Silver Nanocubes Make Point-of-Care Diagnostics Easier to Read
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 27 May 2020 |
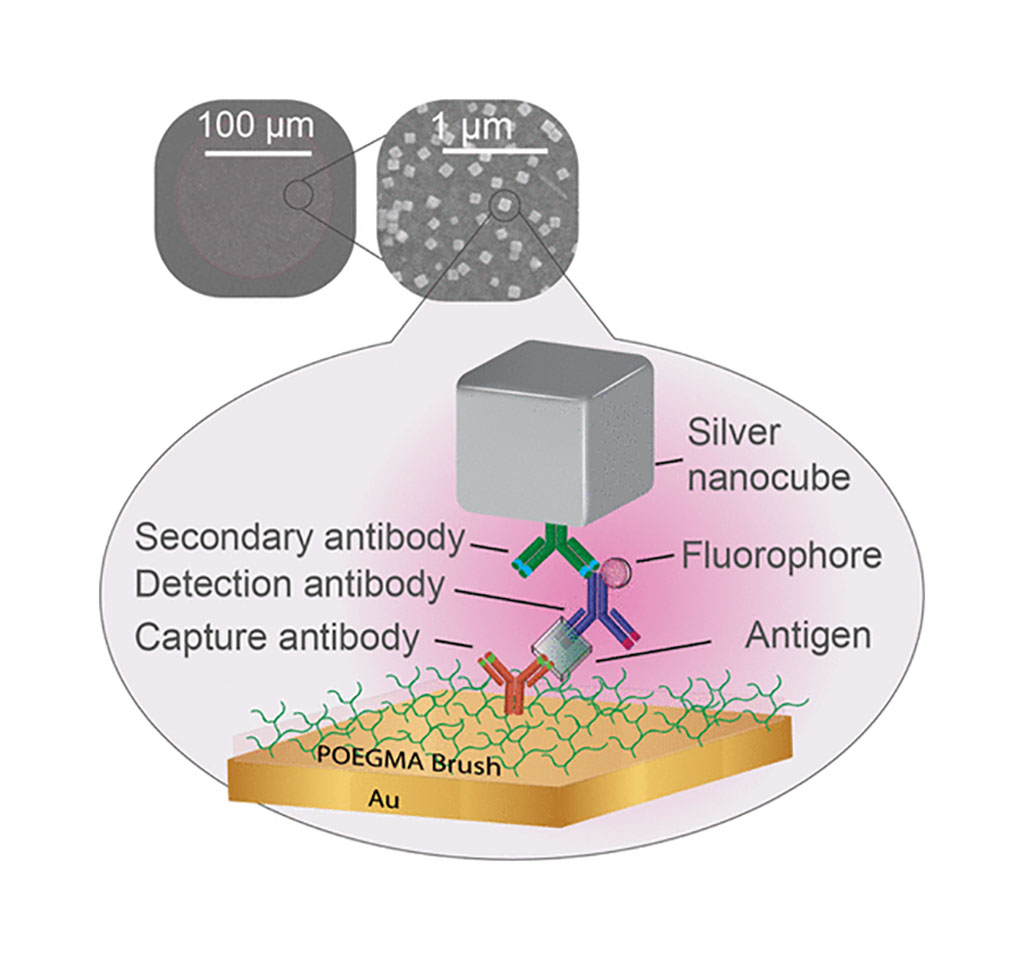
Image: Schematic diagram of ultrabright fluorescence readout of an inkjet-printed immunoassay using plasmonic nanogap cavities (Photo courtesy of Duke University).
Plasmonics is a scientific field that traps energy in a feedback loop called a plasmon onto the surface of silver nanocubes. When fluorescent molecules are sandwiched between one of these nanocubes and a metal surface, the interaction between their electromagnetic fields causes the molecules to emit light much more vigorously.
Fluorescence-based microarrays are promising diagnostic tools due to their high throughput, small sample volume requirements, and multiplexing capabilities. However, their low fluorescence output has limited their implementation for in vitro diagnostics applications in point-of-care (POC) settings.
Biomedical Engineers and their colleagues at the Duke University (Durham, NC, USA) built their super-sensitive diagnostic platform called the D4 Assay onto a thin film of gold, the preferred yin to the plasmonic silver nanocube's yang. The platform starts with a thin layer of polymer brush coating, which stops anything from sticking to the gold surface that the scientists do not want to stick there. They then use an ink-jet printer to attach two groups of molecules tailored to latch on to the biomarker that the test is trying to detect. One set is attached permanently to the gold surface and catches one part of the biomarker. The other is washed off of the surface once the test begins, attaches itself to another piece of the biomarker, and flashes light to indicate it has found its target.
By integration of a sandwich immunoassay microarray within a plasmonic nanogap cavity, the bioengineers demonstrated strongly enhanced fluorescence which is critical for readout by inexpensive POC detectors. The immunoassay consists of inkjet-printed antibodies on a polymer brush which is grown on a gold film. Colloidally synthesized silver nanocubes are placed on top and interact with the underlying gold film creating high local electromagnetic field enhancements. By varying the thickness of the brush from 5 to 20 nm, up to a 151-fold increase in fluorescence and 14-fold improvement in the limit-of-detection is observed for the cardiac biomarker B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) compared to the unenhanced assay, paving the way for a new generation of POC clinical diagnostics.
