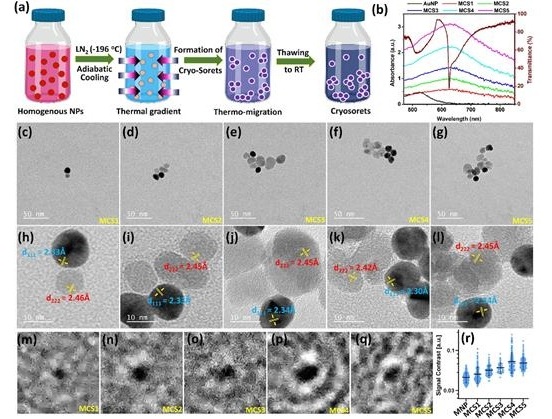
Novel Class of Enhancer RNAs Linked to Growth of Cancers
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 27 Aug 2018 |
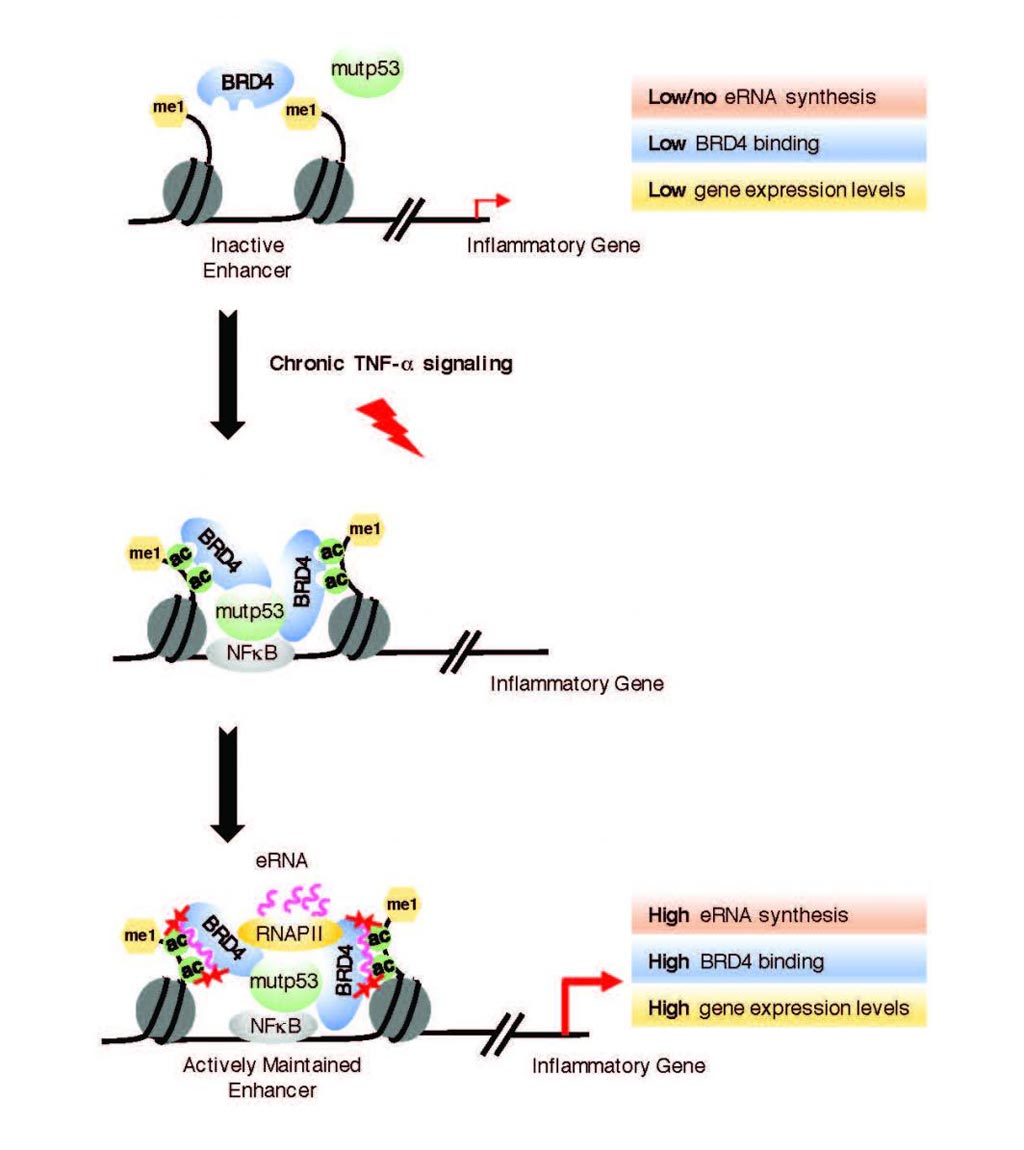
Image: Active enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) interact directly with BRD4, a protein linked to tumor development (Photo courtesy of the Lauberth laboratory, University of California, San Diego).
