ALDOA and FH4 Antibodies Associated with Cerebrovascular Disease
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 28 Jul 2021 |
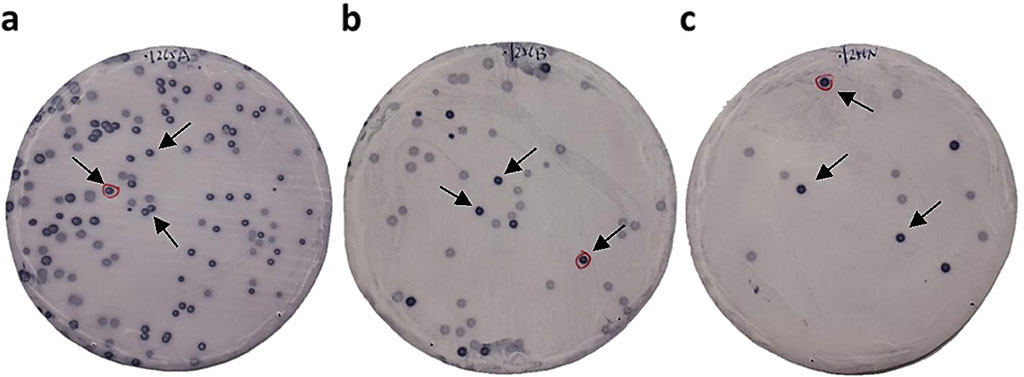
Image: Immunoscreening of TIA antigens by SEREX. Bacterial proteins including phage cDNA products were blotted on nitrocellulose membranes and reacted with the sera of patients with transient ischemic attack (TIA); arrows indicate positive phage clones (Photo courtesy of Chiba University)
Ischemic stroke, including transient ischemic attack (TIA) and cerebral infarction (CI), is the most globally recognized cerebrovascular disorder, and is a serious health problem in the aging society. CI is an episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain infarction, often resulting in fatality and disability. Patients with TIA are at a high risk of CI.
Endogenous antigens cause autoimmune responses that significantly influence the development of atherosclerosis, ultimately leading to the stenosis or blockage of the offending artery. These antigens induce autoantibodies that have been detected in the serum of patients with atherosclerosis-related diseases, such as CI, coronary heart disease (CHD), and diabetes mellitus (DM).
Clinical Biochemists and Geneticists at Chiba University (Chiba, Japan) collected serum samples from healthy donors (HDs) and patients diagnosed with TIA or CI caused by the development of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque. In comparing the serum antibody levels, they set up four independent groups, which included 621 patients and 285 HDs. Of the 621 patients, 92, suffered from TIA, 464, from acute-phase cerebral infarction (aCI), and, 65, from old (chronic-phase) cerebral infarction (oCI). The serological identification of antigens by recombinant cDNA expression cloning (SEREX) is an established method for identifying endogenous antigenic proteins, combining molecular cloning and serological typing by using phage expression libraries.
In 19 patients with TIA, candidate antigens recognized by serum IgG autoantibodies were screened using a human aortic endothelial cell cDNA library. Through amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay (AlphaLISA, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA), serum antibody levels against the candidate antigens were examined in the HDs, 92 TIA, and aCI, cohorts The plasma antibody levels in the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Cohort Study (1991–1993) were also examined. Glutathione-S-transferase (GST), GST–aldolase A (ALDOA), and GST–fumarate hydratase (FH) proteins were electrophoresed through SDS–polyacrylamide gel and analyzed by western blotting.
The team reported that in AlphaLISA, patients with TIA or aCI had significantly higher anti-ALDOA antibody (ALDOA-Ab) and anti-FH antibody (FH-Ab) levels than the HDs. In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, the ALDOA-Ab (odds ratio [OR]: 2.46) and FH-Ab (OR: 2.49) levels were independent predictors of TIA. According to the case–control study, the ALDOA-Ab (OR: 2.50) and FH-Ab (OR: 2.60) levels were associated with aCI risk. In a correlation analysis, both ALDOA-Abs and FH-Abs were well associated with hypertension, coronary heart disease, and habitual smoking. These antibody levels also correlated well with maximum intima–media thickness, which reflects atherosclerotic stenosis.
The authors concluded that the levels of antibodies against ALDOA and FH were significantly higher in patients with TIA or aCI than in HDs. These antibody markers can be novel predictors of TIA and pre-onset aCI, which are induced by atherosclerosis. The study was published on July 9, 2021 in the journal BMC Neurology.
Related Links:
Chiba University
Perkin Elmer
Endogenous antigens cause autoimmune responses that significantly influence the development of atherosclerosis, ultimately leading to the stenosis or blockage of the offending artery. These antigens induce autoantibodies that have been detected in the serum of patients with atherosclerosis-related diseases, such as CI, coronary heart disease (CHD), and diabetes mellitus (DM).
Clinical Biochemists and Geneticists at Chiba University (Chiba, Japan) collected serum samples from healthy donors (HDs) and patients diagnosed with TIA or CI caused by the development of atherosclerotic vulnerable plaque. In comparing the serum antibody levels, they set up four independent groups, which included 621 patients and 285 HDs. Of the 621 patients, 92, suffered from TIA, 464, from acute-phase cerebral infarction (aCI), and, 65, from old (chronic-phase) cerebral infarction (oCI). The serological identification of antigens by recombinant cDNA expression cloning (SEREX) is an established method for identifying endogenous antigenic proteins, combining molecular cloning and serological typing by using phage expression libraries.
