Novel Class of Enhancer RNAs Linked to Growth of Cancers
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 27 Aug 2018 |
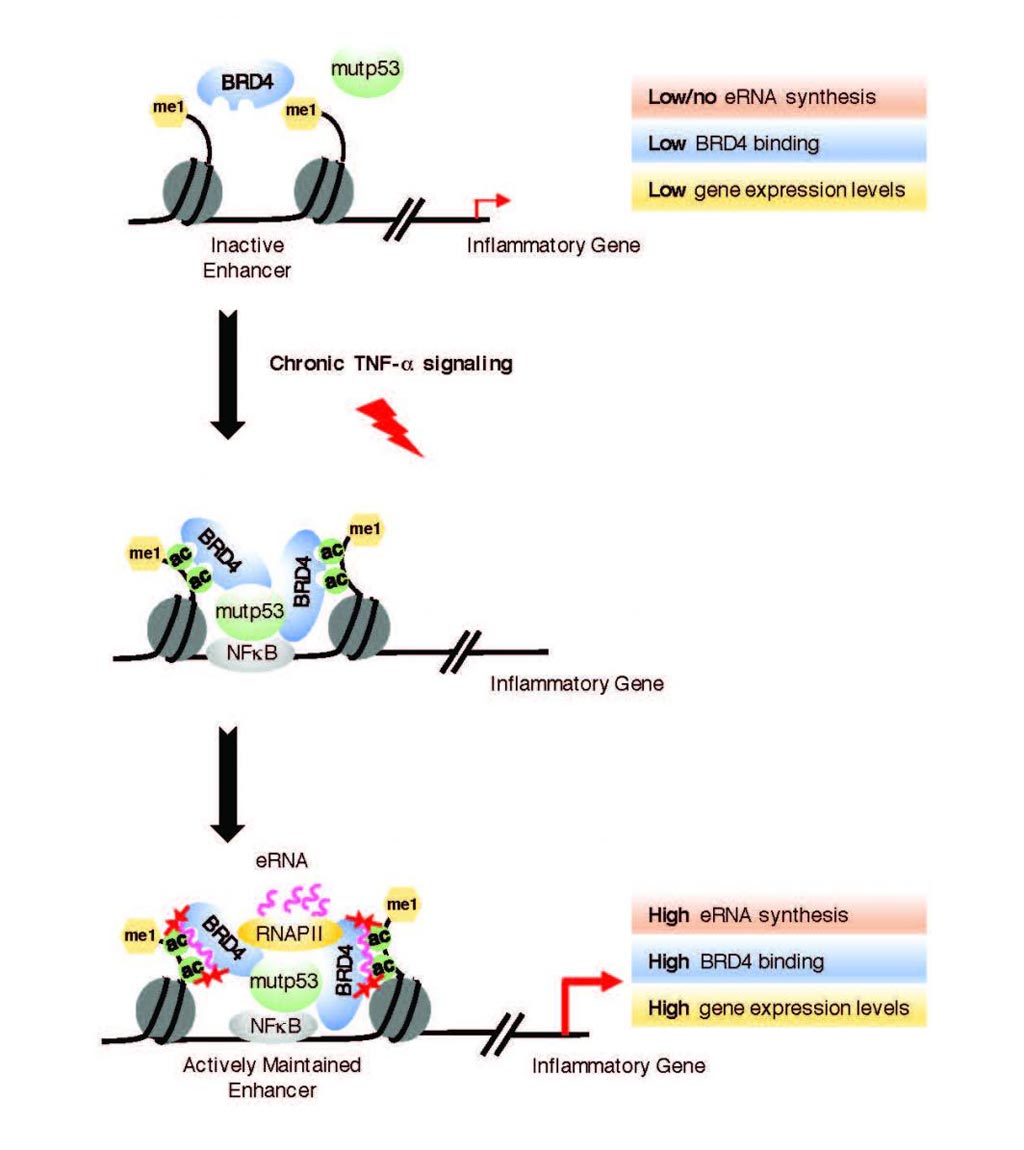
Image: Active enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) interact directly with BRD4, a protein linked to tumor development (Photo courtesy of the Lauberth laboratory, University of California, San Diego).
A recently described class of microRNA has been linked to the cancer-promoting activity of the mutated form of p53 protein.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNA) comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. MiRNAs resemble siRNAs of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
Augmenting the repertoire of "classical" miRNAs, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) identified several thousand enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) that were robustly produced in colon cancer cells in response to chronic immune signaling. Enhancer RNAs are transcribed from DNA sequences upstream and downstream of extragenic enhancer regions. Depending on the directionality of transcription, enhancer regions generate two different types of non-coding transcripts, unidirectional-eRNAs and bidirectional-eRNAs. The nature of the pre-initiation complex and specific transcription factors recruited to the enhancer may control the type of eRNAs generated.
After transcription, the majority of eRNAs remain in the nucleus, and as they are very unstable, they are actively degraded by the nuclear exosome. Not all enhancers are transcribed, with non-transcribed enhancers greatly outnumbering the transcribed ones in the order of magnitude of dozens of thousands in every given cell type. The theory that not all enhancers are transcribed at the same time and that eRNA transcription correlates with enhancer-specific activity support the idea that individual eRNAs carry distinct and relevant biological functions.
The investigators reported in the August 3, 2018, issue of the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology that in human colorectal cancer cells, Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) was recruited to enhancers that were co-occupied by mutant p53 and supported the synthesis of enhancer-directed transcripts (eRNAs) in response to chronic immune signaling. BRD4 selectively associated with eRNAs that were produced from BRD4-bound enhancers.