A recently described class of microRNA has been linked to the cancer-promoting activity of the mutated form of p53 protein.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNA) comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. MiRNAs resemble siRNAs of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
Augmenting the repertoire of "classical" miRNAs, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) identified several thousand enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) that were robustly produced in colon cancer cells in response to chronic immune signaling. Enhancer RNAs are transcribed from DNA sequences upstream and downstream of extragenic enhancer regions. Depending on the directionality of transcription, enhancer regions generate two different types of non-coding transcripts, unidirectional-eRNAs and bidirectional-eRNAs. The nature of the pre-initiation complex and specific transcription factors recruited to the enhancer may control the type of eRNAs generated.
After transcription, the majority of eRNAs remain in the nucleus, and as they are very unstable, they are actively degraded by the nuclear exosome. Not all enhancers are transcribed, with non-transcribed enhancers greatly outnumbering the transcribed ones in the order of magnitude of dozens of thousands in every given cell type. The theory that not all enhancers are transcribed at the same time and that eRNA transcription correlates with enhancer-specific activity support the idea that individual eRNAs carry distinct and relevant biological functions.
The investigators reported in the August 3, 2018, issue of the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology that in human colorectal cancer cells, Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) was recruited to enhancers that were co-occupied by mutant p53 and supported the synthesis of enhancer-directed transcripts (eRNAs) in response to chronic immune signaling. BRD4 selectively associated with eRNAs that were produced from BRD4-bound enhancers.
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) protein family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. BRD4, similar to other BET family members, contains two bromodomains (BDs) that recognize acetylated lysine residues. BRD4 also has an extended C-terminal domain with little sequence homology to other BET family members.
The investigators used biochemical and biophysical methods to show that BRD4 BDs functioned cooperatively as docking sites for eRNAs and that the BDs of BRD2, BRD3, BRDT, BRG1, and BRD7 directly interacted with eRNAs. BRD4-eRNA interactions increased BRD4 binding to acetylated histones in vitro and augmented BRD4 enhancer recruitment and transcriptional cofactor activities.
"Our findings reveal that eRNAs are key regulators of cancer by acting to reinforce BRD4 binding and keep it anchored on DNA, which keeps the tumor-promoting genes turned on at high levels," said senior author Dr. Shannon Lauberth, assistant professor of biology at the University of California, San Diego. "Interestingly, when we deplete several of these eRNAs, we can significantly reduce the expression of the tumor-promoting genes that the eRNAs and BRD4 are co-regulating. Now that we see that eRNAs impact BRD4 function, we have to rethink the way that we therapeutically target BRD4. Taken together, our findings are consistent with the emerging notion that eRNAs are functional molecules, rather than merely reflections of enhancer activation or simply transcriptional noise."
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNA) comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. MiRNAs resemble siRNAs of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
Augmenting the repertoire of "classical" miRNAs, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) identified several thousand enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) that were robustly produced in colon cancer cells in response to chronic immune signaling. Enhancer RNAs are transcribed from DNA sequences upstream and downstream of extragenic enhancer regions. Depending on the directionality of transcription, enhancer regions generate two different types of non-coding transcripts, unidirectional-eRNAs and bidirectional-eRNAs. The nature of the pre-initiation complex and specific transcription factors recruited to the enhancer may control the type of eRNAs generated.
After transcription, the majority of eRNAs remain in the nucleus, and as they are very unstable, they are actively degraded by the nuclear exosome. Not all enhancers are transcribed, with non-transcribed enhancers greatly outnumbering the transcribed ones in the order of magnitude of dozens of thousands in every given cell type. The theory that not all enhancers are transcribed at the same time and that eRNA transcription correlates with enhancer-specific activity support the idea that individual eRNAs carry distinct and relevant biological functions.
The investigators reported in the August 3, 2018, issue of the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology that in human colorectal cancer cells, Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) was recruited to enhancers that were co-occupied by mutant p53 and supported the synthesis of enhancer-directed transcripts (eRNAs) in response to chronic immune signaling. BRD4 selectively associated with eRNAs that were produced from BRD4-bound enhancers.
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) protein family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. BRD4, similar to other BET family members, contains two bromodomains (BDs) that recognize acetylated lysine residues. BRD4 also has an extended C-terminal domain with little sequence homology to other BET family members.
