Blood Sample Storage Evaluated for PEA Analysis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 29 May 2017 |
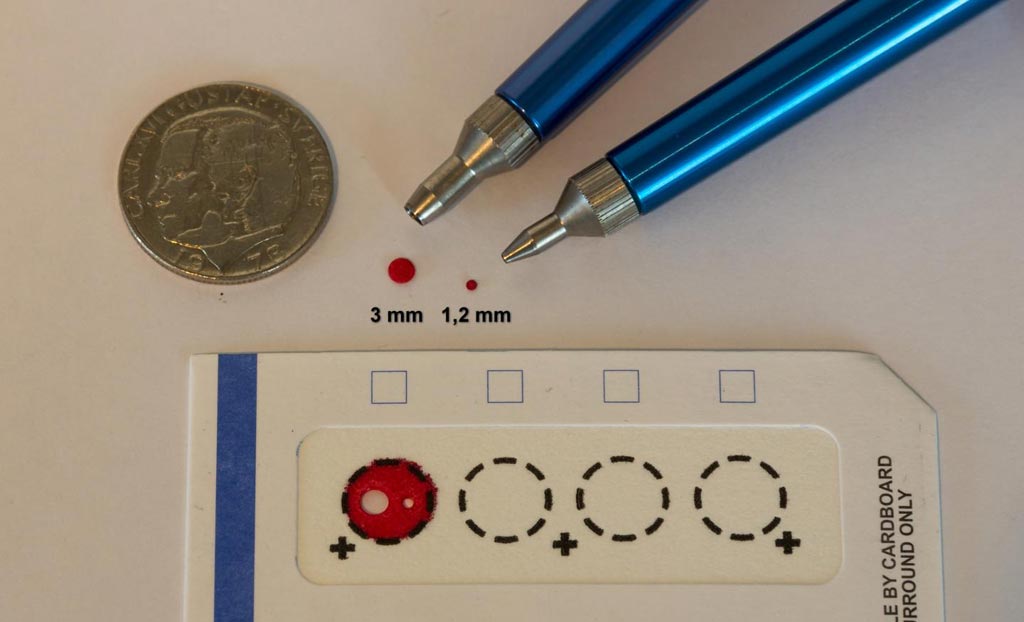
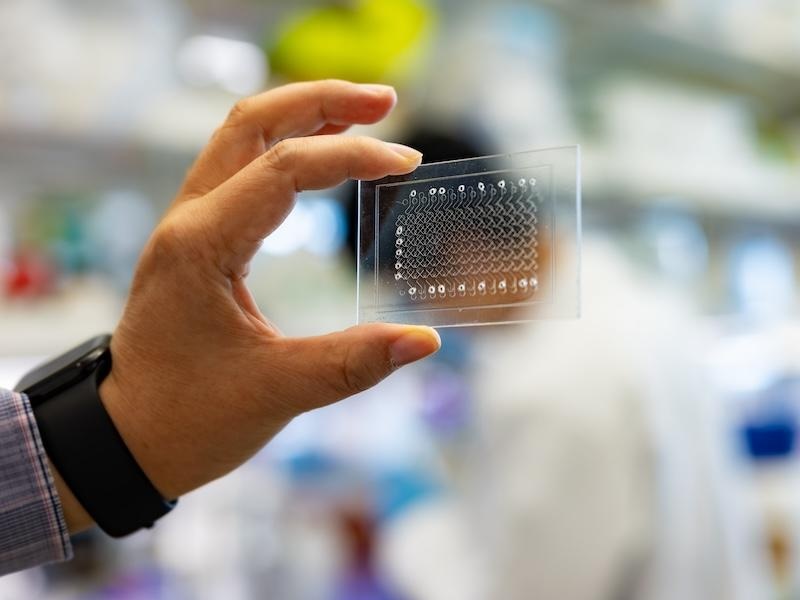
Image: Drops of blood on filter paper, easy to store for future diagnostics (Photo courtesy of Jan Björkeste, Uppsala University).
