BioResearch
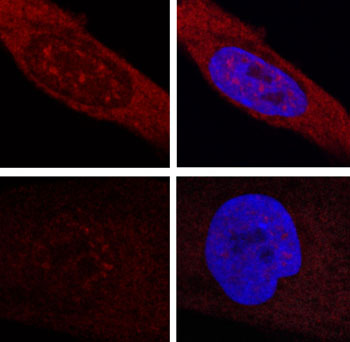
Blocking Mutant RNA Cures Huntington's Disease in Mouse Model
Researchers seeking ways to treat Huntington's disease have suggested going after the messenger RNA that mediates between the mutant gene that causes the disease and the toxic protein that causes the neurological damage that characterizes it. More...23 Nov 2016
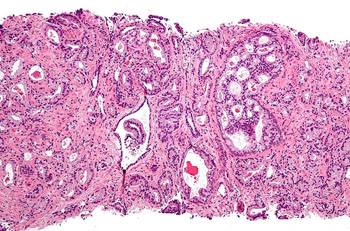
Mitochondrial Protein Linked to Development of Prostate Cancer
Results obtained from experiments with genetically engineered mouse models revealed a direct link between the mitochondrial chaperone protein, TRAP1 (TNF receptor associated protein 1) and the development of prostate cancer. More...23 Nov 2016
Macrophages Form Vascular Mimicry Channels to Supply Growing Tumors
A potential new therapeutic approach to block cancer development is based on the finding that macrophages form primitive non-endothelial “vessels” or vascular mimicry channels that help supply growing tumors with oxygen and nutrients. More...22 Nov 2016
Modified T-Cells Attack Tumors without Triggering Autoimmune Disease
A team of molecular immunologists has devised a method to direct T-cells to recognize and fight cancer cells without risk of the modified cells attacking normal tissues and thereby triggering autoimmune disease. More...22 Nov 2016
Experimental Monobody Drug Inhibits Most Mutated RAS Oncogenes
A novel monobody drug candidate was found to effectively block the action of most of the RAS family of proto-oncogenes, which are mutated in nearly 90% of pancreatic cancers and are also highly prevalent in colon cancer, lung cancer, and melanoma. More...17 Nov 2016
In Other News
Biomarkers Demonstrate Potential as Indicators of HD Progression
Human Monoclonal Antibodies Prevent Congenital Transfer of Zika Virus in Mice
Modulation of Redox Environment Increases Breast Cancer Aggressiveness
Inhibition of Galactin-3 Reverses Insulin Resistance in Diabetes and Obesity Models
Proteins in Cell Nuclear Membrane Actively Influence Gene Expression
Report Describes Mechanism Underlying Genetic Eye Disease
Messenger RNA Quality Control Mechanism Explained
Researchers Describe Aggressive Breast Cancer Molecular Mechanism
Protein Identified Prevents Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Two PARP Family Enzymes Cross-Regulate Macrophage Activation
Researchers to Benefit from New Inverted Microscopes
Gene Therapy Increases Lifespan of Mice with Niemann-Pick Disease
Study Reveals Mechanism Protecting UTI Bacteria from Nitric Acid Damage
Mutated Luciferase Generates Bright Light for Optogenetics Technique
Cell Surface Glycoprotein Critical for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Novel 3D Printing Technique Installs NIV Sensors in Lab-on-a Chip Devices
Enzyme Identified Stabilizes Tau and Prevents Neurodegenerative Disease
Candidate Drug Kills CRCs with Mutated Tumor Suppressor Gene
Novel Immunotherapy Approach Shrinks or Eliminates Advanced Tumors
RNA Binding Protein Required for Successful Infection by HCMV
Experimental Drug Slows Lung Cancer Growth by Blocking Protein Glycosylation
CRISPR/Cas9 Identifies Potential Drug Target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Experimental Drug Shrinks Lung Tumors by Blocking Fatty Acid Synthesis
BioResearch brings the latest research news on the genome, proteome, metabolome, on drug discovery, and therapeutics. Biotech researchers, lab administrators, technologists, drug manufacturers, and suppliers can find the latest research news and information related to their fields of endeavor here.










