Clinical Chemistry
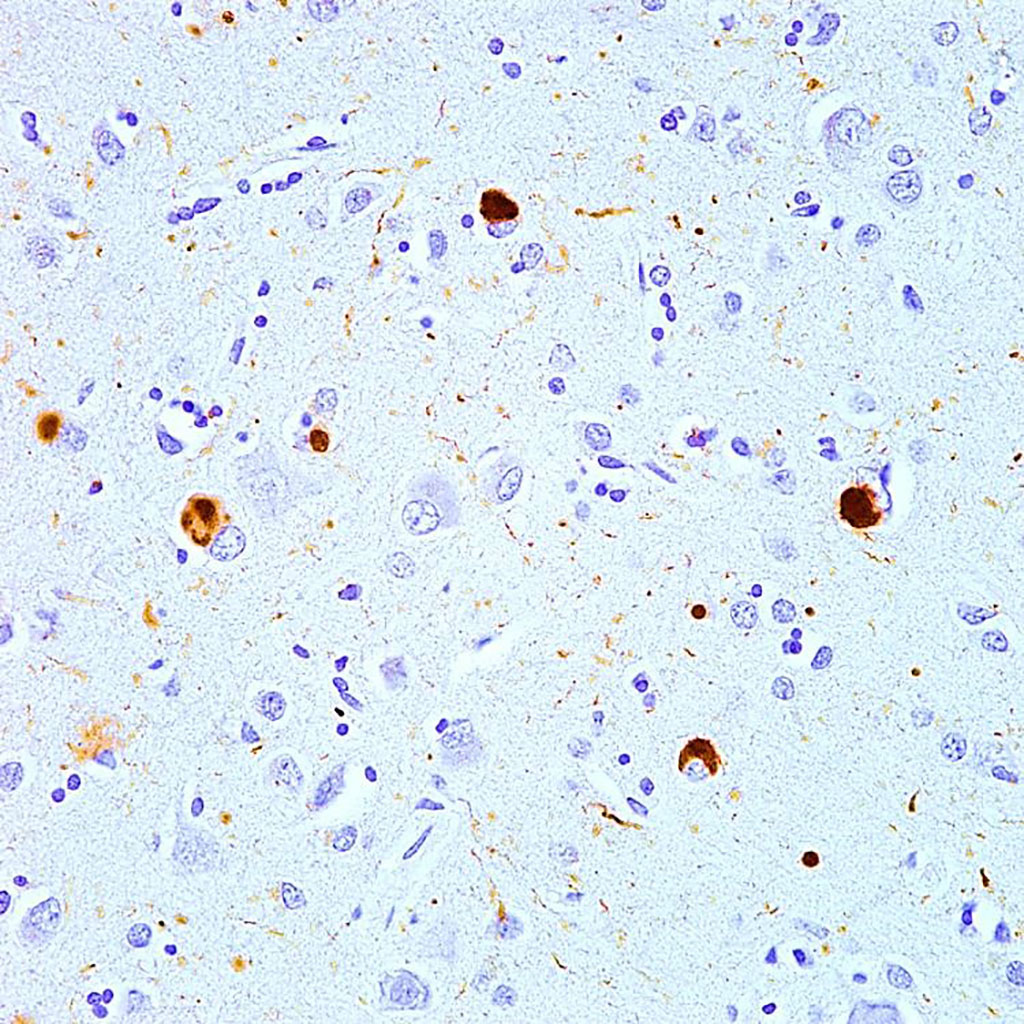
CSF Conversion Assay Identifies Lewy Body Disease Cognitive Impairment
Lewy body dementia, also known as dementia with Lewy bodies, is the second most common type of progressive dementia after Alzheimer's disease. Protein deposits, called Lewy bodies, develop in nerve cells in the brain regions involved in thinking, memory and movement (motor control). More...08 Aug 2021
Urinary Epidermal Growth Factor Investigated for Diabetes Nephropathy
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is an auto-immune metabolic disease with chronic hyperglycemia. For many patients with type 1 diabetes (T1DM), it is challenging to maintain near-normal glucose blood levels and to reduce the risk of both acute (hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis) and chronic microvascular (retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy) and macrovascular complications. More...06 Aug 2021
ALDOA and FH4 Antibodies Associated with Cerebrovascular Disease
Ischemic stroke, including transient ischemic attack (TIA) and cerebral infarction (CI), is the most globally recognized cerebrovascular disorder, and is a serious health problem in the aging society. CI is an episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain infarction, often resulting in fatality and disability. Patients with TIA are at a high risk of CI. More...28 Jul 2021
Elevated PlGF Levels Found with Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) is a severe liver disorder unique to pregnancy, typically occurring after 30 weeks’ gestation. Although uncommon, with an estimated global incidence of 1 in 7,000 to 15,000 pregnancies, AFLP is a life-threatening disease for both mother and child. More...22 Jul 2021

Novel Adipokine Biomarker Reported for Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition occurring due to inadequate production or inadequate action of insulin, ultimately leading to hyperglycemia. Prediabetes, regarded as a precursor of diabetes, is a condition with elevated plasma glucose above normal levels, but below that of clinical disease. More...21 Jul 2021
Two Inflammatory Proteins Linked with Slower Cognitive Decline
Previous meta-analyses of case-control and prospective cohort studies showed that cytokines and inflammatory markers, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), and others are elevated in Alzheimer's dementia cases and predicted incident of all-cause dementia. More...08 Jul 2021
In Other News
Biomarkers Diagnose and Predict Acute Pancreatitis
FABP4 Concentrations Quantified in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Two Immunoassays Compared for Determination of Serum Vitamin D
Monocyte Distribution Width Evaluated as a Sepsis Indicator
Plasma Neurofilament Light Validated Biomarker for Neurological Conditions
Diabetic Biomarkers Concordance Compared in South African Blacks
Plasma ACE2 Predicts Prognosis of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients
Troponin Testing Presents Problems in Kidney-Impaired People
Hyperglycemia Evaluated as a Risk Factor in Pancreatic Cancer
Biomarker Predicts Crohn's Disease Relapse in Children
Serum Leptin Concentration Predict Cardiovascular Outcomes in Hemodialysis Patients
Urinary Sodium/Potassium Ratio Screens for Hyperaldosteronism in Hypertensive Men
Platelet Indices Analyzed for Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus Co-Morbidity
Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is Associated with Insulin Secretion
Serum Based Antigen Test Detects Childhood Tuberculosis
Low Sugar Metabolite Associated with Disability, Neurodegeneration in MS
Non‐Invasive Urine Markers Differentiate Renal Cancer from Oncocytoma
Serum Catestatin Level Is Increased in Women with Preeclampsia
Plasma-Based S100B Testing for Management of Traumatic Brain Injury
Novel Diagnostic Test Assesses Risk of Urinary Uric Acid Crystallization
Maternal Multiomic Changes Could Predict Onset of Labor
Meconium Microbiome Can Help Predict Risk of Developing Allergies
Maternal Free Thyroxine Associated with Gestational Diabetes
The Clinical Chemistry channel updates the reader on tests, techniques, and research in the field - from routine assays to specialized tests on blood, urine, enzymes, lipids, hormones and more.










