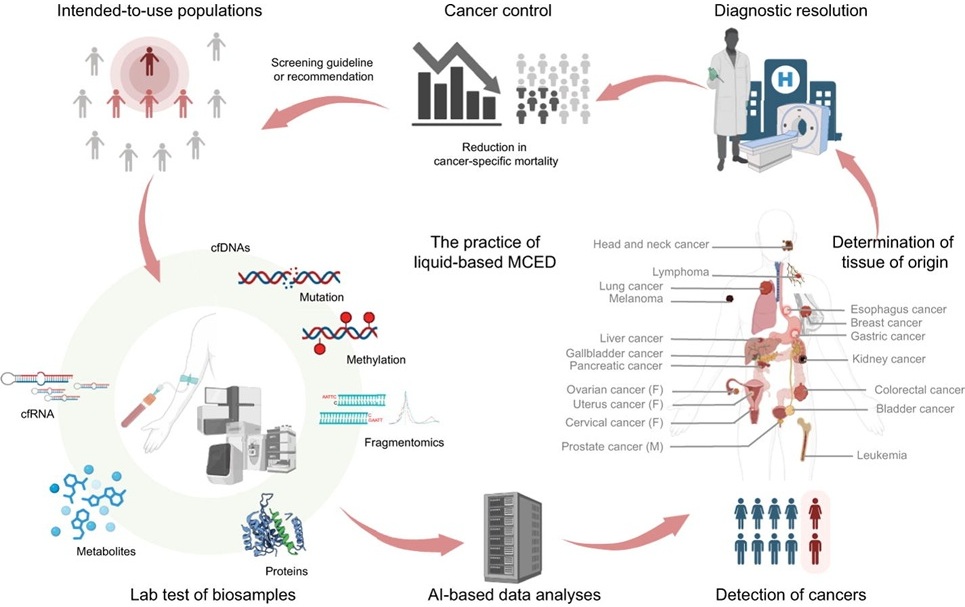
Chemical Analysis of Blood Samples Diagnoses Brain Tumors
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 21 Nov 2019 |
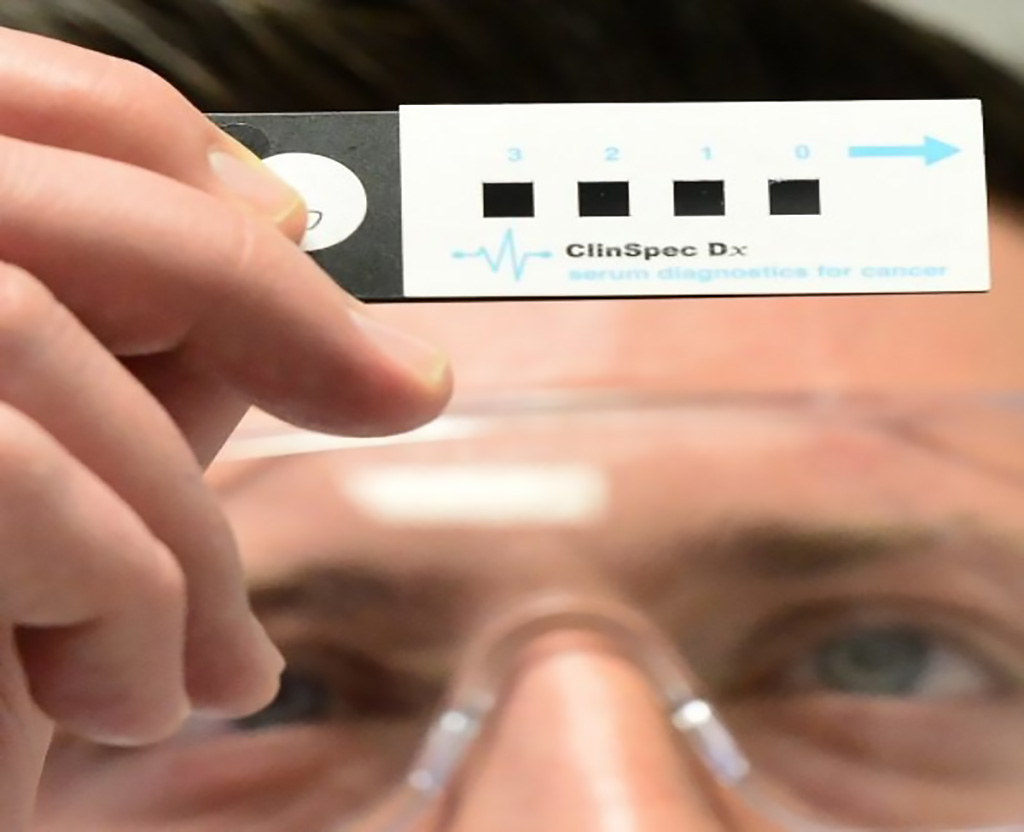
Image: The new ClinSpec Diagnostics’ test can diagnose brain cancer from a blood sample (Photo courtesy of University of Strathclyde).
