Interaction between Proteins Revealed by Cryo-EM Mapping
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 11 Apr 2017 |
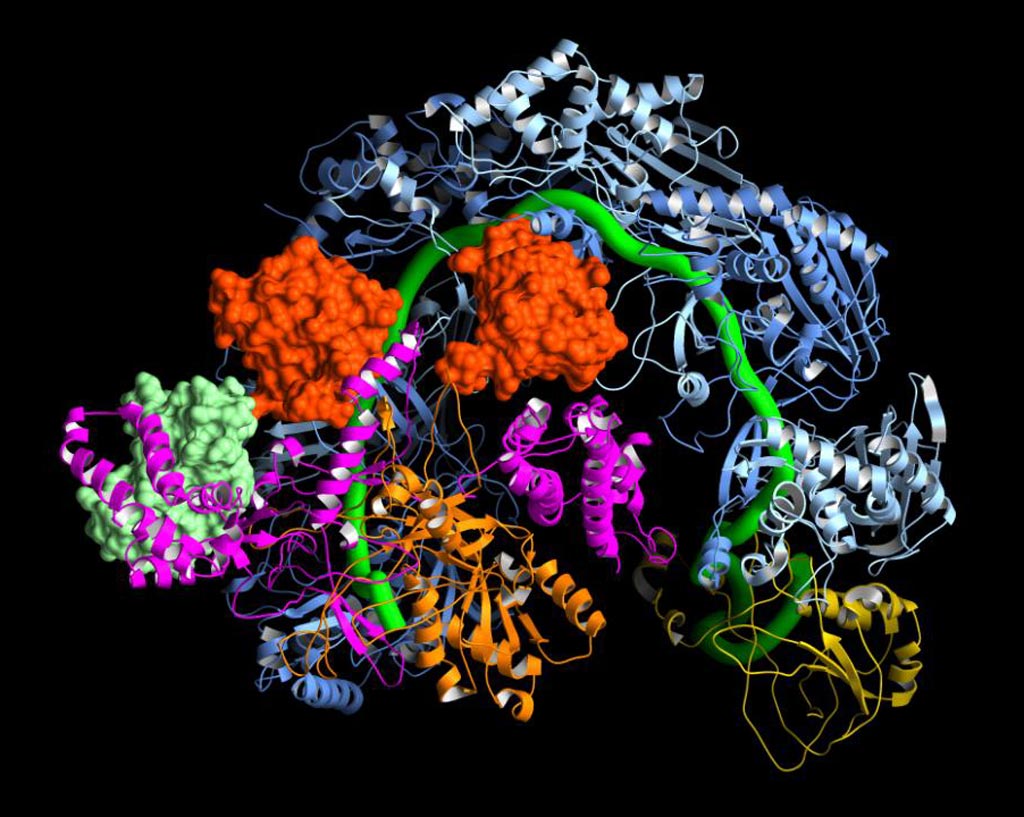
Image: This image shows how the CRISPR surveillance complex is disabled by two copies of anti-CRISPR protein AcrF1 (red) and one AcrF2 (light green). These anti-CRISPRs block access to the CRISPR RNA (green tube) preventing the surveillance complex from scanning and targeting invading viral DNA for destruction (Photo courtesy of The Scripps Research Institute).
Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryro-EM) molecular mapping was used to determine how the bacterial gene editing complex CRISPR/Cas9 interacts with viral anti-CRISPR proteins.
CRISPRs (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) are segments of prokaryotic DNA containing short repetitions of base sequences. Each repetition is followed by short segments of "spacer DNA" from previous exposures to a bacterial virus or plasmid. CRISPRs are found in approximately 40% of sequenced bacteria genomes and 90% of sequenced archaea. CRISPRs are often associated with cas genes that code for proteins related to CRISPRs.
Since 2013, the CRISPR/Cas system has been used in research for gene editing (adding, disrupting, or changing the sequence of specific genes) and gene regulation. By delivering the Cas9 enzyme and appropriate guide RNAs (sgRNAs) into a cell, the organism's genome can be cut at any desired location. The conventional CRISPR/Cas9 system is composed of two parts: the Cas9 enzyme, which cleaves the DNA molecule and specific RNA guides that shepherd the Cas9 protein to the target gene on a DNA strand. Prokaryotes evolved CRISPR-mediated adaptive immune systems for protection from viral infection, and viruses have evolved diverse anti-CRISPR (Acr) proteins that subvert these immune systems.
Investigators at the Scripps Research Institute reported in the March 23, 2017, issue of the journal Cell that they had used Cryo-EM to determine the structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa CRISPR complex bound to two different Acr proteins, AcrF1 and AcrF2, at an average resolution of 3.4 Angstroms.
Researchers have historically relied on NMR and X-ray diffraction techniques to determine the structures of molecular complexes and proteins that play a role in the causes of various disease states. Structural information about a variety of medically important proteins and drugs has been obtained by these methods. Cryo-EM is a complementary analytical technique that provides near-atomic resolution without requirements for crystallization or limits on molecular size and complexity imposed by the other techniques. Cryo-EM allows the observation of specimens that have not been stained or fixed in any way, showing them in their native environment while integrating multiple images to form a three-dimensional model of the sample.
