Уровни воспалительного маркера связаны с ухудшением функции почек
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 14 Nov 2018 |
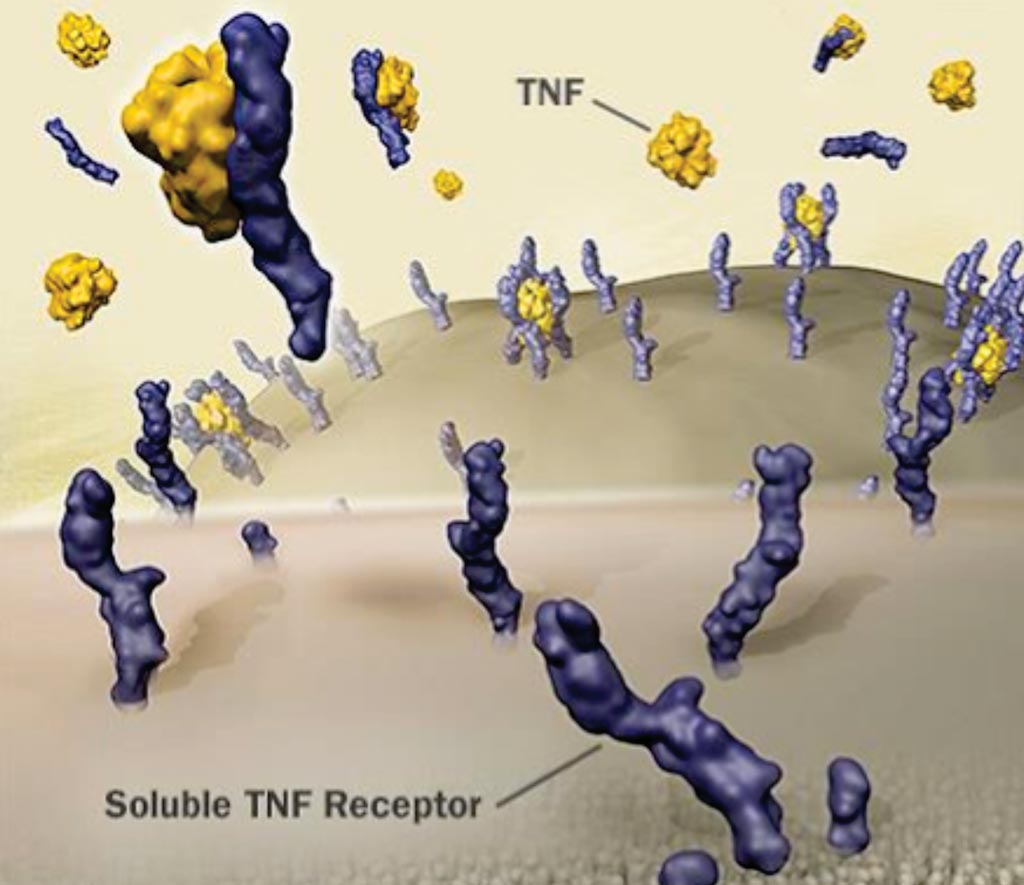
Более высокие уровни воспалительного биомаркера растворимого рецептора-1 фактора некроза опухоли (sTNFR-1) связаны с ухудшением функции почек у здоровых взрослых людей (фото любезно предоставлено Enbrel).
Рецептор-1 фактора некроза опухоли (TNFR-1), который играет важную роль в дисфункции эндотелиальных клеток и воспалении, экспрессируется на поверхности клетки в клубочковом и перитубулярном капиллярном эндотелии почек.
Более высокие концентрации растворимого рецептора-1 (sTNFR-1) связаны с прогрессированием заболевания почек у людей с установленным диабетическим заболеванием почек. Предыдущие исследования показали, что уровни sTNFR-1 в крови связаны с прогрессированием заболевания почек у лиц с установленным заболеванием почек.
Ученые из Школы медицины Вашингтонского университета (Сиэтл, штат Вашингтон, США) и их коллеги провели многонациональное исследование среди 2548 взрослых, средний возраст которых составил 61 год, 51% из них – женщины. Участники исследования, как правило, не имели сведений о наличии у них заболевания почек или сердца в начале исследования, когда измерялись уровни sTNFR-1. Группа исследовала связи между базовыми концентрациями sTNFR-1 и 10-летним снижением оценочной скорости клубочковой фильтрации (eGFR: эпизодическое снижение на 40% и ежегодное пропорциональное снижение). Концентрации креатинина в сыворотке определялись на момент регистрации участников исследования и через 3, 5 и 10 лет.