Brain tumors tend to have ambiguous symptoms, such as headache or memory problems, and a brain scan is currently the only reliable way of diagnosing them. In recent years, the use of infrared (IR) spectroscopy to analyze disease state in biofluids has been largely employed with promising results.
Diagnosis of brain tumors has been previously investigated with attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy on dried human serum samples to eliminate spectral interferences of the water component. Rapid analysis of liquid samples would represent a promising approach for clinical translation.
A team of scientists at the University of Strathclyde (Glasgow, UK) and their colleagues evaluated ATR-FTIR on both liquid and dried samples to investigate “digital drying” as a novel approach for the analysis of spectra obtained from liquid samples. Quantum cascade laser infrared (QCL-IR) based spectroscopic imaging was also utilized on liquid samples to assess the implications of this novel light source on disease classification. The team tried out the new test on blood samples taken from 400 patients with possible signs of brain tumor who had been referred for a brain scan at the Western General Hospital (Edinburgh, UK).
The team reported that of the 400 patients, 40 were subsequently found to have a brain tumour. Using the test, the scientists were able to correctly identify 82% of brain tumors. The test was also able to correctly identify 84% of people who did not have brain tumors, meaning it had a low rate of 'false’ positives. In the case of the most common form of brain tumor, called glioma, the test was 92% accurate at picking up which people had tumors.
Matthew Baker, PhD, Reader in Chemistry, and chief scientific officer at ClinSpec Diagnostics Ltd (Glasgow, Scotland), where the test was developed, and a senior author of the study, said, “These results are extremely promising because they suggest that our technique can accurately spot who is most likely to have a brain tumour and who probably does not. Because the technique requires just a small blood sample, if offers the potential to test a large number of people with suspicious symptoms and give the best indication of who needs an urgent brain scan. This could ultimately speed up diagnosis, reduce the anxiety of waiting for tests and get patients treated as quickly as possible.” The study was presented at the 2019 NCRI Cancer Conference held November 4- 6, 2019, in Glasgow, UK.
Related Links:
University of Strathclyde
Western General Hospital
ClinSpec Diagnostics Ltd
Diagnosis of brain tumors has been previously investigated with attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) spectroscopy on dried human serum samples to eliminate spectral interferences of the water component. Rapid analysis of liquid samples would represent a promising approach for clinical translation.
A team of scientists at the University of Strathclyde (Glasgow, UK) and their colleagues evaluated ATR-FTIR on both liquid and dried samples to investigate “digital drying” as a novel approach for the analysis of spectra obtained from liquid samples. Quantum cascade laser infrared (QCL-IR) based spectroscopic imaging was also utilized on liquid samples to assess the implications of this novel light source on disease classification. The team tried out the new test on blood samples taken from 400 patients with possible signs of brain tumor who had been referred for a brain scan at the Western General Hospital (Edinburgh, UK).
The team reported that of the 400 patients, 40 were subsequently found to have a brain tumour. Using the test, the scientists were able to correctly identify 82% of brain tumors. The test was also able to correctly identify 84% of people who did not have brain tumors, meaning it had a low rate of 'false’ positives. In the case of the most common form of brain tumor, called glioma, the test was 92% accurate at picking up which people had tumors.
Matthew Baker, PhD, Reader in Chemistry, and chief scientific officer at ClinSpec Diagnostics Ltd (Glasgow, Scotland), where the test was developed, and a senior author of the study, said, “These results are extremely promising because they suggest that our technique can accurately spot who is most likely to have a brain tumour and who probably does not. Because the technique requires just a small blood sample, if offers the potential to test a large number of people with suspicious symptoms and give the best indication of who needs an urgent brain scan. This could ultimately speed up diagnosis, reduce the anxiety of waiting for tests and get patients treated as quickly as possible.” The study was presented at the 2019 NCRI Cancer Conference held November 4- 6, 2019, in Glasgow, UK.