The molecular structure obtained during this study explained the mechanism for immune system suppression, and structure-guided mutations showed that the Acr proteins bound to residues essential for crRNA-mediated detection of DNA.
"These findings are important because we knew that anti-CRISPR proteins were blocking bacterial defenses, but we had no idea how," said senior author Dr. Gabriel C. Lander, assistant professor of integrative structural and computational biology at the Scripps Research Institute. "This system can quickly read through massive lengths of DNA and accurately hit its target. If the CRISPR complex identifies a viral DNA target, the surveillance machine recruits other molecules to destroy the virus's genome. These anti-CRISPR proteins keep the bacteria from recognizing the viral DNA. CRISPR systems cannot escape from these anti-CRISPR proteins without completely changing the mechanism they use to recognize DNA."
"Although CRISPR/Cas9 is the "celebrity" CRISPR system, there are 19 different types of CRISPR systems, each of which may have unique advantages for genetic engineering. They are a massive, untapped resource," said Dr. Lander. "The more we learn about the structures of these systems, the more we can take advantage of them as genome-editing tools."
CRISPRs (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) are segments of prokaryotic DNA containing short repetitions of base sequences. Each repetition is followed by short segments of "spacer DNA" from previous exposures to a bacterial virus or plasmid. CRISPRs are found in approximately 40% of sequenced bacteria genomes and 90% of sequenced archaea. CRISPRs are often associated with cas genes that code for proteins related to CRISPRs.
Since 2013, the CRISPR/Cas system has been used in research for gene editing (adding, disrupting, or changing the sequence of specific genes) and gene regulation. By delivering the Cas9 enzyme and appropriate guide RNAs (sgRNAs) into a cell, the organism's genome can be cut at any desired location. The conventional CRISPR/Cas9 system is composed of two parts: the Cas9 enzyme, which cleaves the DNA molecule and specific RNA guides that shepherd the Cas9 protein to the target gene on a DNA strand. Prokaryotes evolved CRISPR-mediated adaptive immune systems for protection from viral infection, and viruses have evolved diverse anti-CRISPR (Acr) proteins that subvert these immune systems.
Investigators at the Scripps Research Institute reported in the March 23, 2017, issue of the journal Cell that they had used Cryo-EM to determine the structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa CRISPR complex bound to two different Acr proteins, AcrF1 and AcrF2, at an average resolution of 3.4 Angstroms.
Researchers have historically relied on NMR and X-ray diffraction techniques to determine the structures of molecular complexes and proteins that play a role in the causes of various disease states. Structural information about a variety of medically important proteins and drugs has been obtained by these methods. Cryo-EM is a complementary analytical technique that provides near-atomic resolution without requirements for crystallization or limits on molecular size and complexity imposed by the other techniques. Cryo-EM allows the observation of specimens that have not been stained or fixed in any way, showing them in their native environment while integrating multiple images to form a three-dimensional model of the sample.
The molecular structure obtained during this study explained the mechanism for immune system suppression, and structure-guided mutations showed that the Acr proteins bound to residues essential for crRNA-mediated detection of DNA.
"These findings are important because we knew that anti-CRISPR proteins were blocking bacterial defenses, but we had no idea how," said senior author Dr. Gabriel C. Lander, assistant professor of integrative structural and computational biology at the Scripps Research Institute. "This system can quickly read through massive lengths of DNA and accurately hit its target. If the CRISPR complex identifies a viral DNA target, the surveillance machine recruits other molecules to destroy the virus's genome. These anti-CRISPR proteins keep the bacteria from recognizing the viral DNA. CRISPR systems cannot escape from these anti-CRISPR proteins without completely changing the mechanism they use to recognize DNA."
"Although CRISPR/Cas9 is the "celebrity" CRISPR system, there are 19 different types of CRISPR systems, each of which may have unique advantages for genetic engineering. They are a massive, untapped resource," said Dr. Lander. "The more we learn about the structures of these systems, the more we can take advantage of them as genome-editing tools."
Latest BioResearch News
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
- Liquid Biopsy More Effective for Analyzing Tumor Drug Resistance Mutations
- New Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Host-Pathogen Interactions
- Method Developed for Enriching Trophoblast Population in Samples
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It is a leading bacterial cause of acute pharyngitis, particularly in children and adolescents, and one of the most common reasons... Read more
Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Sepsis is caused by a patient’s overwhelming immune response to an infection. If undetected or left untreated, sepsis leads to tissue damage, organ failure, permanent disability, and often death.... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants can be lifesaving, but serious complications may arise months after patients leave the hospital. One of the most dangerous is chronic graft-versus-host disease, in... Read more
Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
AI has the potential to transform cancer care, yet progress remains constrained by fragmented, inaccessible data that hinder advances in early diagnosis and precision therapy. Unlocking patterns missed... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more