Диагностический процесс определяет годы наступления болезни Альцгеймера до появления симптомов
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 24 Jul 2019 |
Набор V-PLEX Aβ Peptide Panel 1 (6E10). Фото любезно предоставлено Meso Scale Discovery.
Патология болезни Альцгеймера (БА) сопровождается неверным складыванием амилоида-β (Aβ) и тау из мономерного в обогащенные β-складками патогенные виды. Предполагается, что этот процесс происходит примерно за 10-15 лет до клинического начала заболевания.
Новый двухэтапный диагностический процесс может обнаружить болезнь Альцгеймера почти за десять лет до появления клинических симптомов. Следует надеяться, что метод, который включает измерение как амилоидных, так и тау-белков в крови и спинномозговой жидкости, улучшит результаты клинических испытаний и поможет точнее идентифицировать пациентов на самых ранних стадиях заболевания.
Группа ученых в сотрудничестве с Рурским университетом в Бохуме (Ruhr-University Bochum; Бохум, Германия) провела проспективное исследование 61 субъекта с контролем заболевания (КЗ), при этом 39 случаев БА были доступны из проспективного исследования, разработанного и инициированного геронтопсихиатрическим сектором отделения психиатрии и психотерапии между 2009 и 2013 гг. Для всех субъектов были доступны уровни спинномозговой жидкости (СМЖ) Aβ40, Aβ42, ttau, ptau, соотношение Aβ42/40 и демографические данные.
Все образцы СМЖ оценивались с помощью набора мультиплексной пептидной панели Meso Scale Discovery V-PLEX Aβ с использованием моноклонального антитела 6E10 для обнаружения. Пептиды Aβ Aβ38, 40 и 42 определялись после 16-кратного разбавления образцов СМЖ "Diluent 35" (MSD). Концентрации ttau и ptau в СМЖ измерялись в двух экземплярах с помощью коммерчески доступного ИФА в аккредитованной экспертной лаборатории для диагностики нейрохимической деменции под контролем СМЖ. Иммуно-инфракрасный датчик был функционализирован моноклональным антителом для обнаружения Aβ в плазме крови и СМЖ и моноклональным антителом TAU-5 для обнаружения тау в СМЖ. Зарегистрированная полоса поглощения амида I представляла распределение вторичной структуры биомаркера в соответствующей жидкости организма по его максимальной частоте.
Ученые сообщили, что благодаря комбинации обоих анализов 87 из 100 пациентов с болезнью Альцгеймера в проведенном исследовании были определены правильно, число ложноположительных диагнозов у здоровых субъектов было сокращено до 3 из 100. Второй анализ проводится на СМЖ, которая извлекается из спинного мозга. На этом этапе второй диагностический тест для тау-белков может быть измерен только с использованием СМЖ. Из-за инвазивного характера сбора спинномозговой жидкости команда признала, что этот метод не является идеальным и ведется работа по поиску эффективных способов обнаружения тау в образцах крови. Тем не менее двухэтапный процесс может быть развернут относительно скоро в его нынешней форме с предположением, что второй анализ СМЖ должен проводиться только на субъектах с положительным результатом в первом анализе крови.
Доктор философии, профессор и старший автор исследования Клаус Герверт (Klaus Gerwert) сказал: "Теперь можно начать работу над новыми клиническими исследованиями с участниками испытаний на самых ранних стадиях заболевания. Недавно два крупных многообещающих исследования, в частности Crenezumab и Aducanumab, потерпели неудачу, и не в последнюю очередь потому, что слишком поздно приступили к началу терапии. Новый тест открывает окно для новых возможностей терапии". Исследование было опубликовано онлайн 12 марта 2019 года в журнале "Болезнь Альцгеймера и деменция: диагностика, оценка и мониторинг заболевания" (Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring).
Ссылки по теме:
Рурский университет в Бохуме
Новый двухэтапный диагностический процесс может обнаружить болезнь Альцгеймера почти за десять лет до появления клинических симптомов. Следует надеяться, что метод, который включает измерение как амилоидных, так и тау-белков в крови и спинномозговой жидкости, улучшит результаты клинических испытаний и поможет точнее идентифицировать пациентов на самых ранних стадиях заболевания.
Группа ученых в сотрудничестве с Рурским университетом в Бохуме (Ruhr-University Bochum; Бохум, Германия) провела проспективное исследование 61 субъекта с контролем заболевания (КЗ), при этом 39 случаев БА были доступны из проспективного исследования, разработанного и инициированного геронтопсихиатрическим сектором отделения психиатрии и психотерапии между 2009 и 2013 гг. Для всех субъектов были доступны уровни спинномозговой жидкости (СМЖ) Aβ40, Aβ42, ttau, ptau, соотношение Aβ42/40 и демографические данные.
