Circulating Trophoblast-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Testing Are Feasible
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 26 Dec 2019 |

Image: A CyteFinder instrument is an automated six channel fluorescence microscopes that rapidly image slides and employ machine learning to identify rare cells (Photo courtesy of RareCyte)
Circulating cells from the fetus or placenta in a pregnant woman’s blood, primarily trophoblasts and nucleated fetal red blood cells (fnRBCs), have long been appreciated as potential targets for noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and diagnosis.
While cell-free DNA-based NIPT has taken off in recent years, a number of groups have been focusing their efforts on fetal cell-based methods, which would enable the analysis of pure fetal DNA instead of a mixture of maternal and fetal genetic material and possibly yield more accurate results with higher resolution.
Molecular Geneticists at Baylor College of Medicine (Houston TX, USA) and their colleagues collected two sets of blood samples from a total of 95 pregnant women who were recruited during prenatal visits, one set of 42 samples and another of 53 samples. Most came were from singleton pregnancies, and gestational age ranged from 8 weeks to 29 weeks.
To enrich trophoblasts, the scientists used a previously published positive selection protocol that they had since optimized. It involved antibodies against three trophoblast cell-surface antigens, HLA-G, TROP-2, and EpCAM, and magnetic bead selection. This was followed by immunostaining with anti-cytokeratin and CD45 antibodies. The samples were then spread on a slide and scanned using a CyteFinder instrument (RareCyte, Seattle, WA, USA). After manually identifying trophoblast candidates under the microscope, based on their cytokeratin patterns and the absence of CD45, the team picked individual cells using the RareCyte CytePicker.
The team, on average, identified five to seven trophoblasts per blood sample, with only two samples where no such cells could be found. Subsequent sequencing and genotyping showed that 94% to 96% of the cells scored as trophoblasts under the microscope were indeed of fetal origin. In addition, a little over half the samples had at least two high-quality trophoblasts where the sequencing results could be scored for both aneuploidy and small copy number variants.
For a total of 45 samples, the scientists had diagnostic results from amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) available. For 34 of these, they saw concordance with the single circulating trophoblast (SCT) sequencing results, and for eight cases, the diagnostic results were normal but SCT testing failed.
The authors concluded that SCT analysis is potentially a powerful tool for prenatal testing and diagnosis. They are optimistic that the recovery of trophoblasts can be improved. SCT testing has the potential to deliver a diagnostic result instead of being merely a screening test if an adequate number of trophoblast cells can be obtained for every sampled pregnancy. A longer-term goal would be to detect all de novo point mutations in a fetus. The study was published on November 27, 2019 in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
Related Links:
Baylor College of Medicine
RareCyte
While cell-free DNA-based NIPT has taken off in recent years, a number of groups have been focusing their efforts on fetal cell-based methods, which would enable the analysis of pure fetal DNA instead of a mixture of maternal and fetal genetic material and possibly yield more accurate results with higher resolution.
Molecular Geneticists at Baylor College of Medicine (Houston TX, USA) and their colleagues collected two sets of blood samples from a total of 95 pregnant women who were recruited during prenatal visits, one set of 42 samples and another of 53 samples. Most came were from singleton pregnancies, and gestational age ranged from 8 weeks to 29 weeks.
To enrich trophoblasts, the scientists used a previously published positive selection protocol that they had since optimized. It involved antibodies against three trophoblast cell-surface antigens, HLA-G, TROP-2, and EpCAM, and magnetic bead selection. This was followed by immunostaining with anti-cytokeratin and CD45 antibodies. The samples were then spread on a slide and scanned using a CyteFinder instrument (RareCyte, Seattle, WA, USA). After manually identifying trophoblast candidates under the microscope, based on their cytokeratin patterns and the absence of CD45, the team picked individual cells using the RareCyte CytePicker.
The team, on average, identified five to seven trophoblasts per blood sample, with only two samples where no such cells could be found. Subsequent sequencing and genotyping showed that 94% to 96% of the cells scored as trophoblasts under the microscope were indeed of fetal origin. In addition, a little over half the samples had at least two high-quality trophoblasts where the sequencing results could be scored for both aneuploidy and small copy number variants.
