High GABA Level Astrocytes Are a New Alzheimer's Disease Biomarker and Drug Target
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 25 Jun 2014 |
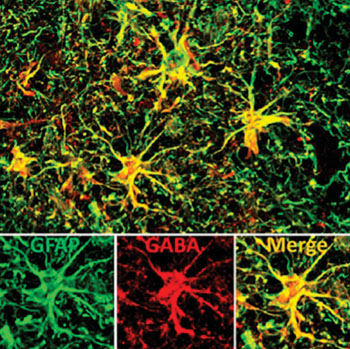
Image: This image shows a microscopic view of the high concentration (red) of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the reactive astrocytes (green) in the human brain with Alzheimer\'s disease (Photo courtesy of Dr. Gong Chen, Pennsylvania State University).
Cells comprising an abnormal class of brain cells called reactive astrocytes contain high levels of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and are being eyed by researchers as a potential biomarker and drug target for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Amyloid plaques and tau tangles are common pathological characteristics of AD. However, drugs designed to reduce production of the Abeta peptides that form amyloid plaques failed to relieve the symptoms of AD patients. Now, a paper published the June 13, 2014, online edition of the journal Nature Communications reported the presence of high GABA content in reactive astrocytes in the dentate gyrus (DG) of a mouse model for AD that resulted in increased tonic inhibition and memory deficit.
Investigators at Pennsylvania State University (University Park, USA) also confirmed the presence of astrocytes with a high GABA content in human AD patient brains. This finding suggested that a high astrocytic GABA level may be a novel biomarker and a potential diagnostic tool for AD.
They also considered the possibility of developing drugs to target these high GABA level astrocytes after it was found that excessive GABA was released through an astrocyte-specific GABA transporter (GAT3/4).
"Our studies of AD mice showed that the high concentration of the GABA neurotransmitter in the reactive astrocytes of the dentate gyrus correlates with the animals' poor performance on tests of learning and memory," said senior author Dr. Gong Chen, professor of biology at Pennsylvania State University. "After we inhibited the astrocytic GABA transporter to reduce GABA inhibition in the brains of the AD mice, we found that they showed better memory capability than the control AD mice. We are very excited and encouraged by this result because it might explain why previous clinical trials failed by targeting amyloid plaques alone. One possible explanation is that while amyloid plaques may be reduced by targeting amyloid proteins, the other downstream alterations triggered by amyloid deposits, such as the excessive GABA inhibition discovered in our study, cannot be corrected by targeting amyloid proteins alone. Our studies suggest that reducing the excessive GABA inhibition to the neurons in the brain's dentate gyrus may lead to a novel therapy for Alzheimer's disease. An ultimate successful therapy may be a cocktail of compounds acting on several drug targets simultaneously."
Related Links:
Pennsylvania State University
Amyloid plaques and tau tangles are common pathological characteristics of AD. However, drugs designed to reduce production of the Abeta peptides that form amyloid plaques failed to relieve the symptoms of AD patients. Now, a paper published the June 13, 2014, online edition of the journal Nature Communications reported the presence of high GABA content in reactive astrocytes in the dentate gyrus (DG) of a mouse model for AD that resulted in increased tonic inhibition and memory deficit.
Investigators at Pennsylvania State University (University Park, USA) also confirmed the presence of astrocytes with a high GABA content in human AD patient brains. This finding suggested that a high astrocytic GABA level may be a novel biomarker and a potential diagnostic tool for AD.
They also considered the possibility of developing drugs to target these high GABA level astrocytes after it was found that excessive GABA was released through an astrocyte-specific GABA transporter (GAT3/4).
"Our studies of AD mice showed that the high concentration of the GABA neurotransmitter in the reactive astrocytes of the dentate gyrus correlates with the animals' poor performance on tests of learning and memory," said senior author Dr. Gong Chen, professor of biology at Pennsylvania State University. "After we inhibited the astrocytic GABA transporter to reduce GABA inhibition in the brains of the AD mice, we found that they showed better memory capability than the control AD mice. We are very excited and encouraged by this result because it might explain why previous clinical trials failed by targeting amyloid plaques alone. One possible explanation is that while amyloid plaques may be reduced by targeting amyloid proteins, the other downstream alterations triggered by amyloid deposits, such as the excessive GABA inhibition discovered in our study, cannot be corrected by targeting amyloid proteins alone. Our studies suggest that reducing the excessive GABA inhibition to the neurons in the brain's dentate gyrus may lead to a novel therapy for Alzheimer's disease. An ultimate successful therapy may be a cocktail of compounds acting on several drug targets simultaneously."
Related Links:
Pennsylvania State University
Latest BioResearch News
- Barcoded DNA Sheds Light on Hidden Complexities in Breast Cancer Detection
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
Heterotopic ossification (HO), the abnormal formation of bone in soft tissue, is a common complication following hip replacement surgery. The condition affects nearly one in three patients and can lead... Read more
New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
Stage 1 testicular germ cell tumor is typically treated with surgery followed by active surveillance. Although most patients experience strong long-term outcomes, about one in four will see their cancer... Read more
New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
Alzheimer’s disease begins developing years before memory loss or other symptoms become visible. Misfolded proteins gradually accumulate in the brain, disrupting normal cellular processes.... Read more
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
Blood sampling is one of the most common clinical procedures, but it can be difficult or uncomfortable for many patients, especially older adults or individuals with certain medical conditions.... Read more
Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing became widely recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic as a powerful method for detecting viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. PCR belongs to a group of diagnostic methods... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















