Clinical Chemistry
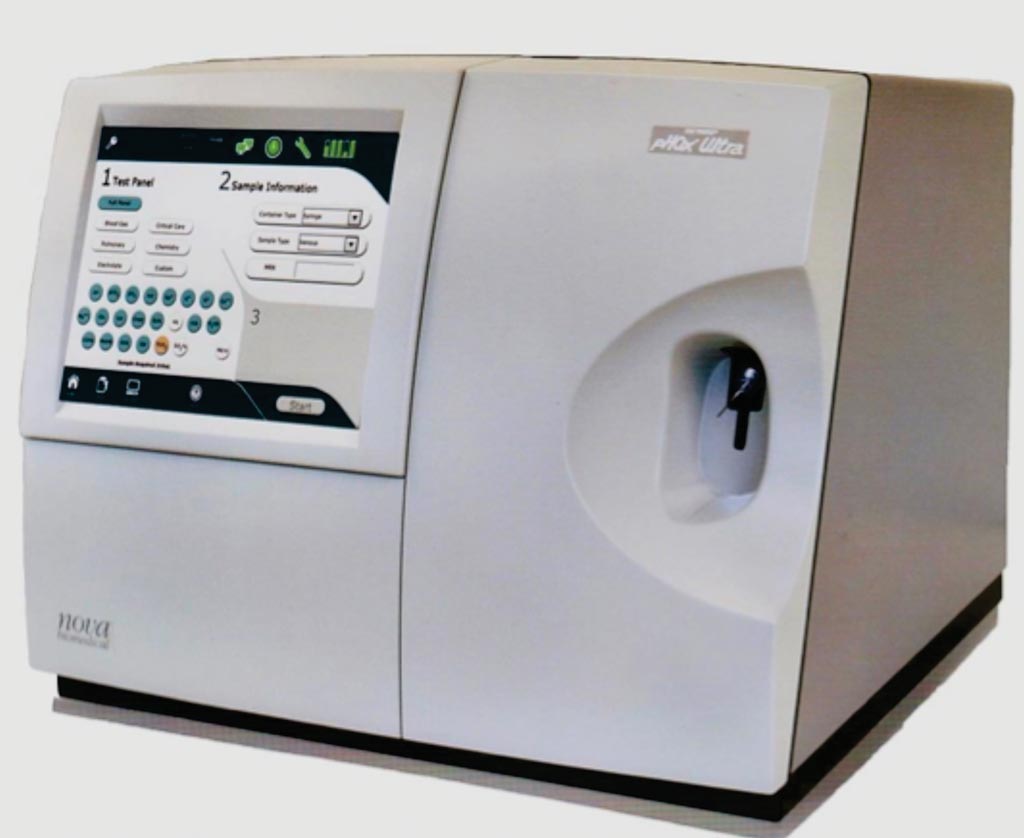
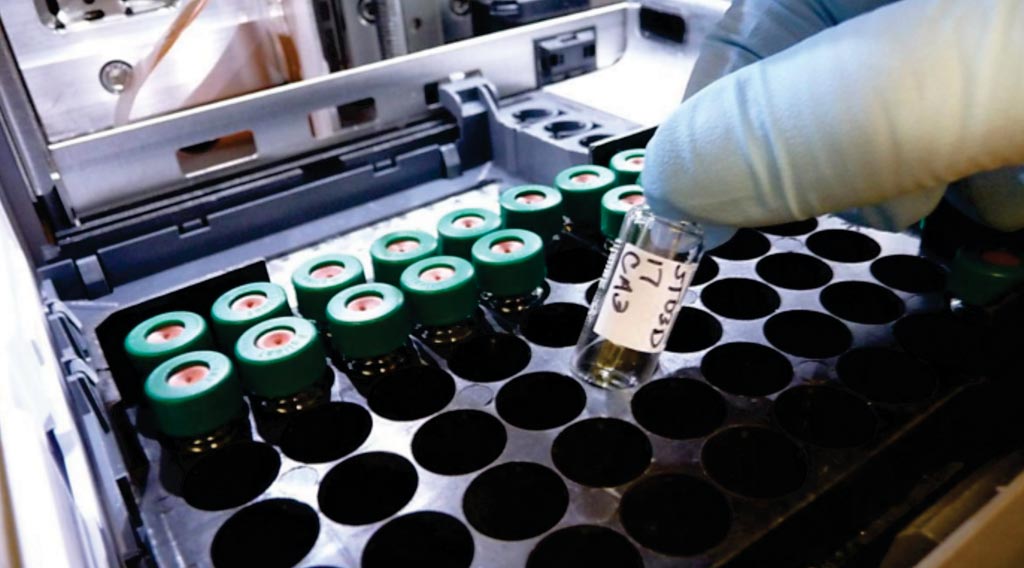