The investigators used biochemical and biophysical methods to show that BRD4 BDs functioned cooperatively as docking sites for eRNAs and that the BDs of BRD2, BRD3, BRDT, BRG1, and BRD7 directly interacted with eRNAs. BRD4-eRNA interactions increased BRD4 binding to acetylated histones in vitro and augmented BRD4 enhancer recruitment and transcriptional cofactor activities.
"Our findings reveal that eRNAs are key regulators of cancer by acting to reinforce BRD4 binding and keep it anchored on DNA, which keeps the tumor-promoting genes turned on at high levels," said senior author Dr. Shannon Lauberth, assistant professor of biology at the University of California, San Diego. "Interestingly, when we deplete several of these eRNAs, we can significantly reduce the expression of the tumor-promoting genes that the eRNAs and BRD4 are co-regulating. Now that we see that eRNAs impact BRD4 function, we have to rethink the way that we therapeutically target BRD4. Taken together, our findings are consistent with the emerging notion that eRNAs are functional molecules, rather than merely reflections of enhancer activation or simply transcriptional noise."
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego
Latest BioResearch News
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
- Liquid Biopsy More Effective for Analyzing Tumor Drug Resistance Mutations
- New Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Host-Pathogen Interactions
- Method Developed for Enriching Trophoblast Population in Samples
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New Reference Measurement Procedure Standardizes Nucleic Acid Amplification Test Results
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) play a key role in diagnosing a wide range of infectious diseases. These tests are generally known for their high sensitivity and specificity, and they can be developed... Read more
Pen-Like Tool Quickly and Non-Invasively Detects Opioids from Skin
Opioid drugs such as fentanyl, morphine, and oxycodone are the primary substances associated with overdose cases in the United States. Standard drug screening procedures typically involve collecting blood,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Could Predict Likelihood of Breast Cancer Spreading to The Bone
When breast cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it becomes secondary or metastatic breast cancer—a stage that, while treatable, is currently incurable. The bone is the most common site for this... Read more
New Infectious Disease Analytics Platform Speeds Up Clinical Decision-Making at POC
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of accurate and timely interpretation of diagnostic data became evident in shaping both public health strategies and clinical outcomes. As the world now grapples... Read moreHematology
view channel
Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most commonly ordered lab tests, crucial for diagnosing diseases, monitoring therapies, and conducting routine health screenings. However, more than 90% of physician... Read more
First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes
Heparin dosing requires careful management to avoid both bleeding and clotting complications. In high-risk situations like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality rates can reach about 50%,... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Blood Test Detects Organ Rejection in Heart Transplant Patients