In 19 patients with TIA, candidate antigens recognized by serum IgG autoantibodies were screened using a human aortic endothelial cell cDNA library. Through amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay (AlphaLISA, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA), serum antibody levels against the candidate antigens were examined in the HDs, 92 TIA, and aCI, cohorts The plasma antibody levels in the Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Cohort Study (1991–1993) were also examined. Glutathione-S-transferase (GST), GST–aldolase A (ALDOA), and GST–fumarate hydratase (FH) proteins were electrophoresed through SDS–polyacrylamide gel and analyzed by western blotting.
The team reported that in AlphaLISA, patients with TIA or aCI had significantly higher anti-ALDOA antibody (ALDOA-Ab) and anti-FH antibody (FH-Ab) levels than the HDs. In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, the ALDOA-Ab (odds ratio [OR]: 2.46) and FH-Ab (OR: 2.49) levels were independent predictors of TIA. According to the case–control study, the ALDOA-Ab (OR: 2.50) and FH-Ab (OR: 2.60) levels were associated with aCI risk. In a correlation analysis, both ALDOA-Abs and FH-Abs were well associated with hypertension, coronary heart disease, and habitual smoking. These antibody levels also correlated well with maximum intima–media thickness, which reflects atherosclerotic stenosis.
The authors concluded that the levels of antibodies against ALDOA and FH were significantly higher in patients with TIA or aCI than in HDs. These antibody markers can be novel predictors of TIA and pre-onset aCI, which are induced by atherosclerosis. The study was published on July 9, 2021 in the journal BMC Neurology.
Related Links:
Chiba University
Perkin Elmer
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
- Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
- Study Compares Analytical Performance of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Assays
- Blood Test Could Predict and Identify Early Relapses in Myeloma Patients
- Compact Raman Imaging System Detects Subtle Tumor Signals
- Noninvasive Blood-Glucose Monitoring to Replace Finger Pricks for Diabetics
- POC Breath Diagnostic System to Detect Pneumonia-Causing Pathogens
- Online Tool Detects Drug Exposure Directly from Patient Samples
- Chemical Imaging Probe Could Track and Treat Prostate Cancer
- Mismatch Between Two Common Kidney Function Tests Indicates Serious Health Problems
- VOCs Show Promise for Early Multi-Cancer Detection
- Portable Raman Spectroscopy Offers Cost-Effective Kidney Disease Diagnosis at POC
- Gold Nanoparticles to Improve Accuracy of Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
- Simultaneous Cell Isolation Technology Improves Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Simple Non-Invasive Hair-Based Test Could Speed ALS Diagnosis
- Paper Strip Saliva Test Detects Elevated Uric Acid Levels Without Blood Draws
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more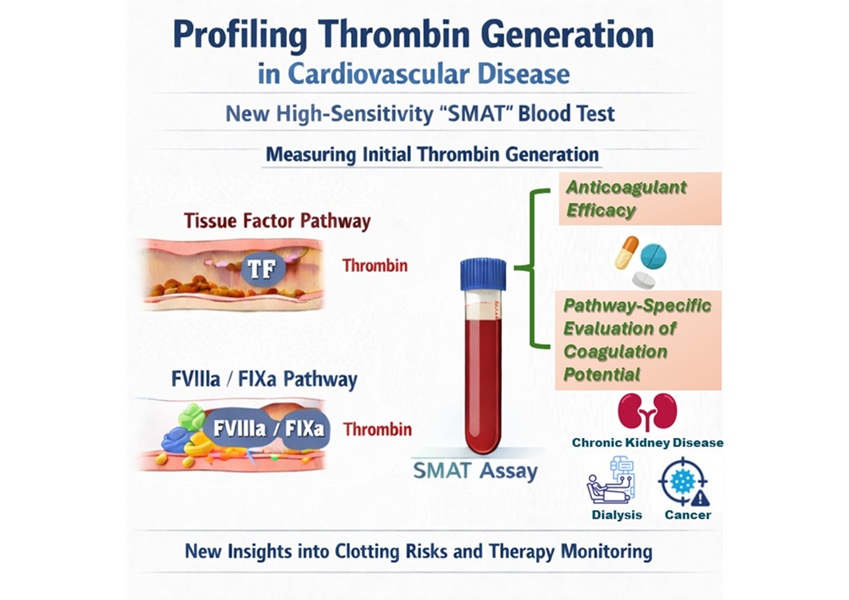
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel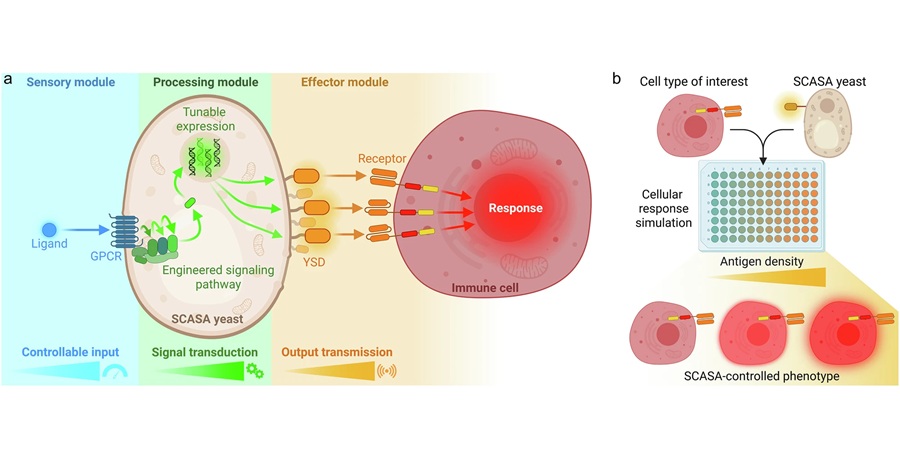
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more