A team of Swedish researchers evaluated and optimized conditions for storing samples of dried blood for current and future proximity extension assay (PEA) analysis.
Dried blood samples are attractive for sample preservation due to the ease and low cost of collection and storage. In a recent study, investigators at Uppsala University evaluated their suitability for protein measurements. The investigators analyzed 92 proteins with relevance for oncology using multiplex proximity extension assays (PEA) in dried blood spots collected on paper and stored for up to 30 years at either plus four degrees Celsius or minus 24 degrees Celsius.
According to the PEA method, a pair of oligonucleotide-labeled antibodies is allowed to pair-wise bind to the target protein present in the dried-blood sample in a homogeneous assay, with no need for washing. When the two probes are in close proximity, a new PCR target sequence is formed by a proximity-dependent DNA polymerization event. The resulting sequence is subsequently detected and quantified using standard real-time PCR. This method, which has been commercialized under the name Proseek Multiplex by Olink, allows detection of levels of 96 proteins (including four controls) from a disc 1.2 millimeters in diameter punched out of a dried blood spot (DBS) on filter paper.
The main findings of the study were that (1) the act of drying only slightly influenced detection of blood proteins in a reproducible manner, (2) detection of some proteins was not significantly affected by storage over the full range of three decades (34% and 76% of the analyzed proteins at plus four degrees Celsius and minus 24 degrees Celsius, respectively), while levels of others decreased slowly during storage with half-lives in the range of 10 to 50 years, and (3) detectability of proteins was less affected in dried samples stored at minus 24 degrees Celsius compared to at four degrees Celsius.
"This has several implications. First, you can prick your own finger and send in a dried blood spot by post. Second, at a minimal cost, it will be possible to build gigantic biobanks of samples obtained on a routine clinical basis. This means that samples can be taken before the clinical debut of a disease, to identify markers of value for early diagnosis, improving the scope for curative treatment," said senior author Dr. Ulf Landegren, professor of molecular medicine at Uppsala University.
The study was published in the May 13, 2017, online edition of the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Dried blood samples are attractive for sample preservation due to the ease and low cost of collection and storage. In a recent study, investigators at Uppsala University evaluated their suitability for protein measurements. The investigators analyzed 92 proteins with relevance for oncology using multiplex proximity extension assays (PEA) in dried blood spots collected on paper and stored for up to 30 years at either plus four degrees Celsius or minus 24 degrees Celsius.
According to the PEA method, a pair of oligonucleotide-labeled antibodies is allowed to pair-wise bind to the target protein present in the dried-blood sample in a homogeneous assay, with no need for washing. When the two probes are in close proximity, a new PCR target sequence is formed by a proximity-dependent DNA polymerization event. The resulting sequence is subsequently detected and quantified using standard real-time PCR. This method, which has been commercialized under the name Proseek Multiplex by Olink, allows detection of levels of 96 proteins (including four controls) from a disc 1.2 millimeters in diameter punched out of a dried blood spot (DBS) on filter paper.
The main findings of the study were that (1) the act of drying only slightly influenced detection of blood proteins in a reproducible manner, (2) detection of some proteins was not significantly affected by storage over the full range of three decades (34% and 76% of the analyzed proteins at plus four degrees Celsius and minus 24 degrees Celsius, respectively), while levels of others decreased slowly during storage with half-lives in the range of 10 to 50 years, and (3) detectability of proteins was less affected in dried samples stored at minus 24 degrees Celsius compared to at four degrees Celsius.
"This has several implications. First, you can prick your own finger and send in a dried blood spot by post. Second, at a minimal cost, it will be possible to build gigantic biobanks of samples obtained on a routine clinical basis. This means that samples can be taken before the clinical debut of a disease, to identify markers of value for early diagnosis, improving the scope for curative treatment," said senior author Dr. Ulf Landegren, professor of molecular medicine at Uppsala University.
