老年妇女的激素水平会改变CVD风险
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 28 Jun 2018 |
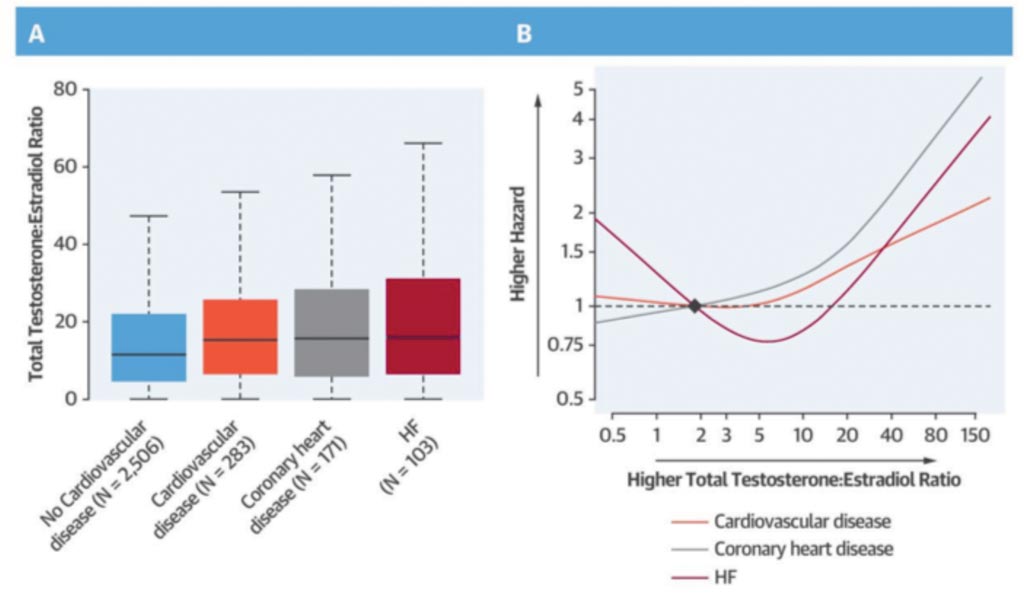
图片:绝经妇女的睾丸酮/雌二醇比率与心血管病、冠心病和心力衰竭(HF)的风险(图片蒙约翰霍普金斯大学惠赐)。
雄激素水平升高、雌激素水平降低与妇女的心血管疾病(CVD)风险有关;然而,研究妇女的性激素与CVD发病事件后,却产生了相互矛盾的结果。
此前的研究显示,妇女绝经前的心脏病发病率低于男子,因为绝经后雌激素水平急剧下降,所以医师一度以为取代雌激素会降低心血管疾病风险。此前其它的研究显示雌激素替代品未必有保护作用,还可能升高脑卒中、凝血和心脏病风险。
一组科学家与美国马里兰州巴尔的摩的约翰霍普金斯大学医学院(www.hopkinsmedicine.org)合作,分析了2,834名绝经妇女的数据,她们参与了联邦资助的多民族动脉粥样硬化研究(MESA)项目。研究开始时参与者的平均年龄为65岁,38%是白人,28%是非裔,22%是拉丁裔,12%是华裔。初诊是在2000年到2002年期间,科学家取血样测量睾丸酮与雌激素的水平。
在12年的随访过程中,通过病历、住院、电话采访和死亡证书发现,这些妇女有283例心血管疾病,包括171例冠心病和心脏病突发、88例脑卒中和103例心力衰竭。科研小组比较心脏病与心血管疾病病例的睾丸酮与雌激素水平时发现,睾丸酮水平升高一般与风险升高相关,雌二醇水平升高一般与风险降低相关。睾丸酮与雌激素的比率每升高一个标准单位,心血管疾病风险就增加19%,冠心病风险增加45%,心力衰竭风险增加31%。
该研究的论文发表于2018年6月号的《美国心脏学会杂志》(of the American College of Cardiology)。资深作者、医学副教授Erin D. Michos大夫说:“医生不常检查女性的性激素水平及其比率。因为睾丸酮(主要的雄性激素)相对于雌二醇(主要的雌性激素)的比例不平衡,这可能影响心脏病风险,所以医生也许应考虑把激素检验作为一项可筛查的风险因子,补充其它风险因子,如血压和胆固醇,以识别心脏病或血管病风险更高的妇女。”
约翰霍普金斯大学医学院>>> www.hopkinsmedicine.org
Latest 血液学 News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more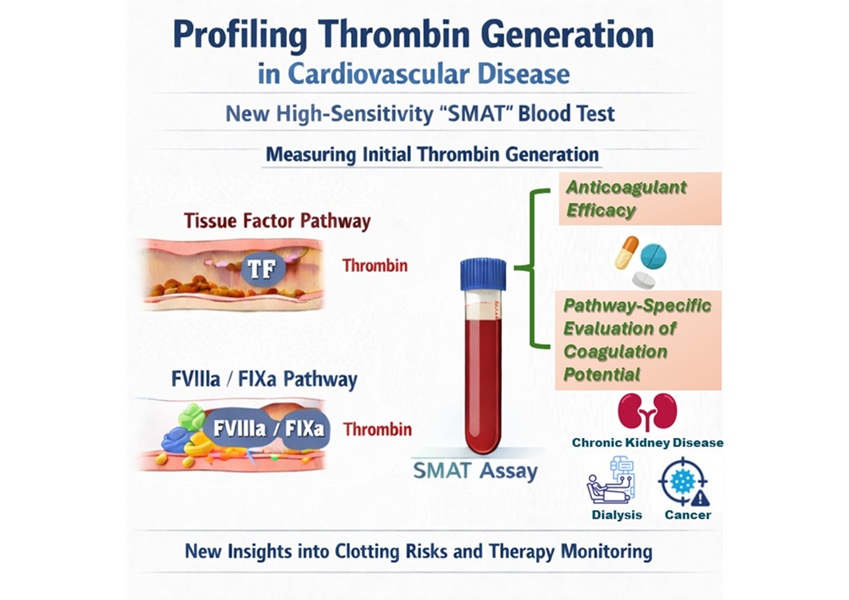
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel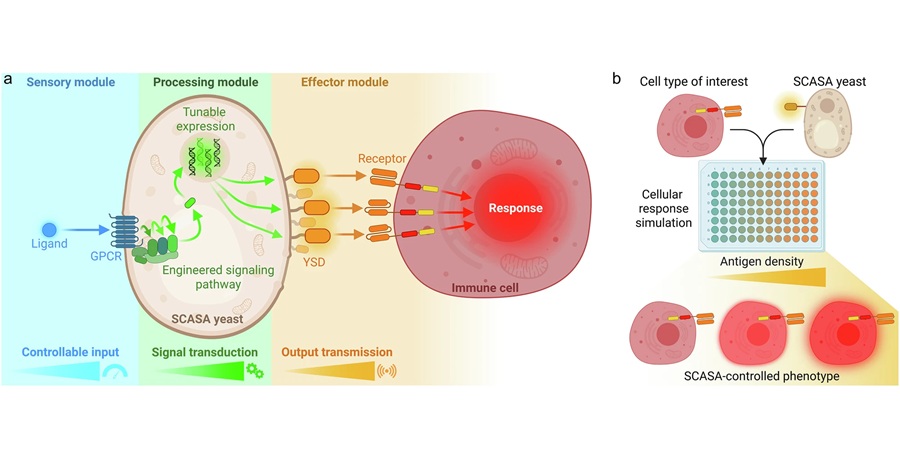
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more