For a total of 45 samples, the scientists had diagnostic results from amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS) available. For 34 of these, they saw concordance with the single circulating trophoblast (SCT) sequencing results, and for eight cases, the diagnostic results were normal but SCT testing failed.
The authors concluded that SCT analysis is potentially a powerful tool for prenatal testing and diagnosis. They are optimistic that the recovery of trophoblasts can be improved. SCT testing has the potential to deliver a diagnostic result instead of being merely a screening test if an adequate number of trophoblast cells can be obtained for every sampled pregnancy. A longer-term goal would be to detect all de novo point mutations in a fetus. The study was published on November 27, 2019 in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
Related Links:
Baylor College of Medicine
RareCyte
Latest Immunology News
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- Luminescent Probe Measures Immune Cell Activity in Real Time
- Blood-Based Immune Cell Signatures Could Guide Treatment Decisions for Critically Ill Patients
- Novel Tool Predicts Most Effective Multiple Sclerosis Medication for Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more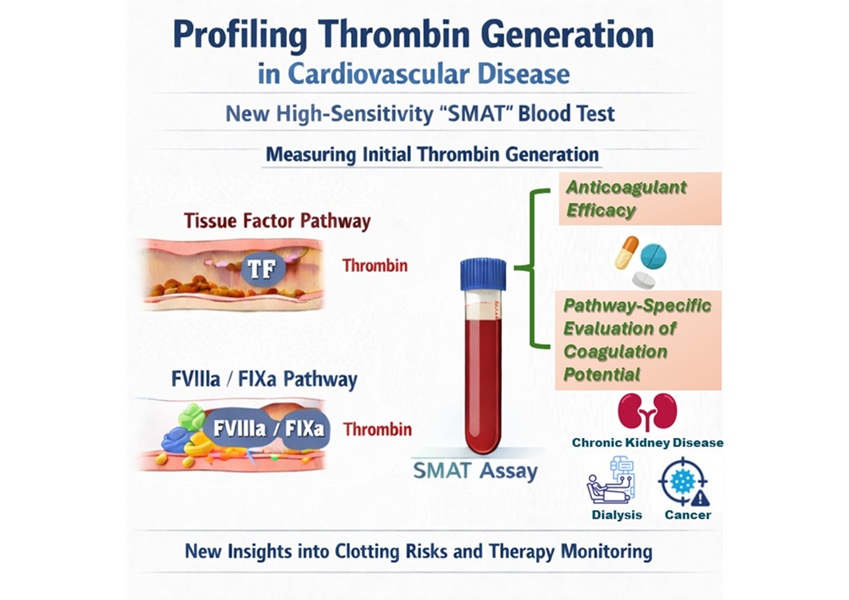
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel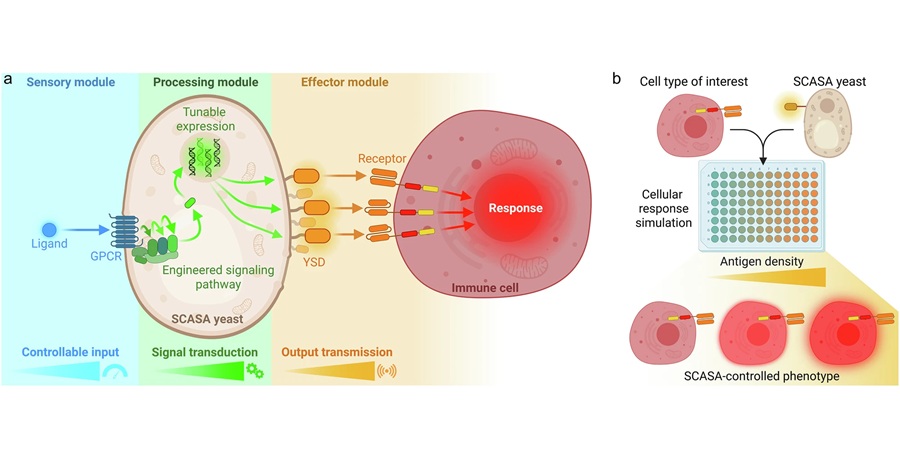
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more