Related Links:
University of Strathclyde
Western General Hospital
ClinSpec Diagnostics Ltd
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- New Clinical Chemistry Analyzer Designed to Meet Growing Demands of Modern Labs

- New Reference Measurement Procedure Standardizes Nucleic Acid Amplification Test Results
- Pen-Like Tool Quickly and Non-Invasively Detects Opioids from Skin
- Simple Urine Test Could Detect Multiple Cancers at Early Stage
- Earwax Test Accurately Detects Parkinson’s by Identifying Odor Molecules
- First-Of-Its-Kind Quantitative Method Assesses Opioid Exposure in Newborns
- Paper-Based Devices Outperform Existing Methods in Diagnosing Asymptomatic Malaria
- Simple Skin Test Could Revolutionize Diagnosis of Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- Portable Diagnostic Tool Uses Bioluminescence to Detect Viruses at POC
- AI-Powered Lung Maturity Test Identifies Newborns at Higher Risk of Respiratory Distress
- AI-Powered Blood Test Accurately Detects Ovarian Cancer
- Automated Decentralized cfDNA NGS Assay Identifies Alterations in Advanced Solid Tumors
- Mass Spectrometry Detects Bacteria Without Time-Consuming Isolation and Multiplication
- First Comprehensive Syphilis Test to Definitively Diagnose Active Infection In 10 Minutes
- Mass Spectrometry-Based Monitoring Technique to Predict and Identify Early Myeloma Relapse
- ‘Brilliantly Luminous’ Nanoscale Chemical Tool to Improve Disease Detection
Channels
Molecular Diagnostics
view channel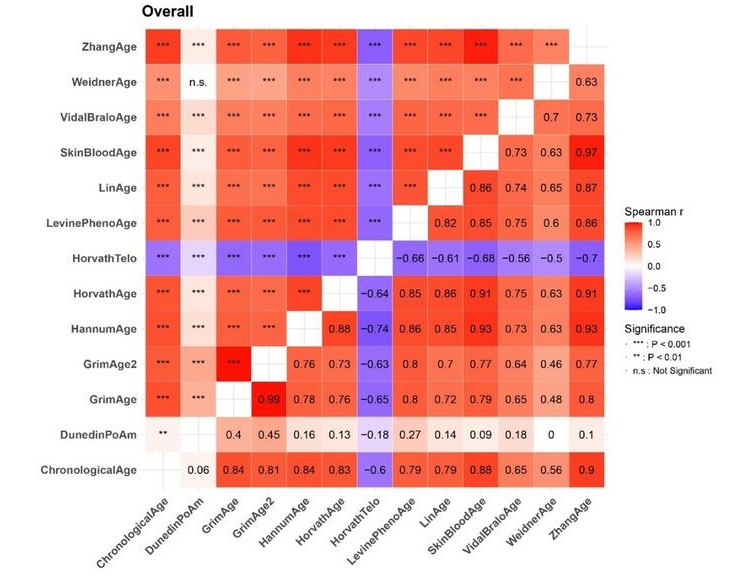
DNA Methylation Signatures of Aging Could Help Assess Mortality Risk
Aging is associated with the progressive degeneration and loss of function across multiple physiological systems. Chronological age is the most common indicator of aging; however, there is significant... Read more
Molecular Diagnostics System Provides Lab-Quality Results at POC
Currently, there is a need for a comprehensive molecular diagnostics ecosystem that enables effective diagnostic stewardship, providing the diagnostic tools to offer the right tests, for the right patient,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most commonly ordered lab tests, crucial for diagnosing diseases, monitoring therapies, and conducting routine health screenings. However, more than 90% of physician... Read more