Ученые сообщили, что средний исходный уровень eGFR составлял 79 мл/мин на 1,73 кв.м. Уровень sTNFR-1 в сыворотке был обратно связан с исходным уровнем eGFR. За среднее время наблюдения 9,3 года у 110 участников развилось снижение eGFR более чем на 40%; более высокая концентрация sTNFR1 была связана с повышенным на 40% риском снижения eGFR (скорректированное отношение рисков 1,43, 95% доверительный интервал [95% ДИ] от 1,16 до 1,77). Самый высокий терциль sTNFR-1 был связан со скорректированным годовым снижением eGFR на 1,94% (95% ДИ от 1,79 до 2,09). Связи сохранялись в подгруппах, сформированных в соответствии с демографическими показателями, наличием гипертонии, диабета и базовым статусом хронического заболевания почек.
Авторы пришли к выводу, что повышенные концентрации sTNFR-1 в сыворотке связаны с более быстрым снижением уровня eGFR в течение десятилетия в многонациональной популяции, независимо от ранее известных факторов риска прогрессирования заболевания почек. sTNFR-1 ассоциировался со значительной разницей в снижении функции почек с течением времени. Темпы снижения в течение 10 лет были почти в 4 раза выше среди людей в категориях с наивысшими, по сравнению с самыми низкими, уровнями sTNFR-1. Эта ассоциация не зависела от ранее известных факторов риска прогрессирования заболевания почек и сохранялась в нескольких подгруппах участников.
Паван К. Бхатраджу (Pavan K. Bhatraju), доктор медицины, ведущий автор исследования, говорит: “Многие люди продолжают постепенно терять функции почек, несмотря на лечение с применением современных лекарственных препаратов. Необходимо срочно использовать новые методы лечения, чтобы предотвратить или замедлить потерю функции почек. В наших исследованиях выявлен новый маркер, который сильно связан со снижением функции почек с течением времени в крупной многонациональной когорте, поэтому мы предлагаем провести последующие исследования, чтобы подтвердить потенциальную роль sTNFR-1 в развитии снижения функции почек”. Исследование было опубликован 4 октября 2018 года в Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Ссылки по теме:
University of Washington School of Medicine
Более высокие концентрации растворимого рецептора-1 (sTNFR-1) связаны с прогрессированием заболевания почек у людей с установленным диабетическим заболеванием почек. Предыдущие исследования показали, что уровни sTNFR-1 в крови связаны с прогрессированием заболевания почек у лиц с установленным заболеванием почек.
Ученые из Школы медицины Вашингтонского университета (Сиэтл, штат Вашингтон, США) и их коллеги провели многонациональное исследование среди 2548 взрослых, средний возраст которых составил 61 год, 51% из них – женщины. Участники исследования, как правило, не имели сведений о наличии у них заболевания почек или сердца в начале исследования, когда измерялись уровни sTNFR-1. Группа исследовала связи между базовыми концентрациями sTNFR-1 и 10-летним снижением оценочной скорости клубочковой фильтрации (eGFR: эпизодическое снижение на 40% и ежегодное пропорциональное снижение). Концентрации креатинина в сыворотке определялись на момент регистрации участников исследования и через 3, 5 и 10 лет.
Ученые сообщили, что средний исходный уровень eGFR составлял 79 мл/мин на 1,73 кв.м. Уровень sTNFR-1 в сыворотке был обратно связан с исходным уровнем eGFR. За среднее время наблюдения 9,3 года у 110 участников развилось снижение eGFR более чем на 40%; более высокая концентрация sTNFR1 была связана с повышенным на 40% риском снижения eGFR (скорректированное отношение рисков 1,43, 95% доверительный интервал [95% ДИ] от 1,16 до 1,77). Самый высокий терциль sTNFR-1 был связан со скорректированным годовым снижением eGFR на 1,94% (95% ДИ от 1,79 до 2,09). Связи сохранялись в подгруппах, сформированных в соответствии с демографическими показателями, наличием гипертонии, диабета и базовым статусом хронического заболевания почек.
Авторы пришли к выводу, что повышенные концентрации sTNFR-1 в сыворотке связаны с более быстрым снижением уровня eGFR в течение десятилетия в многонациональной популяции, независимо от ранее известных факторов риска прогрессирования заболевания почек. sTNFR-1 ассоциировался со значительной разницей в снижении функции почек с течением времени. Темпы снижения в течение 10 лет были почти в 4 раза выше среди людей в категориях с наивысшими, по сравнению с самыми низкими, уровнями sTNFR-1. Эта ассоциация не зависела от ранее известных факторов риска прогрессирования заболевания почек и сохранялась в нескольких подгруппах участников.
Паван К. Бхатраджу (Pavan K. Bhatraju), доктор медицины, ведущий автор исследования, говорит: “Многие люди продолжают постепенно терять функции почек, несмотря на лечение с применением современных лекарственных препаратов. Необходимо срочно использовать новые методы лечения, чтобы предотвратить или замедлить потерю функции почек. В наших исследованиях выявлен новый маркер, который сильно связан со снижением функции почек с течением времени в крупной многонациональной когорте, поэтому мы предлагаем провести последующие исследования, чтобы подтвердить потенциальную роль sTNFR-1 в развитии снижения функции почек”. Исследование было опубликован 4 октября 2018 года в Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.