Maiken H. Mikkelsen, PhD, an assistant professor and a senior author of the study, said, “One of the big challenges in point-of-care tests is the ability to read out results, which usually requires very expensive detectors. That's a major roadblock to having disposable tests to allow patients to monitor chronic diseases at home or for use in low-resource settings. We see this technology not only as a way to get around that bottleneck, but also as a way to enhance the accuracy and threshold of these diagnostic devices.” The study was published on May 5, 2020 in the journal Nano Letters.
Related Links:
Duke University
Fluorescence-based microarrays are promising diagnostic tools due to their high throughput, small sample volume requirements, and multiplexing capabilities. However, their low fluorescence output has limited their implementation for in vitro diagnostics applications in point-of-care (POC) settings.
Biomedical Engineers and their colleagues at the Duke University (Durham, NC, USA) built their super-sensitive diagnostic platform called the D4 Assay onto a thin film of gold, the preferred yin to the plasmonic silver nanocube's yang. The platform starts with a thin layer of polymer brush coating, which stops anything from sticking to the gold surface that the scientists do not want to stick there. They then use an ink-jet printer to attach two groups of molecules tailored to latch on to the biomarker that the test is trying to detect. One set is attached permanently to the gold surface and catches one part of the biomarker. The other is washed off of the surface once the test begins, attaches itself to another piece of the biomarker, and flashes light to indicate it has found its target.
By integration of a sandwich immunoassay microarray within a plasmonic nanogap cavity, the bioengineers demonstrated strongly enhanced fluorescence which is critical for readout by inexpensive POC detectors. The immunoassay consists of inkjet-printed antibodies on a polymer brush which is grown on a gold film. Colloidally synthesized silver nanocubes are placed on top and interact with the underlying gold film creating high local electromagnetic field enhancements. By varying the thickness of the brush from 5 to 20 nm, up to a 151-fold increase in fluorescence and 14-fold improvement in the limit-of-detection is observed for the cardiac biomarker B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) compared to the unenhanced assay, paving the way for a new generation of POC clinical diagnostics.
Maiken H. Mikkelsen, PhD, an assistant professor and a senior author of the study, said, “One of the big challenges in point-of-care tests is the ability to read out results, which usually requires very expensive detectors. That's a major roadblock to having disposable tests to allow patients to monitor chronic diseases at home or for use in low-resource settings. We see this technology not only as a way to get around that bottleneck, but also as a way to enhance the accuracy and threshold of these diagnostic devices.” The study was published on May 5, 2020 in the journal Nano Letters.
Related Links:
Duke University
Latest Immunology News
- Blood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
- Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
- Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
- Blood Test Could Identify Colon Cancer Patients to Benefit from NSAIDs
- Blood Test Could Detect Adverse Immunotherapy Effects
- Routine Blood Test Can Predict Who Benefits Most from CAR T-Cell Therapy
- New Test Distinguishes Vaccine-Induced False Positives from Active HIV Infection
- Gene Signature Test Predicts Response to Key Breast Cancer Treatment
- Chip Captures Cancer Cells from Blood to Help Select Right Breast Cancer Treatment
- Blood-Based Liquid Biopsy Model Analyzes Immunotherapy Effectiveness
- Signature Genes Predict T-Cell Expansion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- Molecular Microscope Diagnostic System Assesses Lung Transplant Rejection
- Blood Test Tracks Treatment Resistance in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer
- Luminescent Probe Measures Immune Cell Activity in Real Time
- Blood-Based Immune Cell Signatures Could Guide Treatment Decisions for Critically Ill Patients
- Novel Tool Predicts Most Effective Multiple Sclerosis Medication for Patients
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Light-Based Sensor Detects Early Molecular Signs of Cancer in Blood
Early cancer diagnosis is often hindered by the extremely low concentration of biomarkers present at the onset of disease. Proteins, DNA fragments, and other molecular markers can reveal cancer risk or... Read more
New Testing Method Predicts Trauma Patient Recovery Days in Advance
Trauma patients with nearly identical injuries often experience very different recoveries, even when treated similarly. Traditional assessments based on injury severity do not always explain why some patients... Read moreHematology
view channel
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read more
Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are a cornerstone of modern medicine, yet red blood cells can deteriorate quietly while sitting in cold storage for weeks. Although blood units have a fixed expiration date, cells from... Read more
Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
High-volume hemostasis sections must sustain rapid turnaround while managing reruns and reflex testing. Manual tube handling and preanalytical checks can strain staff time and increase opportunities for error.... Read more
High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
Blood clotting is essential for preventing bleeding, but even small imbalances can lead to serious conditions such as thrombosis or dangerous hemorrhage. In cardiovascular disease, clinicians often struggle... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel
AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
Microscopes have long been central to diagnosing disease by allowing doctors to examine stained tissue samples. However, modern medical research now generates vast amounts of additional data, including... Read more
AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
Malaria remains one of the world’s deadliest infectious diseases, killing hundreds of thousands each year, mostly in under-resourced regions where laboratory infrastructure is limited. Diagnosis still... Read moreIndustry
view channel
WHX Labs in Dubai spotlights leadership skills shaping next-generation laboratories
WHX Labs in Dubai (formerly Medlab Middle East), held at Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) from 10–13 February, brings together international experts to discuss the factors redefining laboratory leadership,... Read moreNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more