Novel Cell-Based Assay Provides Sensitive and Specific Autoantibody Detection in Demyelination
Posted on 10 Apr 2025
Anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) antibodies serve as markers for an autoimmune demyelinating disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system, leading to sensory impairment. Anti-MAG-IgM antibodies play a significant role in the pathology of this disorder, a connection that has been confirmed through pathological studies involving nerve biopsies. These antibodies target the human natural killer-1 (HNK-1) glycoepitope, which is abundantly expressed on MAG. A recent study published in Frontiers in Neurology has demonstrated that a new cell-based immunofluorescence assay (CBA) offers both sensitive and specific detection of IgM antibodies against MAG. This anti-MAG CBA is a valuable addition to EUROIMMUN’s (Lübeck, Germany) expanding range of assays designed to detect neural autoantibodies, which includes over 60 autoantibody specificities, with many being novel and exclusive.
The CBA utilizes transfected human cells that express the MAG/HNK-1 antigen. This method enables the antigen to be expressed in its native, folded form on the cell membrane substrates, allowing the detection of antibodies binding to these conformational epitopes. For control purposes, a biochip with mock-transfected cells is incubated alongside the transfected cells. In a collaborative study, researchers from the University of Verona (Verona, Italy) and the Paediatric Research Institute (Padua, Italy) compared the CBA with the established gold standard method, the ELISA, for detecting anti-MAG IgM. The study involved sera from 95 patients with clinical and neurophysiological evidence of anti-MAG-associated neuropathy, as well as control samples from 55 patients with other types of peripheral neuropathy. The CBA demonstrated a sensitivity of 98.9% and a specificity of 100% compared to the ELISA. The positive predictive value was 100%, and the negative predictive value was 98.2%.
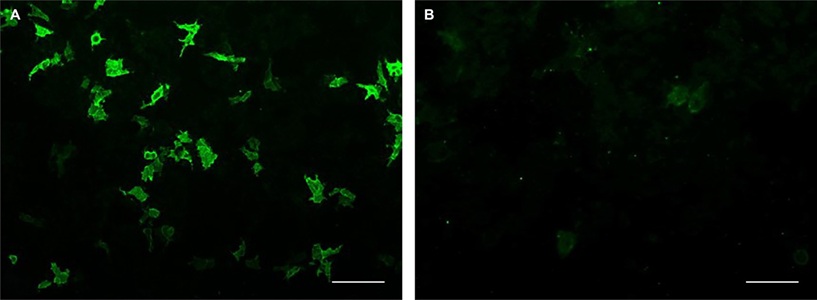
The CBA technology offers several advantages. It reduces inter-assay variability and allows for the efficient preparation of large batches of standardized substrates in a short time. Its fluorescence stability permits multiple analysts to evaluate the slides, and images can be shared across different centers. The procedure is straightforward and can be conducted in any laboratory experienced with indirect immunofluorescence techniques. Fluorescent CBA is already employed in many labs to detect other neural antibody markers, such as antibodies to neuronal cell surface antigens in autoimmune encephalitis and antibodies to aquaporin-4 in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. The researchers conclude that the CBA is an easy-to-use and standardized technique for detecting anti-MAG antibodies, offering a sensitive and specific alternative to the more time-consuming ELISA. Additionally, the CBA allows for titration-based determination of antibody levels, which is essential for understanding clinical correlations. Future large-scale studies will further investigate the relationship between anti-MAG titers and clinical activity to confirm and expand upon these findings.
Related Links:
EUROIMMUN
University of Verona
Paediatric Research Institute













