Advanced Imaging Reveals Mechanisms Causing Autoimmune Disease
Posted on 11 Apr 2025
Myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease, leads to muscle weakness that can affect a range of muscles, including those needed for basic actions like blinking, smiling, or moving. Researchers have long understood that the condition arises from miscommunication between the nerves and muscles. The immune system mistakenly generates autoantibodies, which are antibodies that attack the body’s own tissues and proteins. In myasthenia gravis, these autoantibodies specifically target acetylcholine receptors (AChRs), which are crucial for initiating normal muscle contractions. While medications aimed at boosting acetylcholine levels and suppressing the immune system can offer relief, their effectiveness varies, leading researchers to hypothesize that the disease may involve different underlying mechanisms in different individuals.
In a collaborative effort, scientists from UC San Diego (La Jolla, CA, USA) and Yale University (New Haven, CT, USA) employed advanced cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to examine the structure of human muscle AChRs in great detail. Their findings, published in the journal Cell, focused on analyzing the autoantibodies from six distinct myasthenia gravis patients. They found that these autoantibodies disrupt the normal functioning of AChRs in several ways. Some antibodies block the binding process of acetylcholine, while others activate the immune system’s complement pathway, leading to the destruction of the receptors. Crucially, all the autoantibodies directly impair the receptor’s ability to function as an ion channel. These discoveries challenge prior beliefs about how myasthenia gravis antibodies interfere with receptor activity.
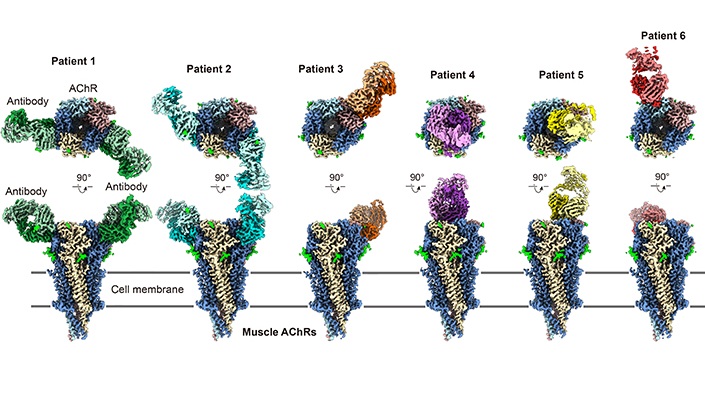
The researchers suggest that future treatments for myasthenia gravis could focus on targeting specific antibody interactions, rather than relying solely on general immunosuppression therapies. To conduct their study, they gathered blood samples from patients and used cell-based functional assays to explore the harmful properties of the autoantibodies. They also performed high-resolution structural studies and electrophysiological experiments to understand how these antibodies interact with and disrupt the function of AChRs. This collaborative research emphasizes the growing importance of personalized medicine and demonstrates how partnerships between institutions can drive breakthroughs that have direct clinical implications.
“By mapping antibody binding sites on the receptor, we revealed a surprising diversity in how autoantibodies contribute to myasthenia gravis. This knowledge helps explain why some patients respond differently to treatments and provides a foundation for developing more personalized therapies,” said Neurobiology Professor Ryan Hibbs, the study’s senior author. “This study not only advances our understanding of myasthenia gravis but also sheds light on other autoimmune diseases in which antibodies attack ion channels, offering hope for more precise and effective treatment strategies.”
Related Links:
UC San Diego
Yale University














