Developing POC Tests for Alzheimer’s to Improve Monitoring and Management of the Disease
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 22 Mar 2016 |
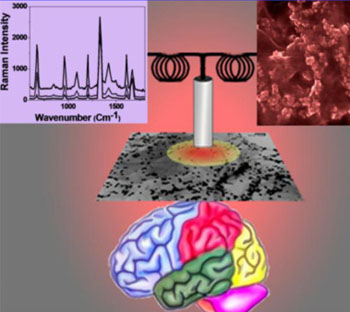
Image: Illustration of a protocol showing a pathway to develop core-shell nanoparticle/hybrid graphene oxide based multi-functional platform label-free SERS detection of β-amyloid toward developing a portable point-of-care blood test to monitor Alzheimer’s disease progression (Figure courtesy of Teresa Demeritt et al., 2015, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces; Copyright ACS-2015).
Toward development of a portable point-of-care (POC) biosensor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a new review explores recent advancements in nano-enabling electrochemical beta-amyloid (β-A) -sensing technologies. A simple, rapid POC biomarker test could greatly improve AD management and personalized treatment, also in developing countries.
The authors of the review, from the College of Medicine at Florida International University (Miami, FL, USA), are taking a new approach to diagnosing AD: measuring β-A in the blood with a POC test. AD is caused by high levels of β-A in the brain that lead to degeneration of brain cells. Various types of scans and immunoassays, such as MRI and ELISA, are available to estimate β-A levels in the brain. But the peptide can also be found at lower levels in blood, making it a useful biomarker for a simple test.
Currently there is no sensitive or inexpensive way to measure β-A levels in blood samples. The authors of the new review plan to change that. “We want to develop a point-of-care system where a small drop of blood plasma can reveal their β-A level immediately so that a doctor can tailor a patient’s therapy immediately,” said lead author Dr. Ajeet Kaushik, “The drugs used to treat AD can have side effects, so it’s better for patients not to overdose. With the right data, doctors can respond quickly to changes in a patient’s brain by reducing or increasing their dose.”
In the review, Dr. Kaushik and colleagues looked at each of the methods available to measure β-A concentration in brain tissue and in blood. None of the existing tests can be done at the bedside and all need special expertise and large samples. They also take a long time to generate a useful result—the main existing test, an ELISA, takes 6–8 hours. In comparison, the cheap, simple biosensor Dr. Kaushik and colleagues describe can measure β-A in the blood at low (pico molar) concentrations in just 30 minutes.
“Even though existing technologies are well established, we need to move towards small sample, high accuracy tests that can be used in all environments, from developed countries to rural settings. Our goal is to develop a test that’s sensitive, small, and affordable,” said Dr. Kaushik. To develop the new biosensor, the team will need many bio-fluid samples taken at different stages of the disease. Finding these samples will be challenging, but the review demonstrates that a biosensor is achievable. Such a test would also “show if and when the disease reaches an untreatable level. In the future we hope a rapid biosensor test for AD will help scientists study disease progression and help clinicians deliver personalized therapy to patients.”
The study, by Kaushik A et al., was published online ahead of print January 28, 2016, in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Related Links:
Florida International University
The authors of the review, from the College of Medicine at Florida International University (Miami, FL, USA), are taking a new approach to diagnosing AD: measuring β-A in the blood with a POC test. AD is caused by high levels of β-A in the brain that lead to degeneration of brain cells. Various types of scans and immunoassays, such as MRI and ELISA, are available to estimate β-A levels in the brain. But the peptide can also be found at lower levels in blood, making it a useful biomarker for a simple test.
Currently there is no sensitive or inexpensive way to measure β-A levels in blood samples. The authors of the new review plan to change that. “We want to develop a point-of-care system where a small drop of blood plasma can reveal their β-A level immediately so that a doctor can tailor a patient’s therapy immediately,” said lead author Dr. Ajeet Kaushik, “The drugs used to treat AD can have side effects, so it’s better for patients not to overdose. With the right data, doctors can respond quickly to changes in a patient’s brain by reducing or increasing their dose.”
In the review, Dr. Kaushik and colleagues looked at each of the methods available to measure β-A concentration in brain tissue and in blood. None of the existing tests can be done at the bedside and all need special expertise and large samples. They also take a long time to generate a useful result—the main existing test, an ELISA, takes 6–8 hours. In comparison, the cheap, simple biosensor Dr. Kaushik and colleagues describe can measure β-A in the blood at low (pico molar) concentrations in just 30 minutes.
“Even though existing technologies are well established, we need to move towards small sample, high accuracy tests that can be used in all environments, from developed countries to rural settings. Our goal is to develop a test that’s sensitive, small, and affordable,” said Dr. Kaushik. To develop the new biosensor, the team will need many bio-fluid samples taken at different stages of the disease. Finding these samples will be challenging, but the review demonstrates that a biosensor is achievable. Such a test would also “show if and when the disease reaches an untreatable level. In the future we hope a rapid biosensor test for AD will help scientists study disease progression and help clinicians deliver personalized therapy to patients.”
The study, by Kaushik A et al., was published online ahead of print January 28, 2016, in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Related Links:
Florida International University
Latest Pathology News
- AI Tool Predicts Chemotherapy Response from Biopsy Slides
- Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
- World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
- Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
DNA Aptamers Offer New Tool for Easy Alzheimer's Blood Test
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia and is marked by progressive loss of nerve cells that begins many years before symptoms become noticeable. Detecting early signs of neurodegeneration... Read more
Jumping "DNA Parasites” Linked to Early Tumor Development
Cancer genomes accumulate complex structural variants that can be difficult to resolve with standard short-read sequencing, obscuring clinically relevant drivers of disease. Transposable elements, particularly... Read more
AI-Based Liquid Biopsy Detects Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis and Chronic Disease Signals
Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis often develop silently for years before symptoms appear, making early diagnosis difficult. Detecting these conditions earlier could allow treatment before irreversible damage... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Study Highlights Accuracy Gaps in Consumer Gut Microbiome Kits
Direct-to-consumer gut microbiome kits promise personalized insights by profiling fecal bacteria and generating health readouts, but their analytical accuracy remains uncertain. A new study shows that... Read more
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more









 Analyzer.jpg)