Все образцы СМЖ оценивались с помощью набора мультиплексной пептидной панели Meso Scale Discovery V-PLEX Aβ с использованием моноклонального антитела 6E10 для обнаружения. Пептиды Aβ Aβ38, 40 и 42 определялись после 16-кратного разбавления образцов СМЖ "Diluent 35" (MSD). Концентрации ttau и ptau в СМЖ измерялись в двух экземплярах с помощью коммерчески доступного ИФА в аккредитованной экспертной лаборатории для диагностики нейрохимической деменции под контролем СМЖ. Иммуно-инфракрасный датчик был функционализирован моноклональным антителом для обнаружения Aβ в плазме крови и СМЖ и моноклональным антителом TAU-5 для обнаружения тау в СМЖ. Зарегистрированная полоса поглощения амида I представляла распределение вторичной структуры биомаркера в соответствующей жидкости организма по его максимальной частоте.
Ученые сообщили, что благодаря комбинации обоих анализов 87 из 100 пациентов с болезнью Альцгеймера в проведенном исследовании были определены правильно, число ложноположительных диагнозов у здоровых субъектов было сокращено до 3 из 100. Второй анализ проводится на СМЖ, которая извлекается из спинного мозга. На этом этапе второй диагностический тест для тау-белков может быть измерен только с использованием СМЖ. Из-за инвазивного характера сбора спинномозговой жидкости команда признала, что этот метод не является идеальным и ведется работа по поиску эффективных способов обнаружения тау в образцах крови. Тем не менее двухэтапный процесс может быть развернут относительно скоро в его нынешней форме с предположением, что второй анализ СМЖ должен проводиться только на субъектах с положительным результатом в первом анализе крови.
Доктор философии, профессор и старший автор исследования Клаус Герверт (Klaus Gerwert) сказал: "Теперь можно начать работу над новыми клиническими исследованиями с участниками испытаний на самых ранних стадиях заболевания. Недавно два крупных многообещающих исследования, в частности Crenezumab и Aducanumab, потерпели неудачу, и не в последнюю очередь потому, что слишком поздно приступили к началу терапии. Новый тест открывает окно для новых возможностей терапии". Исследование было опубликовано онлайн 12 марта 2019 года в журнале "Болезнь Альцгеймера и деменция: диагностика, оценка и мониторинг заболевания" (Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring).
Ссылки по теме:
Рурский университет в Бохуме
Latest Иммунология News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more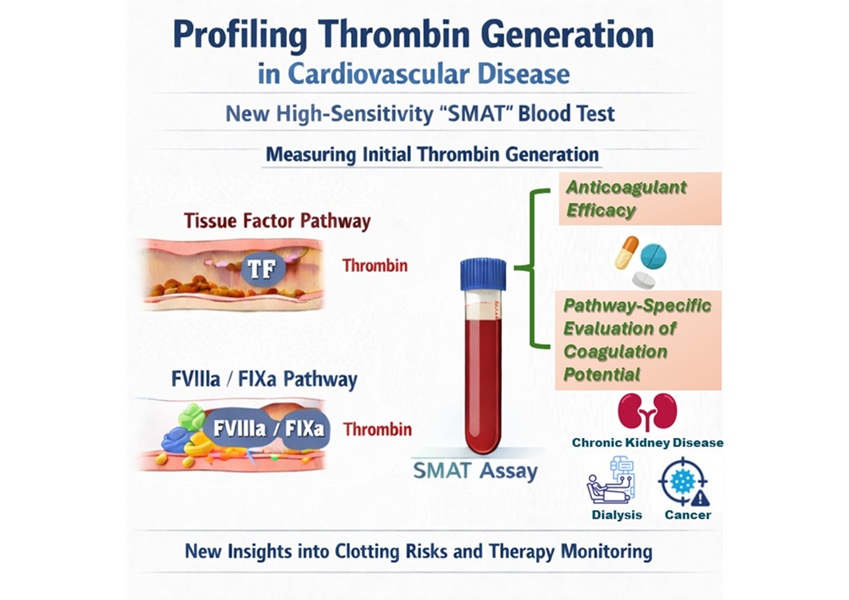
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel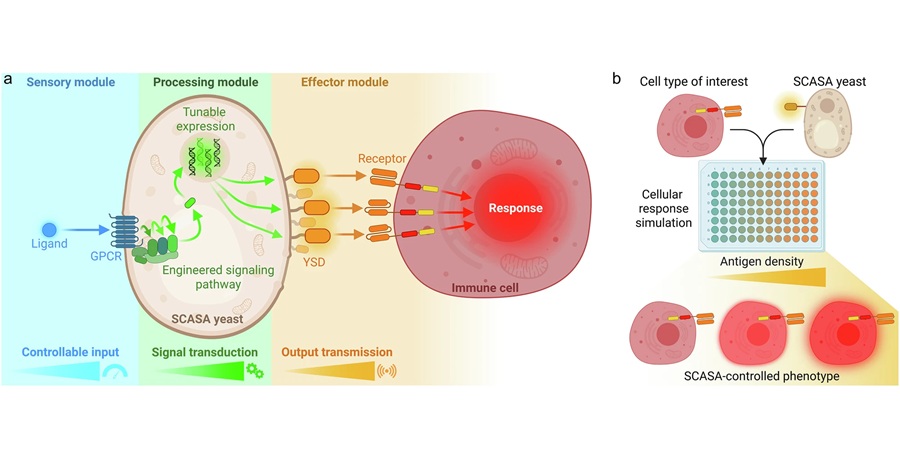
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more