New Benchtop Devices Provide Automated Sample Decapping, Recapping, and Identification
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 20 Apr 2014 |

Image: New LabElite line of benchtop devices provides automated sample decapping, recapping, and identification (Photo courtesy of Hamilton Storage Technologies).
A new line of benchtop devices provides flexible solutions for sample processing, tracking, and security for automated and manual liquid handling workflows.
The LabElite line from Hamilton Storage Technologies (Franklin, MA, USA) offers laboratories an easy and efficient way to automatically process and track samples while ensuring sample integrity. LabElite devices quickly process all common labware types, providing a flexible solution for optimizing workflows. Three models are available to meet a user’s application, throughput, and sample tracking needs.
The all-in-one LabElite I.D. Capper enables labs to combine decapping/recapping and high-speed barcode reading within one device without additional user interaction. The I.D. Capper is specifically designed to reduce sample contamination and assist with sample tracking during end-to-end automated liquid-handling processing. The I.D. Capper includes all the new features and benefits standard to the other LabElite devices.
“This newest innovation from Hamilton provides the market with the first product where the user has the ability to positively identify the tube chosen for decapping/recapping and track it throughout the workflow,” said Peter Hoffmann, project leader, storage technologies, Hamilton Bonaduz AG.
When sample tracking is not required, the next-generation LabElite DeCapper is available for decapping and recapping tubes in 48-cryovial or 96-microtube racks. A new feature can automatically move the racks from portrait to landscape formats for processing. Additionally, an innovative “secure mode” provides sample security by decapping and recapping only one row at a time, minimizing the time a tube is open and eliminating the risk of cross contamination. This feature also enables the rows to be paused for “point-of-use” pipetting between capping and recapping, which is very useful for manual workflows. The DeCapper can process all common tubes, including Matrix, FluidX, Greiner Bio-One, Micronic, Nunc, and Corning, with internal and external thread caps.
For labs with manual workflows that need an efficient, high-speed 2D barcode reader for tube racks, the LabElite I.D. Reader is an ideal choice. This device decodes multiple types of labware including 2D barcoded tubes in all common 12-, 24-, 48-, 96- and 384-tube racks including honeycomb-shaped racks, providing complete sample tracking during processing. In addition, the reader can identify racks that are labeled with a 2D barcode on the bottom. The technology uses high-speed decoding algorithms and parallel processing, which provides the fastest run times currently available. A 96-tube rack runs in less than 3 seconds and a 384-tube rack in less than 5 seconds. Optional 1D barcode reading of the rack label is also available. The I.D. Reader supports all common tubes, including Matrix, FluidX, Greiner Bio-One, Micronic, Nunc, Corning, Matrical, WHEATON, ABgene, and REMP.
The LabElite I.D. Capper, DeCapper and I.D. Reader are for research only, not for use in clinical diagnostic procedures.
Related Links:
Hamilton Storage Technologies
LabElite Line
The LabElite line from Hamilton Storage Technologies (Franklin, MA, USA) offers laboratories an easy and efficient way to automatically process and track samples while ensuring sample integrity. LabElite devices quickly process all common labware types, providing a flexible solution for optimizing workflows. Three models are available to meet a user’s application, throughput, and sample tracking needs.
The all-in-one LabElite I.D. Capper enables labs to combine decapping/recapping and high-speed barcode reading within one device without additional user interaction. The I.D. Capper is specifically designed to reduce sample contamination and assist with sample tracking during end-to-end automated liquid-handling processing. The I.D. Capper includes all the new features and benefits standard to the other LabElite devices.
“This newest innovation from Hamilton provides the market with the first product where the user has the ability to positively identify the tube chosen for decapping/recapping and track it throughout the workflow,” said Peter Hoffmann, project leader, storage technologies, Hamilton Bonaduz AG.
When sample tracking is not required, the next-generation LabElite DeCapper is available for decapping and recapping tubes in 48-cryovial or 96-microtube racks. A new feature can automatically move the racks from portrait to landscape formats for processing. Additionally, an innovative “secure mode” provides sample security by decapping and recapping only one row at a time, minimizing the time a tube is open and eliminating the risk of cross contamination. This feature also enables the rows to be paused for “point-of-use” pipetting between capping and recapping, which is very useful for manual workflows. The DeCapper can process all common tubes, including Matrix, FluidX, Greiner Bio-One, Micronic, Nunc, and Corning, with internal and external thread caps.