The study was published in the May 13, 2017, online edition of the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- New Biomarker Panel to Enable Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer
- Ultrarapid Whole Genome Sequencing for Neonatal and Pediatric Patients Delivers Results In 48 Hours
- AI-Enabled Blood Test Demonstrates Diagnostic, Prognostic and Predictive Utility Across Cancer Continuum
- DNA Methylation Signatures of Aging Could Help Assess Mortality Risk
- Molecular Diagnostics System Provides Lab-Quality Results at POC
- Cellular Signature Identifies Patients with Treatment Resistant Prostate Tumors
- MCED Could Be Valuable Supplement to Traditional Cancer Screening Approaches
- Newly-Cleared Technology a Game Changer for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease
- Innovative Liquid Biopsy Test Uses RNA to Detect Early-Stage Cancer
- Rapid Tests for Chagas Disease Improves Diagnostic Access
- Simple Blood Test to Predict Alzheimer’s Clinical Progression in Earliest Stages
- Saliva Test Could Identify People Genetically Susceptible to Type 2 Diabetes
- Pioneering Analyzer with Advanced Biochip Technology Sets New Standard in Lab Diagnostics
- RNA-Seq Based Diagnostic Test Enhances Diagnostic Accuracy of Pediatric Leukemia
- New Technique for Measuring Acidic Glycan in Blood Simplifies Schizophrenia Diagnosis
- Injury Molecular Fingerprint Enables Real-Time Diagnostics for On-Site Treatment
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New Clinical Chemistry Analyzer Designed to Meet Growing Demands of Modern Labs
A new clinical chemistry analyzer is designed to provide outstanding performance and maximum efficiency, without compromising affordability, to meet the growing demands of modern laboratories.... Read more
New Reference Measurement Procedure Standardizes Nucleic Acid Amplification Test Results
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) play a key role in diagnosing a wide range of infectious diseases. These tests are generally known for their high sensitivity and specificity, and they can be developed... Read moreHematology
view channel
Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most commonly ordered lab tests, crucial for diagnosing diseases, monitoring therapies, and conducting routine health screenings. However, more than 90% of physician... Read more
