Pain-On-A-Chip Microfluidic Device Determines Types of Chronic Pain from Blood Samples
Posted on 10 Apr 2025
Chronic pain is a widespread condition that remains difficult to manage, and existing clinical methods for its treatment rely largely on self-reporting, which can be subjective and especially problematic for patients who cannot communicate verbally. As a result, there is a pressing need for new techniques to detect pain biomarkers. Researchers have now created a novel preclinical method to differentiate between subtypes of chronic pain, such as fibromyalgia and peripheral neuropathy.
In a preclinical study, researchers from Monash University (Melbourne, Australia) collaborated with Flinders University (Adelaide, Australia) to develop an innovative, minimally invasive technology known as “pain-on-a-chip.” This microfluidic device uses live sensory nerves on a chip to offer an objective way of diagnosing chronic pain conditions. The device works by identifying the cells responsible for initiating pain sensations, known as ‘nociceptors,’ which are involved in various pain-related conditions, including chronic pain.
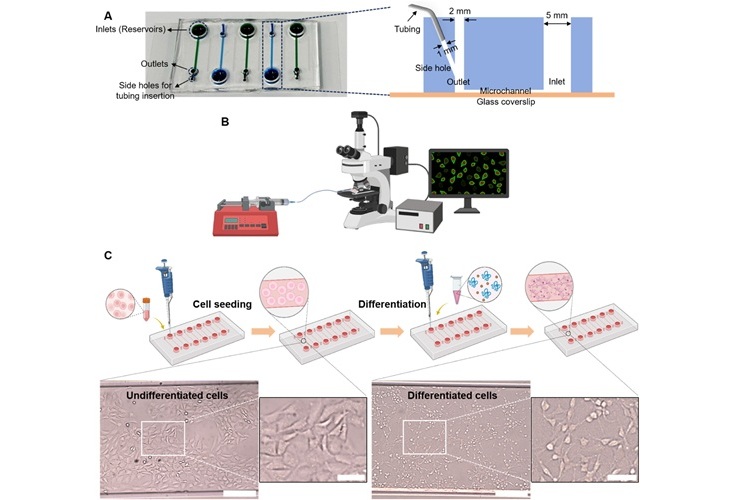
The research team, whose findings were published in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics, employed the nociceptor-based microfluidic biosensor, or pain-on-a-chip, to analyze blood samples from two distinct animal models of chronic pain—one focused on fibromyalgia and the other on diabetic neuropathy. With their pain-on-a-chip approach, the researchers were able to show that the device could objectively differentiate the nociceptor cell responses to the two chronic pain subtypes. These results open the door to the development of a groundbreaking tool for diagnosing chronic pain based on blood sampling.
“Improving pain classification and identifying new treatments requires new strategies that objectively recognize specific pain conditions and minimize subjectivity,” said Professor Nicolas Voelcker from Monash University, one of the study’s lead authors. “Our pain-on-a-chip concept has the potential to provide a biosensor platform for a minimally invasive and objective analysis method to discriminate between chronic pain subtypes.”
“Chronic pain stemming from conditions such as fibromyalgia and neuropathy can be very isolating and extremely debilitating,” added Dr. Dusan Matusica from Flinders University, who was also a lead author. “Our research lays the foundation for the development of an objective discriminatory tool for the determination of chronic pain states based on blood sampling. Such a diagnostic tool set is currently missing in both preclinical and clinical applications.”