For labs with manual workflows that need an efficient, high-speed 2D barcode reader for tube racks, the LabElite I.D. Reader is an ideal choice. This device decodes multiple types of labware including 2D barcoded tubes in all common 12-, 24-, 48-, 96- and 384-tube racks including honeycomb-shaped racks, providing complete sample tracking during processing. In addition, the reader can identify racks that are labeled with a 2D barcode on the bottom. The technology uses high-speed decoding algorithms and parallel processing, which provides the fastest run times currently available. A 96-tube rack runs in less than 3 seconds and a 384-tube rack in less than 5 seconds. Optional 1D barcode reading of the rack label is also available. The I.D. Reader supports all common tubes, including Matrix, FluidX, Greiner Bio-One, Micronic, Nunc, Corning, Matrical, WHEATON, ABgene, and REMP.
The LabElite I.D. Capper, DeCapper and I.D. Reader are for research only, not for use in clinical diagnostic procedures.
Related Links:
Hamilton Storage Technologies
LabElite Line
Latest BioResearch News
- Genome Analysis Predicts Likelihood of Neurodisability in Oxygen-Deprived Newborns
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Gene Fusion Protein Proposed as Prostate Cancer Biomarker
- NIV Test to Diagnose and Monitor Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Semen Exosome MicroRNA Proves Biomarker for Prostate Cancer
- Genetic Loci Link Plasma Lipid Levels to CVD Risk
- Newly Identified Gene Network Aids in Early Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Link Confirmed between Living in Poverty and Developing Diseases
- Genomic Study Identifies Kidney Disease Loci in Type I Diabetes Patients
- Liquid Biopsy More Effective for Analyzing Tumor Drug Resistance Mutations
- New Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Host-Pathogen Interactions
- Method Developed for Enriching Trophoblast Population in Samples
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel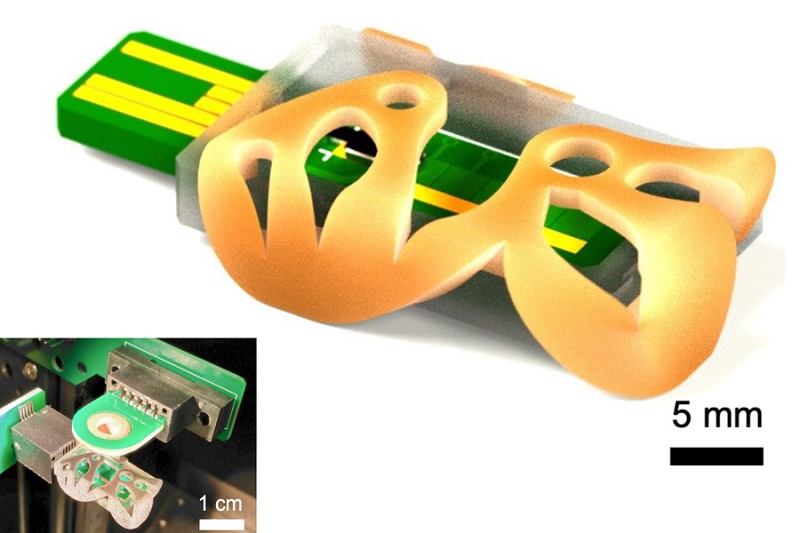
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more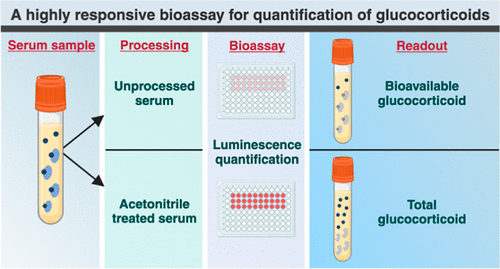
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel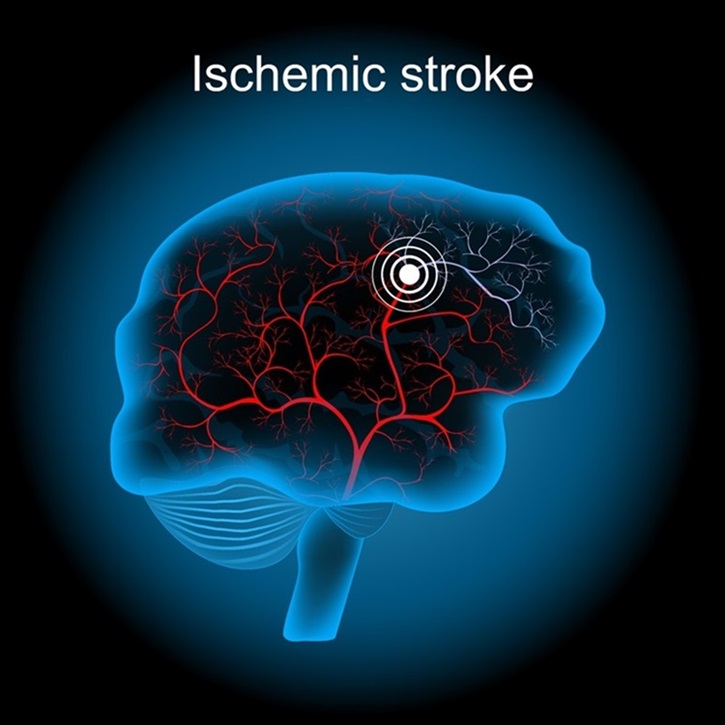