Following a heart transplant, patients are required to undergo surgical biopsies so that physicians can assess the possibility of organ rejection. Rejection happens when the recipient’s immune system identifies... Read more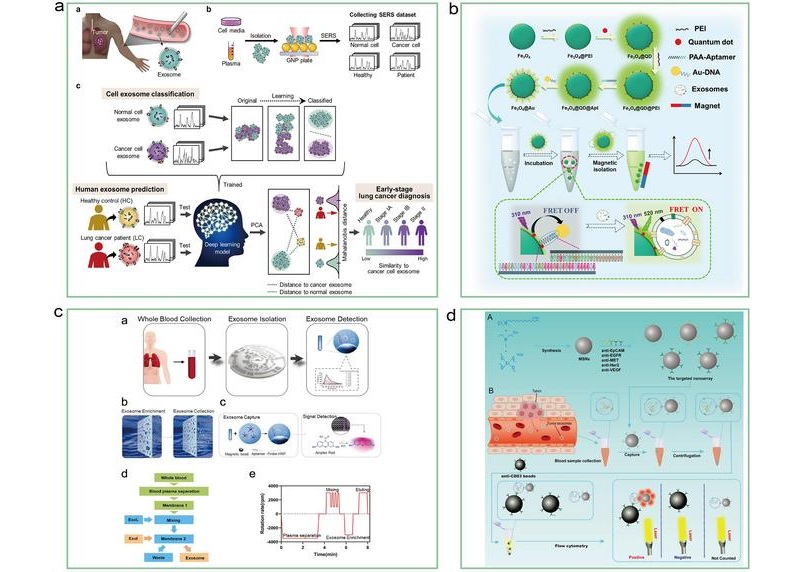
Liquid Biopsy Approach to Transform Diagnosis, Monitoring and Treatment of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer continues to be a major contributor to cancer-related deaths globally, with its biological complexity and diverse regulatory processes making diagnosis and treatment particularly difficult.... Read more
Computational Tool Exposes Hidden Cancer DNA Changes Influencing Treatment Resistance
Structural changes in tumor DNA are among the most damaging genetic alterations in cancer, yet they often go undetected, particularly when tissue samples are degraded or of low quality. These hidden genomic... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel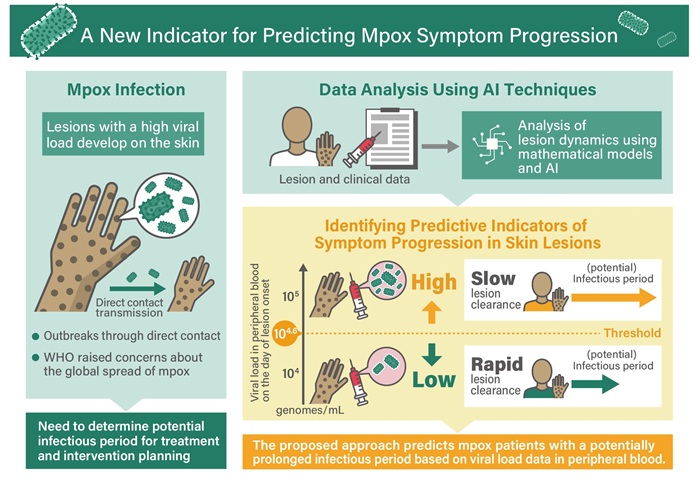
Viral Load Tests Can Help Predict Mpox Severity
Mpox is a viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and a characteristic rash, which evolves significantly over time and varies between patients. The disease spreads mainly through direct contact with... Read more
Gut Microbiota Analysis Enables Early and Non-Invasive Detection of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder marked by abnormal glucose metabolism during pregnancy, typically emerging in the mid to late stages. It significantly heightens the risk of... Read morePathology
view channelAI Performs Virtual Tissue Staining at Super-Resolution
Conventional histopathology, essential for diagnosing various diseases, typically involves chemically staining tissue samples to reveal cellular structures under a microscope. This process, known as “histochemical... Read moreAI-Driven Preliminary Testing for Pancreatic Cancer Enhances Prognosis
Pancreatic cancer poses a major global health threat due to its high mortality rate, with 467,409 deaths and 510,992 new cases reported worldwide in 2022. Often referred to as the "king" of all cancers,... Read more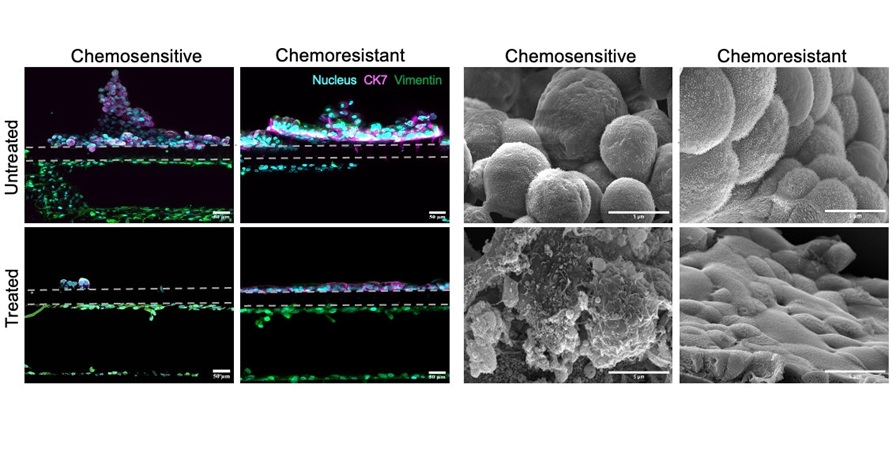
Cancer Chip Accurately Predicts Patient-Specific Chemotherapy Response
Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), one of the two primary types of esophageal cancer, ranks as the sixth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and currently lacks effective targeted therapies.... Read more
Clinical AI Solution for Automatic Breast Cancer Grading Improves Diagnostic Accuracy
Labs that use traditional image analysis methods often suffer from bottlenecks and delays. By digitizing their pathology practices, labs can streamline their work, allowing them to take on larger caseloads... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Inexpensive DNA Coated Electrode Paves Way for Disposable Diagnostics
Many people around the world still lack access to affordable, easy-to-use diagnostics for diseases like cancer, HIV, and influenza. Conventional sensors, while accurate, often rely on expensive equipment... Read more
New Miniature Device to Transform Testing of Blood Cancer Treatments
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment for blood cancers like leukemia, offering hope to patients when other treatments fail. However, despite its promise,... Read moreIndustry
view channel
AMP Releases Best Practice Recommendations to Guide Clinical Laboratories Offering HRD Testing
Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) testing identifies tumors that are unable to effectively repair DNA damage through the homologous recombination repair pathway. This deficiency is often linked... Read more