First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes
Heparin dosing requires careful management to avoid both bleeding and clotting complications. In high-risk situations like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality rates can reach about 50%,... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Evolutionary Clinical Trial to Identify Novel Biomarker-Driven Therapies for Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer, which occurs when cancer spreads from the breast to other parts of the body, is one of the most difficult cancers to treat. Nearly 90% of patients with metastatic cancer will... Read more
Groundbreaking Lateral Flow Test Quantifies Nucleosomes in Whole Venous Blood in Minutes
Diagnosing immune disruptions quickly and accurately is crucial in conditions such as sepsis, where timely intervention is critical for patient survival. Traditional testing methods can be slow, expensive,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel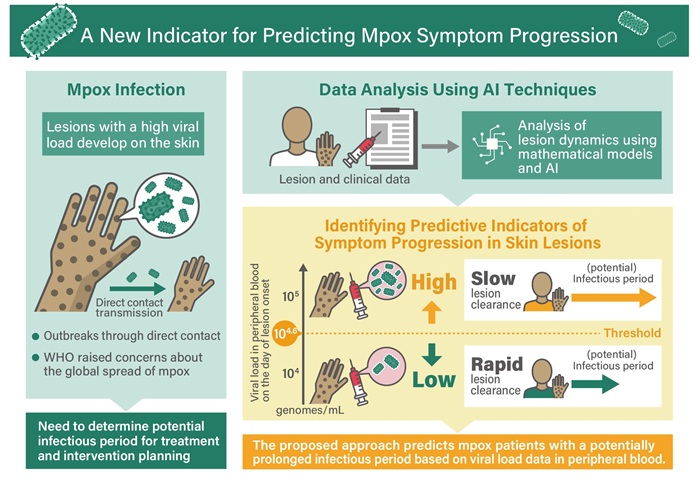
Viral Load Tests Can Help Predict Mpox Severity
Mpox is a viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and a characteristic rash, which evolves significantly over time and varies between patients. The disease spreads mainly through direct contact with... Read more
Gut Microbiota Analysis Enables Early and Non-Invasive Detection of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder marked by abnormal glucose metabolism during pregnancy, typically emerging in the mid to late stages. It significantly heightens the risk of... Read morePathology
view channel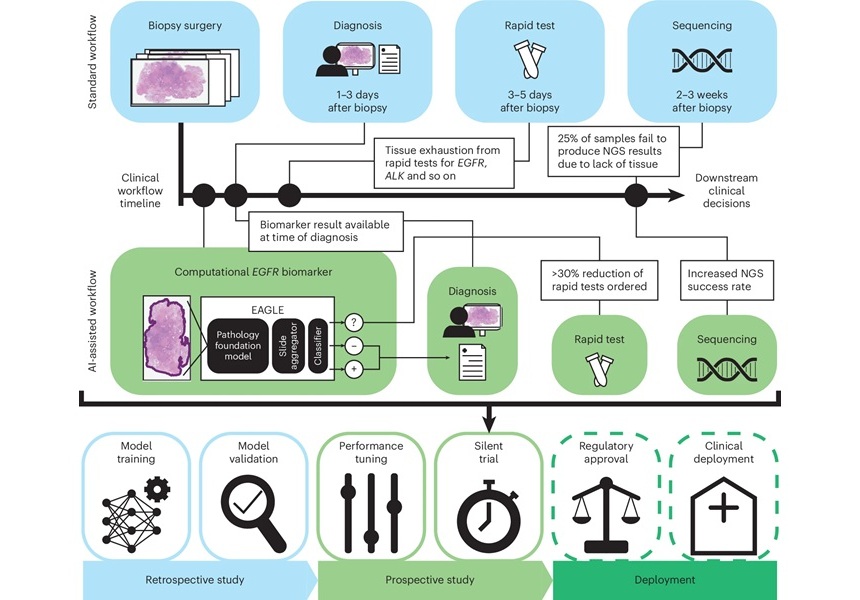
AI Accurately Predicts Genetic Mutations from Routine Pathology Slides for Faster Cancer Care
Current cancer treatment decisions are often guided by genetic testing, which can be expensive, time-consuming, and not always available at leading hospitals. For patients with lung adenocarcinoma, a critical... Read more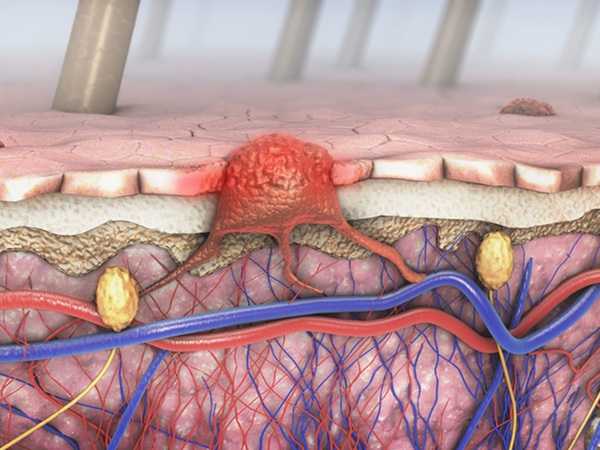
AI Tool Enhances Interpretation of Tissue Samples by Pathologists
Malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer, is diagnosed by pathologists based on tissue samples. A crucial aspect of this process is estimating the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), immune... Read more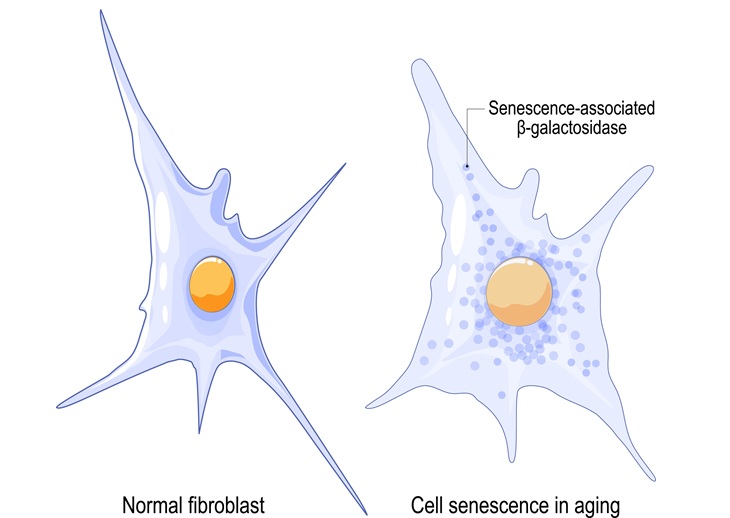
AI-Assisted Technique Tracks Cells Damaged from Injury, Aging and Disease
Senescent cells, which stop growing and reproducing due to injury, aging, or disease, play a critical role in wound repair and aging-related diseases like cancer and heart disease. These cells, however,... Read more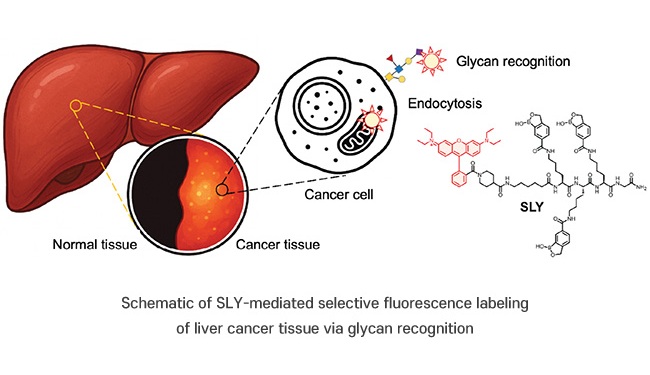
Novel Fluorescent Probe Shows Potential in Precision Cancer Diagnostics and Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common type of liver cancer, is difficult to diagnose early and accurately due to the limitations of current diagnostic methods. Glycans, carbohydrate structures present... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Multifunctional Nanomaterial Simultaneously Performs Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment, and Immune Activation
Cancer treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, have significant limitations. These treatments not only target cancerous areas but also damage healthy tissues, causing side effects... Read more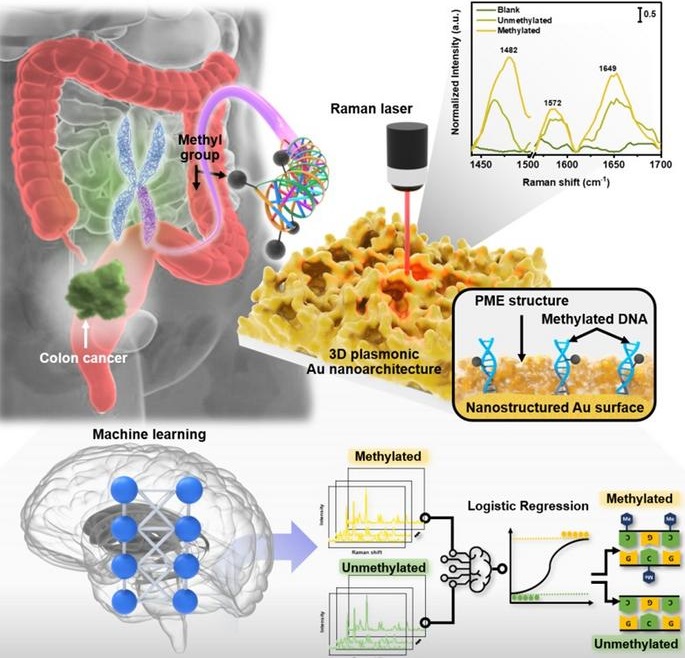
Ultra-Sensitive Biosensor Based on Light and AI Enables Early Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis is often delayed due to the difficulty in detecting early-stage cancer markers. In particular, the concentration of methylated DNA in the bloodstream during the early stages of cancer... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Quanterix Completes Acquisition of Akoya Biosciences
Quanterix Corporation (Billerica, MA, USA) has completed its previously announced acquisition of Akoya Biosciences (Marlborough, MA, USA), paving the way for the creation of the first integrated solution... Read more
Lunit and Microsoft Collaborate to Advance AI-Driven Cancer Diagnosis
Lunit (Seoul, South Korea) and Microsoft (Redmond, WA, USA) have entered into a collaboration to accelerate the delivery of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered healthcare solutions. In conjunction with... Read more