Cell Surface Glycoprotein Critical for Acute Myeloid Leukemia
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 Nov 2016
The cell surface glycoprotein CD98 was identified as a key factor required for growth and spread of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).Posted on 08 Nov 2016
AML is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells that accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of normal blood cells. The symptoms of AML are caused by replacement of normal bone marrow with leukemic cells, which causes a drop in red blood cells, platelets, and normal white blood cells. Symptoms include fatigue, shortness of breath, easy bruising and bleeding, and increased risk of infection. AML progresses rapidly and is typically fatal within weeks or months if left untreated.
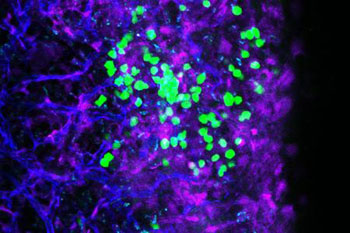
Image: Leukemia cells (green) interact with blood vessels (blue) via the molecule CD98 (Photo courtesy of the University of California, San Diego).
CD98 has been shown to control how cells adhere and to play a role in the proliferation and activation of certain immune cells. CD98 levels are also known to be elevated in some solid tumors, and linked to poor prognosis. To better understand the role of CD98 in AML, investigators at the University of California, San Diego (USA) genetically engineered several lines of mice that lacked the gene for production of the molecule.
They reported in the October 27, 2016, online edition of the journal Cancer Cell that CD98 promoted AML propagation and lethality by driving engagement of leukemia cells with their microenvironment and maintaining leukemic stem cells. In addition, delivery of the humanized anti-CD98 antibody IGN523 blocked growth of patient-derived AML, highlighting the importance of this pathway in human disease.
"This study suggests that human AML cannot get established without CD98, and that blocking the molecule with anti-CD98 antibodies could be beneficial for the treatment of AML in both adults and children," said senior author Dr. Tannishtha Reya, professor of pharmacology at the University of California, San Diego.
"To improve therapeutic strategies for this disease, we need to look not just at the cancer cells themselves, but also at their interactions with surrounding cells, tissues, molecules, and blood vessels in the body," said Dr. Reya. "In this study, we identified CD98 as a critical molecule driving AML growth. We showed that blocking CD98 can effectively reduce leukemia burden and improve survival by preventing cancer cells from receiving support from the surrounding environment."
Related Links:
University of California, San Diego