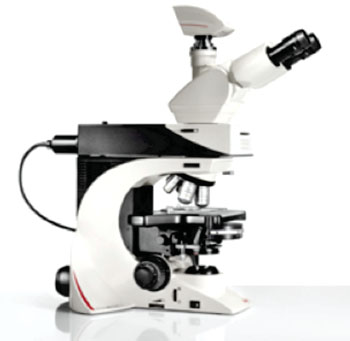
New LED Microscope Completes Line of Clinical and Research Tools
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 26 Jul 2015 |
A popular microscope used for both clinical and research applications is now available with LED illumination.
The Leica (Wetzlar, Germany) DM2500 and DM2500 LED microscopes represent a class of tools for demanding tasks in life science routine and research applications. With their powerful transmitted light illumination, high-quality optical performance, and state-of-the-art accessories, the Leica DM2500 and DM2500 LED are especially well-suited for challenging life science research tasks that require differential interference contrast or high-performance fluorescence.
The difference between the two microscopes is their illumination: The Leica DM2500 LED is equipped with LED illumination for transmitted light, whereas the Leica DM2500 works with halogen. Both types of illumination render a realistic impression of the colors of the sample, so that users in clinical applications, such as the frequently used HE specimen staining, are able to assess the colors of their samples accurately. With the launch of the Leica DM2500 LED, Leica Microsystems has completed its Leica DM1000 to 3000 series of microscopes. All the models in this series are now available with LED illumination. The microscopes are certified for in vitro diagnostics (IVD) use.
The ultra-bright LED illumination of the newly released Leica DM2500 LED offers a constant color temperature at all light intensities, enabling particularly fine differentiation of colors in stained specimens. Users benefit from the brightness and color accuracy of the LED illumination in all other transmitted light contrasting techniques, such as brightfield, polarized light, and darkfield. LEDs offer the general advantages of no sample heating, low energy consumption, and long life time.
"The specially-developed LED illumination makes the Leica DM2500 LED an ideal microscope for challenging experiments requiring different contrasting techniques and for users who prefer a manual instrument," said Dr. Jasna Gilbert, product manager at Leica Microsystems. "The Leica DM2500 LED has now completed our DM1000 to 3000 series. All the models are available with either LED or halogen illumination. Besides the new illumination, the Leica DM2500 LED offers all the other benefits of the microscope series such as the unique ergonomics design for user comfort and convenience."
Related Links:
Leica
The Leica (Wetzlar, Germany) DM2500 and DM2500 LED microscopes represent a class of tools for demanding tasks in life science routine and research applications. With their powerful transmitted light illumination, high-quality optical performance, and state-of-the-art accessories, the Leica DM2500 and DM2500 LED are especially well-suited for challenging life science research tasks that require differential interference contrast or high-performance fluorescence.
The difference between the two microscopes is their illumination: The Leica DM2500 LED is equipped with LED illumination for transmitted light, whereas the Leica DM2500 works with halogen. Both types of illumination render a realistic impression of the colors of the sample, so that users in clinical applications, such as the frequently used HE specimen staining, are able to assess the colors of their samples accurately. With the launch of the Leica DM2500 LED, Leica Microsystems has completed its Leica DM1000 to 3000 series of microscopes. All the models in this series are now available with LED illumination. The microscopes are certified for in vitro diagnostics (IVD) use.
The ultra-bright LED illumination of the newly released Leica DM2500 LED offers a constant color temperature at all light intensities, enabling particularly fine differentiation of colors in stained specimens. Users benefit from the brightness and color accuracy of the LED illumination in all other transmitted light contrasting techniques, such as brightfield, polarized light, and darkfield. LEDs offer the general advantages of no sample heating, low energy consumption, and long life time.
"The specially-developed LED illumination makes the Leica DM2500 LED an ideal microscope for challenging experiments requiring different contrasting techniques and for users who prefer a manual instrument," said Dr. Jasna Gilbert, product manager at Leica Microsystems. "The Leica DM2500 LED has now completed our DM1000 to 3000 series. All the models are available with either LED or halogen illumination. Besides the new illumination, the Leica DM2500 LED offers all the other benefits of the microscope series such as the unique ergonomics design for user comfort and convenience."
Related Links:
Leica
Read the full article by registering today, it's FREE! 

Register now for FREE to LabMedica.com and get access to news and events that shape the world of Clinical Laboratory Medicine. 
- Free digital version edition of LabMedica International sent by email on regular basis
- Free print version of LabMedica International magazine (available only outside USA and Canada).
- Free and unlimited access to back issues of LabMedica International in digital format
- Free LabMedica International Newsletter sent every week containing the latest news
- Free breaking news sent via email
- Free access to Events Calendar
- Free access to LinkXpress new product services
- REGISTRATION IS FREE AND EASY!
Sign in: Registered website members
Sign in: Registered magazine subscribers
Latest BioResearch News
- Barcoded DNA Sheds Light on Hidden Complexities in Breast Cancer Detection
- CRISPR-Based Platform Pinpoints Drivers of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patient Cells
- Protective Brain Protein Emerges as Biomarker Target in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
Heterotopic ossification (HO), the abnormal formation of bone in soft tissue, is a common complication following hip replacement surgery. The condition affects nearly one in three patients and can lead... Read more
New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
Stage 1 testicular germ cell tumor is typically treated with surgery followed by active surveillance. Although most patients experience strong long-term outcomes, about one in four will see their cancer... Read more
New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
Alzheimer’s disease begins developing years before memory loss or other symptoms become visible. Misfolded proteins gradually accumulate in the brain, disrupting normal cellular processes.... Read more
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
Blood sampling is one of the most common clinical procedures, but it can be difficult or uncomfortable for many patients, especially older adults or individuals with certain medical conditions.... Read more
Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing became widely recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic as a powerful method for detecting viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. PCR belongs to a group of diagnostic methods... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more