Nanotechnology For Cervical Cancer Diagnosis Could Replace Invasive Pap Smears
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 31 Jan 2025 |
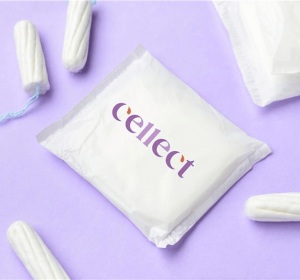
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer in women globally, almost always caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), which spreads through sexual contact. The Pap test (or Pap smear) is used to screen for cervical cancer, but access to regular testing is often limited, which raises concerns, as early detection is critical for effective treatment. Menstrual blood, like urine, contains cells and biomarkers that can be tested to provide valuable health information and signal the need for more specific and selective tests. Now, an innovative technology utilizes nanomaterials in menstrual products to detect HPV and cervical cancer using menstrual blood, potentially eliminating the need for Pap smears.
CELLECT Laboratories (Waterloo, ON, Canada) is pioneering the use of nanotechnology-powered menstrual products to non-invasively collect and preserve DNA for diagnosing HPV, cervical cancer, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), and other reproductive and gynecological conditions. CELLECT has developed a nanomaterial that can be incorporated into tampons or pads, passively capturing and preserving DNA and cells from menstrual blood. This material can then be tested for HPV, cervical cancer, and other DNA-related conditions, including sexually transmitted infections. The lab processing techniques used by CELLECT mirror those employed in standard HPV tests, enabling the differentiation between high-risk and low-risk HPV strains. CELLECT provides a non-invasive alternative to Pap smears by using menstrual products to collect menstrual blood, thereby eliminating the need for more invasive procedures like swabs or speculums.
For women who do not menstruate, CELLECT is also exploring the use of other vaginal fluids, such as discharges, as an alternative sample. The company’s proprietary technology is designed to work with very small volumes of fluid — as little as 15 mm³ — while still achieving the same diagnostic results. This ensures that the solution is inclusive and adaptable, offering a non-invasive and accurate method for women at various health stages. CELLECT has received attention from healthcare professionals and potential users, who are enthusiastic about the prospect of a non-invasive alternative to Pap smears. The company is well-positioned to bring about significant change, providing an accessible and inclusive screening method for people who menstruate, particularly those overlooked by traditional gynecological care models. With early successes in prototype development, CELLECT is on track to revolutionize healthcare.
Related Links:
CELLECT Laboratories
Latest Technology News
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
- AI Predicts Colorectal Cancer Survival Using Clinical and Molecular Features
- Diagnostic Chip Monitors Chemotherapy Effectiveness for Brain Cancer
- Machine Learning Models Diagnose ALS Earlier Through Blood Biomarkers
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel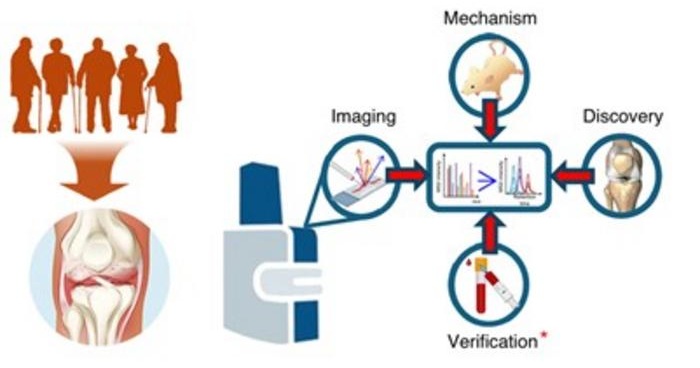
Bone Molecular Maps to Transform Early Osteoarthritis Detection
Osteoarthritis affects more than 500 million people worldwide and is a major cause of pain, disability, and reduced quality of life. By the time it is diagnosed through symptoms and visible cartilage loss,... Read more
POC Testing for Hepatitis B DNA as Effective as Traditional Laboratory Testing
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer over time. Despite being preventable through vaccination and treatable in its chronic... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more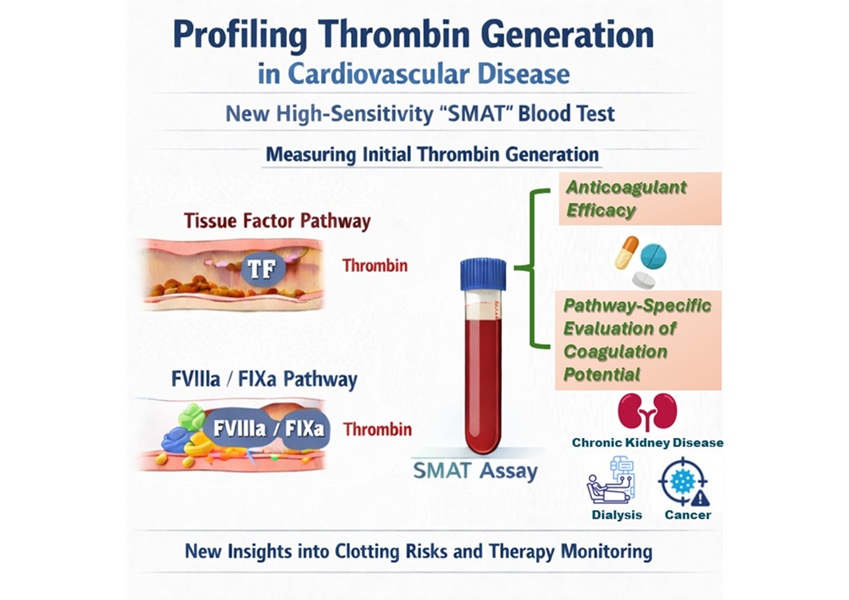
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
Malaria remains one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, killing hundreds of thousands each year, mostly in under-resourced regions where laboratory infrastructure is limited. Diagnosis still... Read more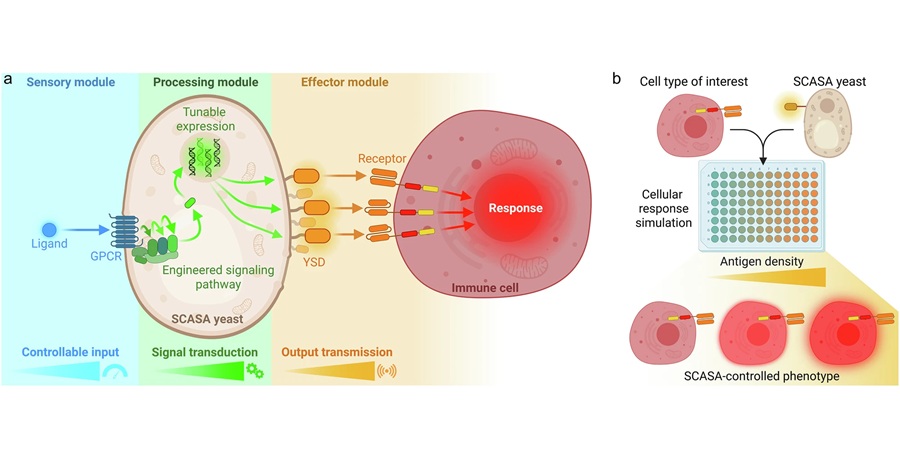
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read moreIndustry
view channel
WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
WHX Labs in Dubai (formerly Medlab Middle East), held at Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) from 10–13 February, brings together international experts to discuss the factors redefining laboratory leadership,... Read moreNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more