Game-Changing Blood Test for Stroke Detection Could Bring Life-Saving Care to Patients
Stroke is the primary cause of disability globally and ranks as the second leading cause of death. However, timely early intervention can prevent severe outcomes. Most strokes are ischemic, resulting from... Read moreBlood Proteins Could Warn of Cancer Seven Years before Diagnosis
Two studies have identified proteins in the blood that could potentially alert individuals to the presence of cancer more than seven years before the disease is clinically diagnosed. Researchers found... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more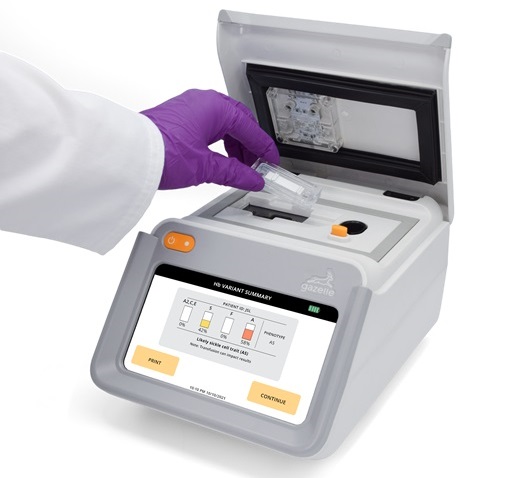
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel.jpg)
AI Predicts Tumor-Killing Cells with High Accuracy
Cellular immunotherapy involves extracting immune cells from a patient's tumor, potentially enhancing their cancer-fighting capabilities through engineering, and then expanding and reintroducing them into the body.... Read more
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Integrated Solution Ushers New Era of Automated Tuberculosis Testing
Tuberculosis (TB) is responsible for 1.3 million deaths every year, positioning it as one of the top killers globally due to a single infectious agent. In 2022, around 10.6 million people were diagnosed... Read more
Automated Sepsis Test System Enables Rapid Diagnosis for Patients with Severe Bloodstream Infections
Sepsis affects up to 50 million people globally each year, with bacteraemia, formerly known as blood poisoning, being a major cause. In the United States alone, approximately two million individuals are... Read moreEnhanced Rapid Syndromic Molecular Diagnostic Solution Detects Broad Range of Infectious Diseases
GenMark Diagnostics (Carlsbad, CA, USA), a member of the Roche Group (Basel, Switzerland), has rebranded its ePlex® system as the cobas eplex system. This rebranding under the globally renowned cobas name... Read more
Clinical Decision Support Software a Game-Changer in Antimicrobial Resistance Battle