Ссылки по теме:
University of Washington School of Medicine
Latest Химия News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more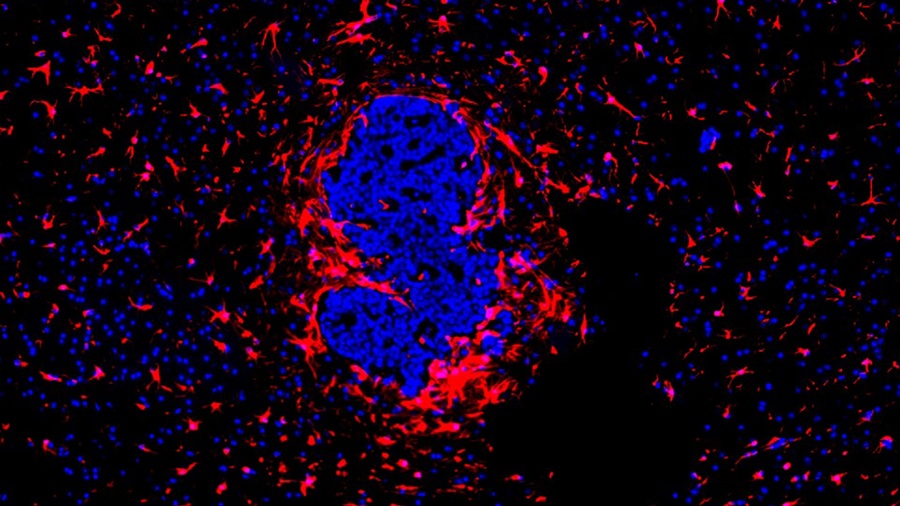
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more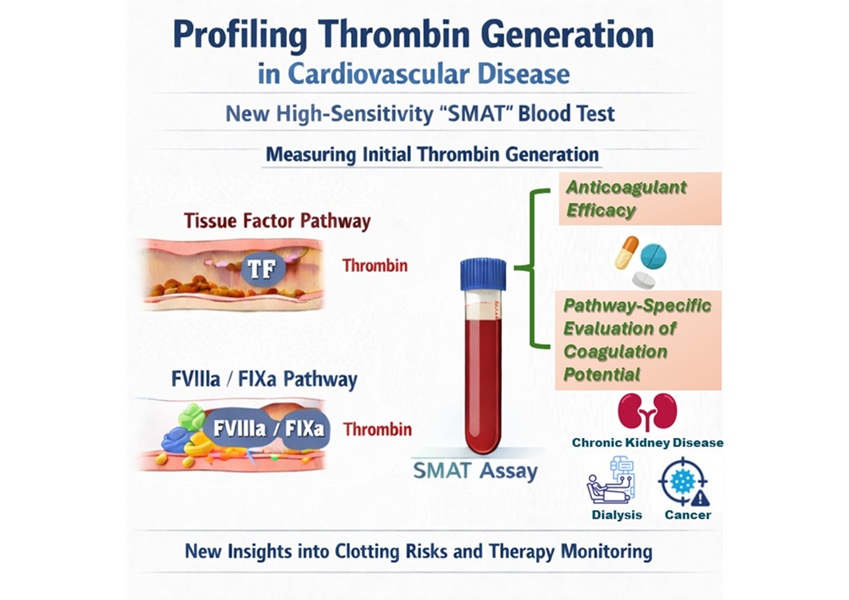
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel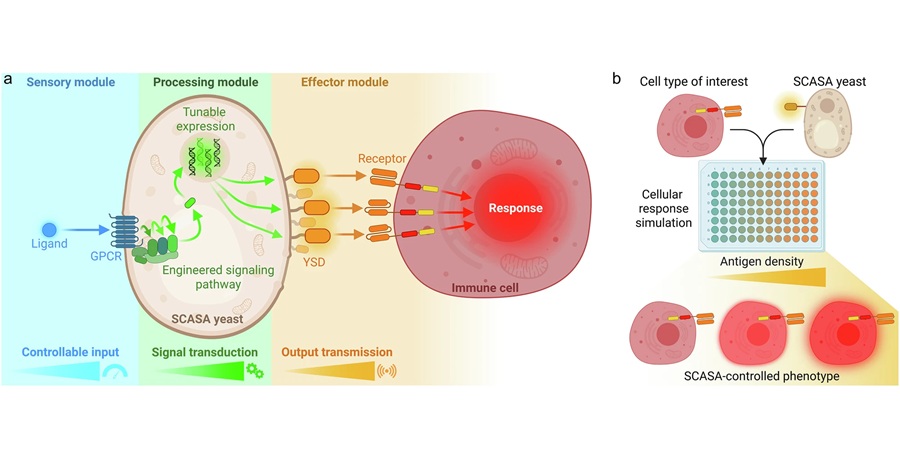
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more