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) protein family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. BRD4, similar to other BET family members, contains two bromodomains (BDs) that recognize acetylated lysine residues. BRD4 also has an extended C-terminal domain with little sequence homology to other BET family members.
The investigators used biochemical and biophysical methods to show that BRD4 BDs functioned cooperatively as docking sites for eRNAs and that the BDs of BRD2, BRD3, BRDT, BRG1, and BRD7 directly interacted with eRNAs. BRD4-eRNA interactions increased BRD4 binding to acetylated histones in vitro and augmented BRD4 enhancer recruitment and transcriptional cofactor activities.
"Our findings reveal that eRNAs are key regulators of cancer by acting to reinforce BRD4 binding and keep it anchored on DNA, which keeps the tumor-promoting genes turned on at high levels," said senior author Dr. Shannon Lauberth, assistant professor of biology at the University of California, San Diego. "Interestingly, when we deplete several of these eRNAs, we can significantly reduce the expression of the tumor-promoting genes that the eRNAs and BRD4 are co-regulating. Now that we see that eRNAs impact BRD4 function, we have to rethink the way that we therapeutically target BRD4. Taken together, our findings are consistent with the emerging notion that eRNAs are functional molecules, rather than merely reflections of enhancer activation or simply transcriptional noise."
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and short interfering RNAs (siRNA) comprise a class of about 20 nucleotides-long RNA fragments that block gene expression by attaching to molecules of messenger RNA in a fashion that prevents them from transmitting the protein synthesizing instructions they had received from the DNA. MiRNAs resemble siRNAs of the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway, except miRNAs derive from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins, whereas siRNAs derive from longer regions of double-stranded RNA. With their capacity to fine-tune protein expression via sequence-specific interactions, miRNAs help regulate cell maintenance and differentiation.
Augmenting the repertoire of "classical" miRNAs, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) identified several thousand enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) that were robustly produced in colon cancer cells in response to chronic immune signaling. Enhancer RNAs are transcribed from DNA sequences upstream and downstream of extragenic enhancer regions. Depending on the directionality of transcription, enhancer regions generate two different types of non-coding transcripts, unidirectional-eRNAs and bidirectional-eRNAs. The nature of the pre-initiation complex and specific transcription factors recruited to the enhancer may control the type of eRNAs generated.
After transcription, the majority of eRNAs remain in the nucleus, and as they are very unstable, they are actively degraded by the nuclear exosome. Not all enhancers are transcribed, with non-transcribed enhancers greatly outnumbering the transcribed ones in the order of magnitude of dozens of thousands in every given cell type. The theory that not all enhancers are transcribed at the same time and that eRNA transcription correlates with enhancer-specific activity support the idea that individual eRNAs carry distinct and relevant biological functions.
The investigators reported in the August 3, 2018, issue of the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology that in human colorectal cancer cells, Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) was recruited to enhancers that were co-occupied by mutant p53 and supported the synthesis of enhancer-directed transcripts (eRNAs) in response to chronic immune signaling. BRD4 selectively associated with eRNAs that were produced from BRD4-bound enhancers.
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) protein family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT. BRD4, similar to other BET family members, contains two bromodomains (BDs) that recognize acetylated lysine residues. BRD4 also has an extended C-terminal domain with little sequence homology to other BET family members.
The investigators used biochemical and biophysical methods to show that BRD4 BDs functioned cooperatively as docking sites for eRNAs and that the BDs of BRD2, BRD3, BRDT, BRG1, and BRD7 directly interacted with eRNAs. BRD4-eRNA interactions increased BRD4 binding to acetylated histones in vitro and augmented BRD4 enhancer recruitment and transcriptional cofactor activities.
"Our findings reveal that eRNAs are key regulators of cancer by acting to reinforce BRD4 binding and keep it anchored on DNA, which keeps the tumor-promoting genes turned on at high levels," said senior author Dr. Shannon Lauberth, assistant professor of biology at the University of California, San Diego. "Interestingly, when we deplete several of these eRNAs, we can significantly reduce the expression of the tumor-promoting genes that the eRNAs and BRD4 are co-regulating. Now that we see that eRNAs impact BRD4 function, we have to rethink the way that we therapeutically target BRD4. Taken together, our findings are consistent with the emerging notion that eRNAs are functional molecules, rather than merely reflections of enhancer activation or simply transcriptional noise."
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego
Latest BioResearch News
- Barcoded DNA Sheds Light on Hidden Complexities in Breast Cancer Detection
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
Heterotopic ossification (HO), the abnormal formation of bone in soft tissue, is a common complication following hip replacement surgery. The condition affects nearly one in three patients and can lead... Read more
New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
Stage 1 testicular germ cell tumor is typically treated with surgery followed by active surveillance. Although most patients experience strong long-term outcomes, about one in four will see their cancer... Read more
New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
Alzheimer’s disease begins developing years before memory loss or other symptoms become visible. Misfolded proteins gradually accumulate in the brain, disrupting normal cellular processes.... Read more
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
Blood sampling is one of the most common clinical procedures, but it can be difficult or uncomfortable for many patients, especially older adults or individuals with certain medical conditions.... Read more
Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing became widely recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic as a powerful method for detecting viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. PCR belongs to a group of diagnostic methods... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