First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes
Heparin dosing requires careful management to avoid both bleeding and clotting complications. In high-risk situations like extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), mortality rates can reach about 50%,... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Evolutionary Clinical Trial to Identify Novel Biomarker-Driven Therapies for Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer, which occurs when cancer spreads from the breast to other parts of the body, is one of the most difficult cancers to treat. Nearly 90% of patients with metastatic cancer will... Read more
Groundbreaking Lateral Flow Test Quantifies Nucleosomes in Whole Venous Blood in Minutes
Diagnosing immune disruptions quickly and accurately is crucial in conditions such as sepsis, where timely intervention is critical for patient survival. Traditional testing methods can be slow, expensive,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel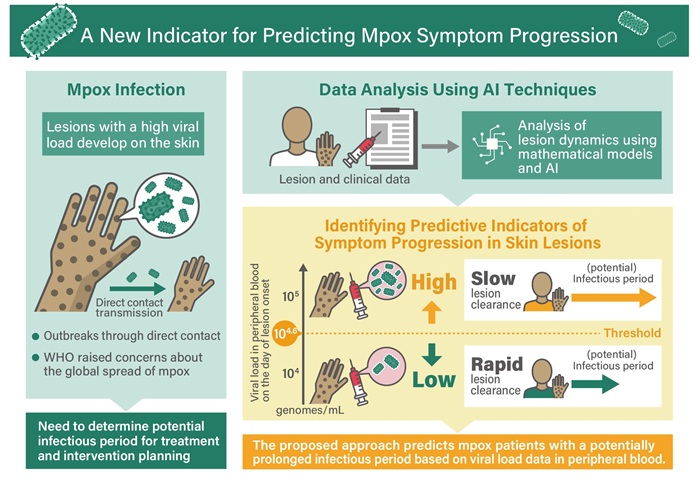
Viral Load Tests Can Help Predict Mpox Severity
Mpox is a viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and a characteristic rash, which evolves significantly over time and varies between patients. The disease spreads mainly through direct contact with... Read more
Gut Microbiota Analysis Enables Early and Non-Invasive Detection of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder marked by abnormal glucose metabolism during pregnancy, typically emerging in the mid to late stages. It significantly heightens the risk of... Read morePathology
view channel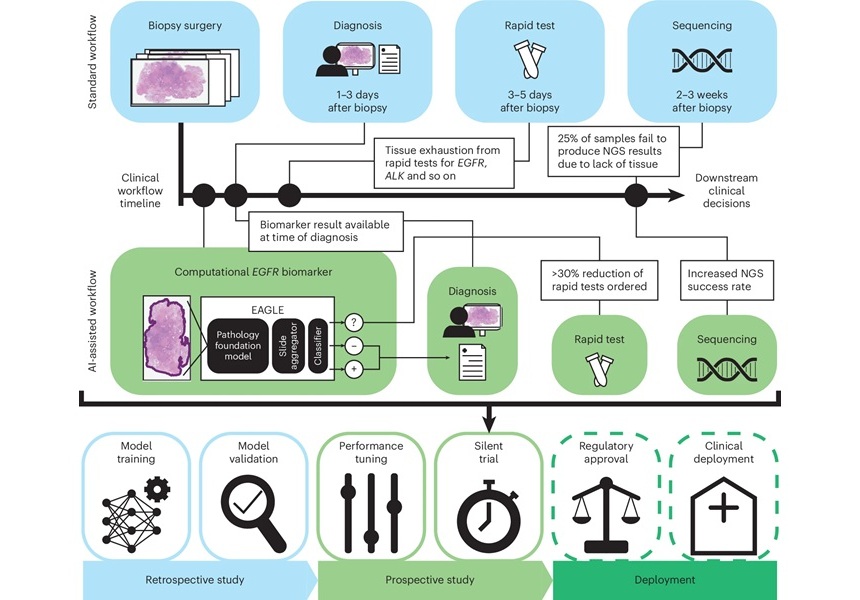
AI Accurately Predicts Genetic Mutations from Routine Pathology Slides for Faster Cancer Care
Current cancer treatment decisions are often guided by genetic testing, which can be expensive, time-consuming, and not always available at leading hospitals. For patients with lung adenocarcinoma, a critical... Read more
AI Tool Enhances Interpretation of Tissue Samples by Pathologists
Malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer, is diagnosed by pathologists based on tissue samples. A crucial aspect of this process is estimating the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), immune... Read more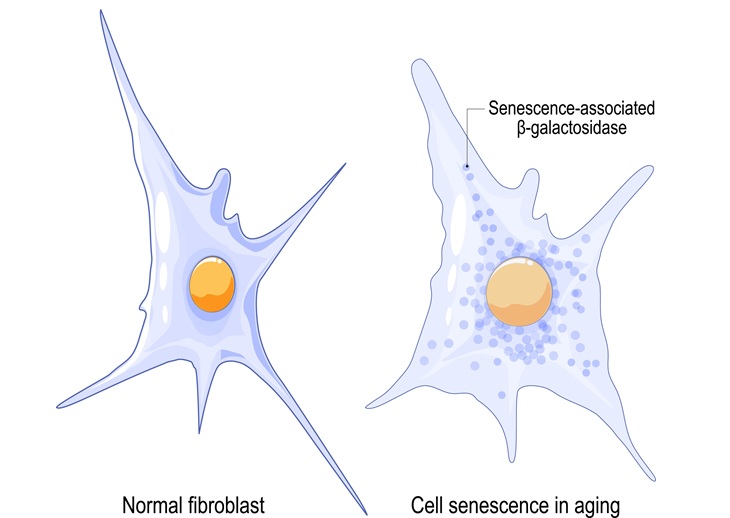
