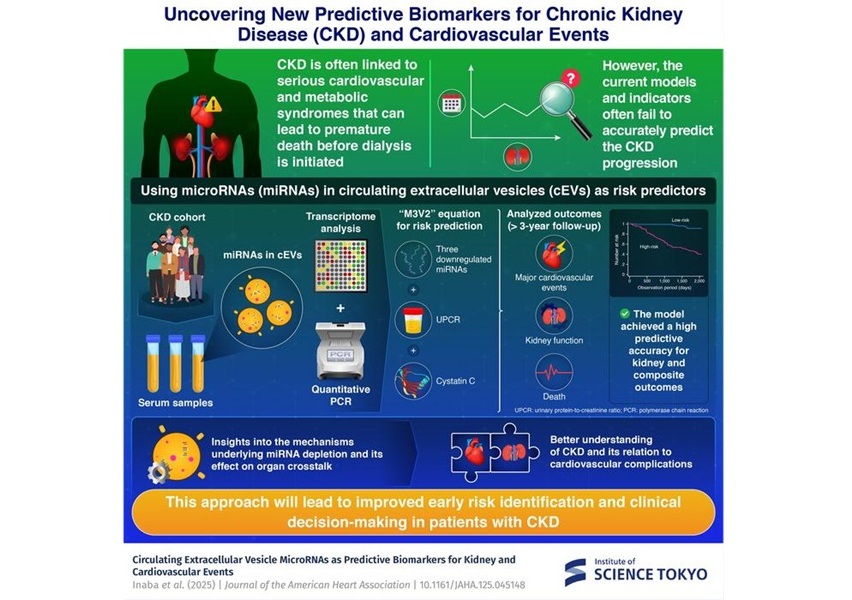
MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 850 million people worldwide and is a rapidly growing public health threat. Although it progressively damages kidney function, many patients die prematurely... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read more
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read more
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more






















