Blood Test Aids Early Detection of Rheumatoid Arthritis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 09 Mar 2015 |
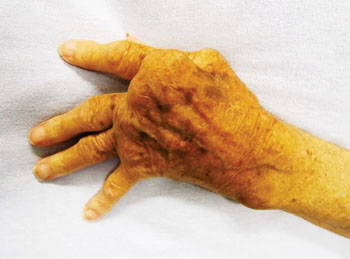
Image: Severe rheumatoid arthritis in a hand which was never treated (Photo courtesy of James Heilman, MD).
A blood test that measures the levels of a certain protein can be used in conjunction with clinical assessments to assist with the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is now available in North America.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects joints and it may result in deformed and painful joints, which can lead to loss of function. The disease may also have signs and symptoms in organs other than joints.
The JOINTstat test (Augurex Life Science; Vancouver, BC, Canada) measures 14-3-3η (eta), a protein involved in joint damage that leads to debilitation in patients with RA, a disease that affects one out of every 100 Canadians. High levels of 14-3-3η protein indicate that the patient should be referred to a rheumatologist. JOINTstat has been evaluated in clinical studies in over 3,000 patients and has been available in the USA since late 2013.
Extracellular 14-3-3η protein is a potent ligand and activator of intracellular signaling pathways that lead to the upregulation of inflammation and joint damage factors involved in RA pathogenesis. A quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used to assess 14-3-3η protein levels. Studies have shown that when the test is positive, greater than 0.19 ng/mL, it provides a 5 to 50 times greater likelihood of having RA versus non-RA. At high levels of greater than 80 ng/mL is an indicator of RA that will lead to more joint damage over three years and at lower levels of less than 0.4 ng/mL or negative in RA diagnosed patients indicates a higher likelihood of response to RA therapy.
Walter Maksymowych, MD, FRCPC, a professor in the department of medicine, division of rheumatology at the University of Alberta (Edmonton, AB, Canada) said, “When diagnosed early, rheumatoid arthritis can be better managed with drug therapies, resulting in better outcomes by limiting disease progression. Current diagnostic tests are limited in their ability to catch the disease early. With the availability of JOINTstat in Canada, physicians now have the opportunity to treat rheumatoid arthritis early, prior to the onset of significant joint damage. This represents an important milestone towards the goal of personalized medicine.” The study was presented at the Canadian Rheumatology Association (CRA) Annual Scientific Meeting held February 4–7, 2015, in Québec City (QC, Canada).
Related Links:
Augurex Life Science
University of Alberta
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects joints and it may result in deformed and painful joints, which can lead to loss of function. The disease may also have signs and symptoms in organs other than joints.
The JOINTstat test (Augurex Life Science; Vancouver, BC, Canada) measures 14-3-3η (eta), a protein involved in joint damage that leads to debilitation in patients with RA, a disease that affects one out of every 100 Canadians. High levels of 14-3-3η protein indicate that the patient should be referred to a rheumatologist. JOINTstat has been evaluated in clinical studies in over 3,000 patients and has been available in the USA since late 2013.
Extracellular 14-3-3η protein is a potent ligand and activator of intracellular signaling pathways that lead to the upregulation of inflammation and joint damage factors involved in RA pathogenesis. A quantitative enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay is used to assess 14-3-3η protein levels. Studies have shown that when the test is positive, greater than 0.19 ng/mL, it provides a 5 to 50 times greater likelihood of having RA versus non-RA. At high levels of greater than 80 ng/mL is an indicator of RA that will lead to more joint damage over three years and at lower levels of less than 0.4 ng/mL or negative in RA diagnosed patients indicates a higher likelihood of response to RA therapy.
Walter Maksymowych, MD, FRCPC, a professor in the department of medicine, division of rheumatology at the University of Alberta (Edmonton, AB, Canada) said, “When diagnosed early, rheumatoid arthritis can be better managed with drug therapies, resulting in better outcomes by limiting disease progression. Current diagnostic tests are limited in their ability to catch the disease early. With the availability of JOINTstat in Canada, physicians now have the opportunity to treat rheumatoid arthritis early, prior to the onset of significant joint damage. This represents an important milestone towards the goal of personalized medicine.” The study was presented at the Canadian Rheumatology Association (CRA) Annual Scientific Meeting held February 4–7, 2015, in Québec City (QC, Canada).
Related Links:
Augurex Life Science
University of Alberta
Latest Immunology News
- Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
- Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
- New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. Delays in identifying the exact infection can lead to inappropriate... Read more
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read more
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more






