AI-Assisted Technique Tracks Cells Damaged from Injury, Aging and Disease
Senescent cells, which stop growing and reproducing due to injury, aging, or disease, play a critical role in wound repair and aging-related diseases like cancer and heart disease. These cells, however,... Read more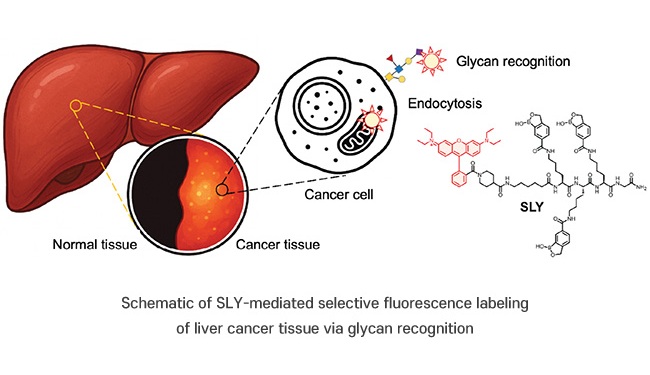
Novel Fluorescent Probe Shows Potential in Precision Cancer Diagnostics and Fluorescence-Guided Surgery
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a common type of liver cancer, is difficult to diagnose early and accurately due to the limitations of current diagnostic methods. Glycans, carbohydrate structures present... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Multifunctional Nanomaterial Simultaneously Performs Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment, and Immune Activation
Cancer treatments, including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, have significant limitations. These treatments not only target cancerous areas but also damage healthy tissues, causing side effects... Read more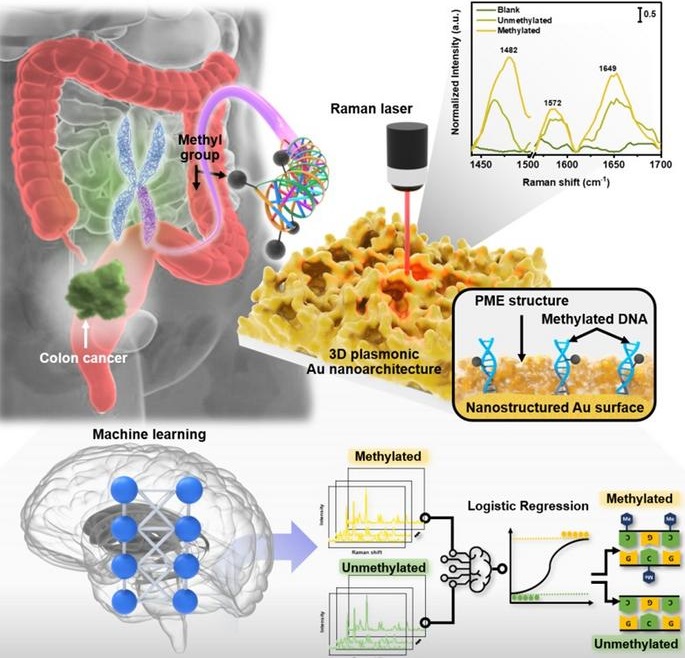
Ultra-Sensitive Biosensor Based on Light and AI Enables Early Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer diagnosis is often delayed due to the difficulty in detecting early-stage cancer markers. In particular, the concentration of methylated DNA in the bloodstream during the early stages of cancer... Read moreIndustry
view channel
2025 COMPAMED Innovation Forum Highlights Pioneering Work in Cancer Diagnostics
Cancer cases are among the biggest challenges faced by global healthcare systems. The incidence has risen in recent decades, not least on account of demographic change and escalating risk factors.... Read more
Quanterix Completes Acquisition of Akoya Biosciences
Quanterix Corporation (Billerica, MA, USA) has completed its previously announced acquisition of Akoya Biosciences (Marlborough, MA, USA), paving the way for the creation of the first integrated solution... Read more
Lunit and Microsoft Collaborate to Advance AI-Driven Cancer Diagnosis
Lunit (Seoul, South Korea) and Microsoft (Redmond, WA, USA) have entered into a collaboration to accelerate the delivery of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered healthcare solutions. In conjunction with... Read more