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a serious global public health concern that claims millions of lives every year. It primarily results from the inappropriate and excessive use of antibiotics, which reduces... Read morePathology
view channel
New AI Tool Classifies Brain Tumors More Quickly and Accurately
Precision in diagnosing and categorizing tumors is essential for delivering effective treatment to patients. Currently, the gold standard for identifying various types of brain tumors involves DNA methylation-based... Read more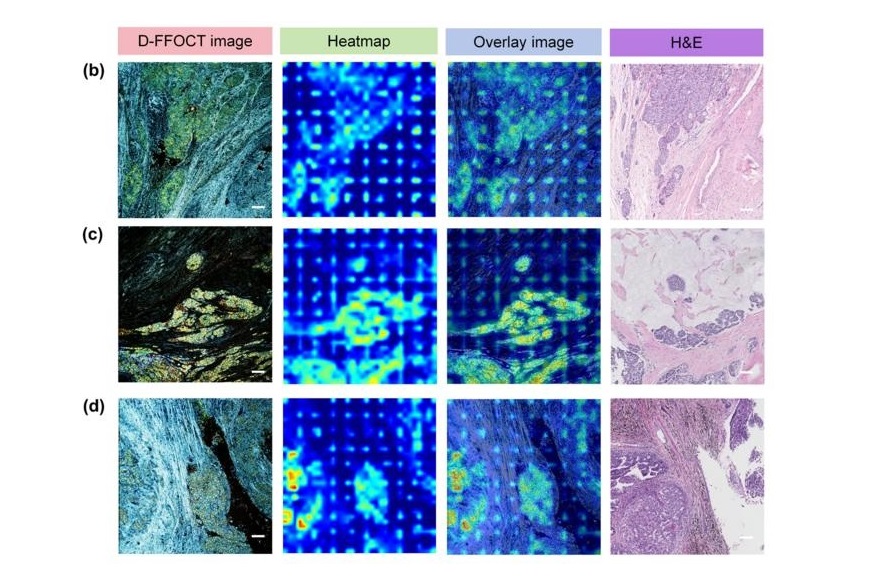
AI Integrated With Optical Imaging Technology Enables Rapid Intraoperative Diagnosis
Rapid and accurate intraoperative diagnosis is essential for tumor surgery as it guides surgical decisions with precision. Traditional intraoperative assessments, such as frozen sections based on H&E... Read more
HPV Self-Collection Solution Improves Access to Cervical Cancer Testing
Annually, over 604,000 women across the world are diagnosed with cervical cancer, and about 342,000 die from this disease, which is preventable and primarily caused by the Human Papillomavirus (HPV).... Read moreHyperspectral Dark-Field Microscopy Enables Rapid and Accurate Identification of Cancerous Tissues
Breast cancer remains a major cause of cancer-related mortality among women. Breast-conserving surgery (BCS), also known as lumpectomy, is the removal of the cancerous lump and a small margin of surrounding tissue.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more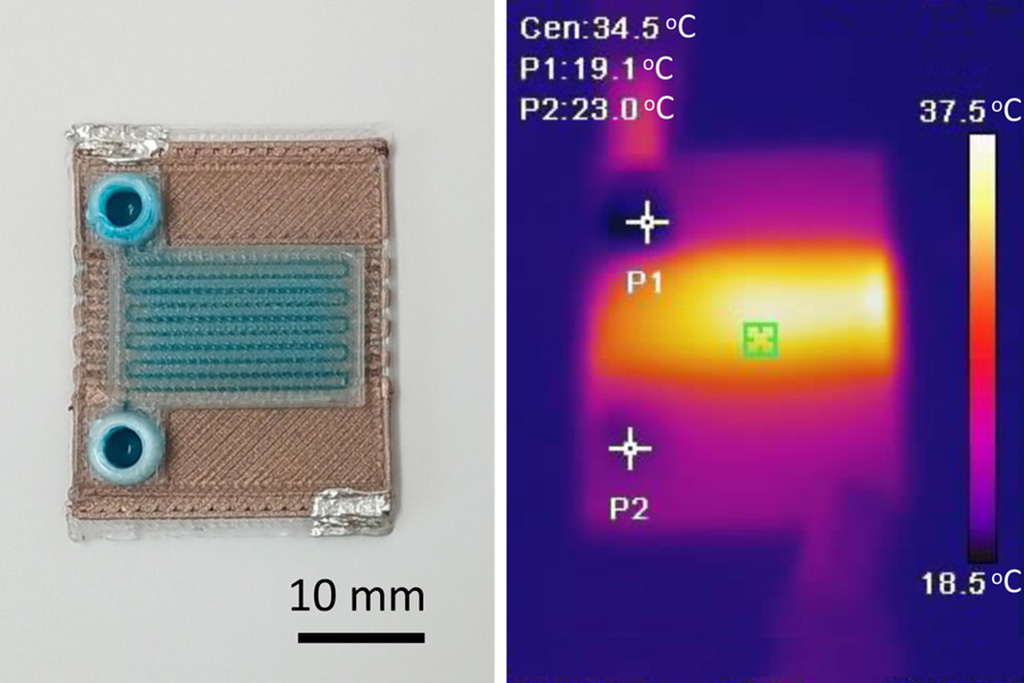
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Danaher and Johns Hopkins University Collaborate to Improve Neurological Diagnosis
Unlike severe traumatic brain injury (TBI), mild TBI often does not show clear correlations with abnormalities detected through head computed tomography (CT) scans. Consequently, there is a pressing need... Read more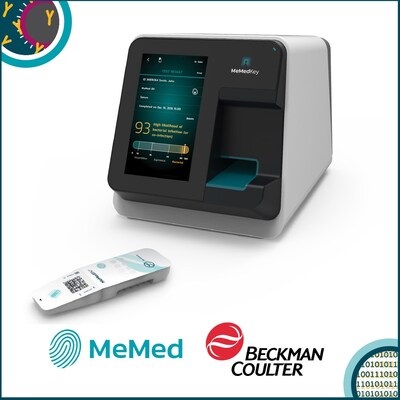
Beckman Coulter and MeMed Expand Host Immune Response Diagnostics Partnership
Beckman Coulter Diagnostics (Brea, CA, USA) and MeMed BV (Haifa, Israel) have expanded their host immune response diagnostics partnership. Beckman Coulter is now an authorized distributor of the MeMed... Read more_1.jpg)












_1.jpg)