Blood Test Identifies Amino Acid Metabotypes Associated with Autism
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) could benefit from new and improved diagnostic methods and the arrival of a newly commercialized blood test, along with other efforts headed toward a similar end goal, and could be nudging the field toward earlier detection and intervention. More...06 Mar 2019

Vitamin D Measured in Human Hair
Vitamin D deficiency has reached epidemic proportions worldwide, with over one billion people estimated to be affected. Deficiency has been linked with bone health, but it could also be a risk factor for depression, cardiovascular disease, inflammation, diabetes and cancer. More...05 Mar 2019

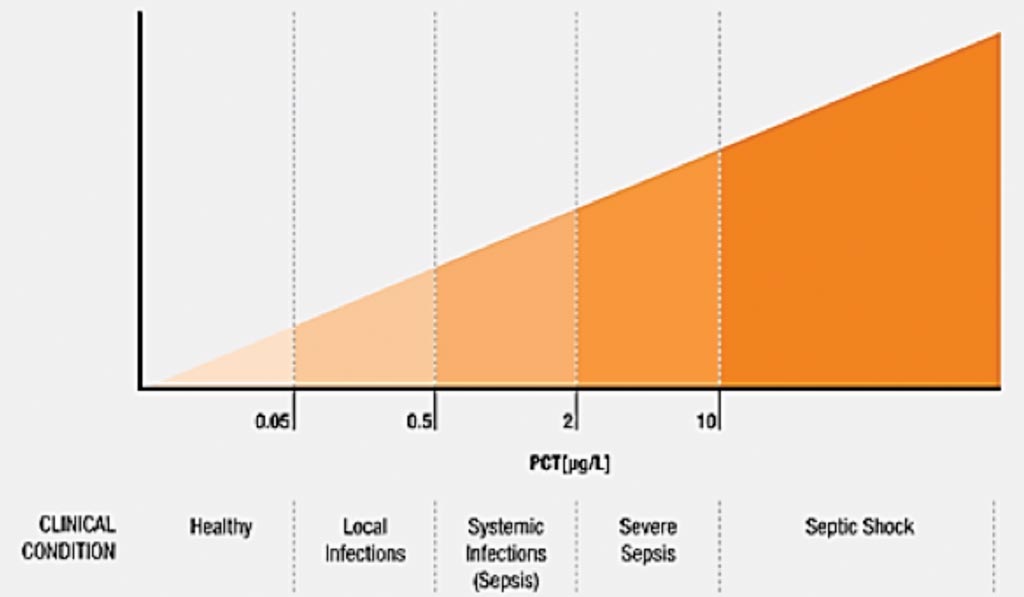
Procalcitonin Evaluated as Sepsis Diagnostic Marker
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to an infection and occurs when the body's response to chemicals released into the bloodstream is out of balance, triggering changes that can damage multiple organ systems. More...27 Feb 2019
Simple Bile Acid Blood Test Predicts Stillbirth Risk
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) is caused by a build-up of bile acids in the blood, and symptoms include pruritus. ICP is a liver disorder affecting approximately 5,300 pregnancies annually in the UK, more than 14 every day. More...25 Feb 2019
In Other News
HDL Cholesterol Measurement Unaffected by Serum Amyloid A
Markers in Male Reproductive Impairments Causing Miscarriages
Protein Linked to Increased Risk for CVD and Stroke
Sweat Chloride Quantified Using Capillary Electrophoresis
New Glucose Biosensor Introduced for Diabetes Management
HDL Subclasses Linked to Mortality in Heart Failure Patients
Long-Term Risk for CVD Stratified by Fasting Glucose Level
High-Sensitivity CRP Testing Underutilized
Retina Protein Antibodies Used As Kidney Cancer Marker
Biochemical Hypoglycemia Associated with Risk of Hypoglycemia
Calprotectin Independently Predicts Relapse in Treated RA
Fructosamine Reference Range Established for Brazil
Urinary Biomarkers Associated with Kidney Disease Risk Factors
Test Detects Protein Associated with Alzheimer’s and CTE
Bilirubin Improves Risk Prediction of Cardiovascular Death
Serum Magnesium Levels Associated with CAP Mortality
Diagnostic Accuracy Demonstrated in Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
Salivary Urea Nitrogen Dipstick Detects Acute Kidney Disease
Molecular Cause Found for Rare Autoimmune Disorders
HbA1c Assessed in Diabetics Awaiting Liver Transplantation
Assay Improves Measurement of Blood Ammonia
Macrocytic Anemia Associated with HBV Liver Impairment Severity
Vitamin D Measured in Patients with Diabetic Foot
The Clinical Chemistry channel updates the reader on tests, techniques, and research in the field - from routine assays to specialized tests on blood, urine, enzymes, lipids, hormones and more.










