Microbiology
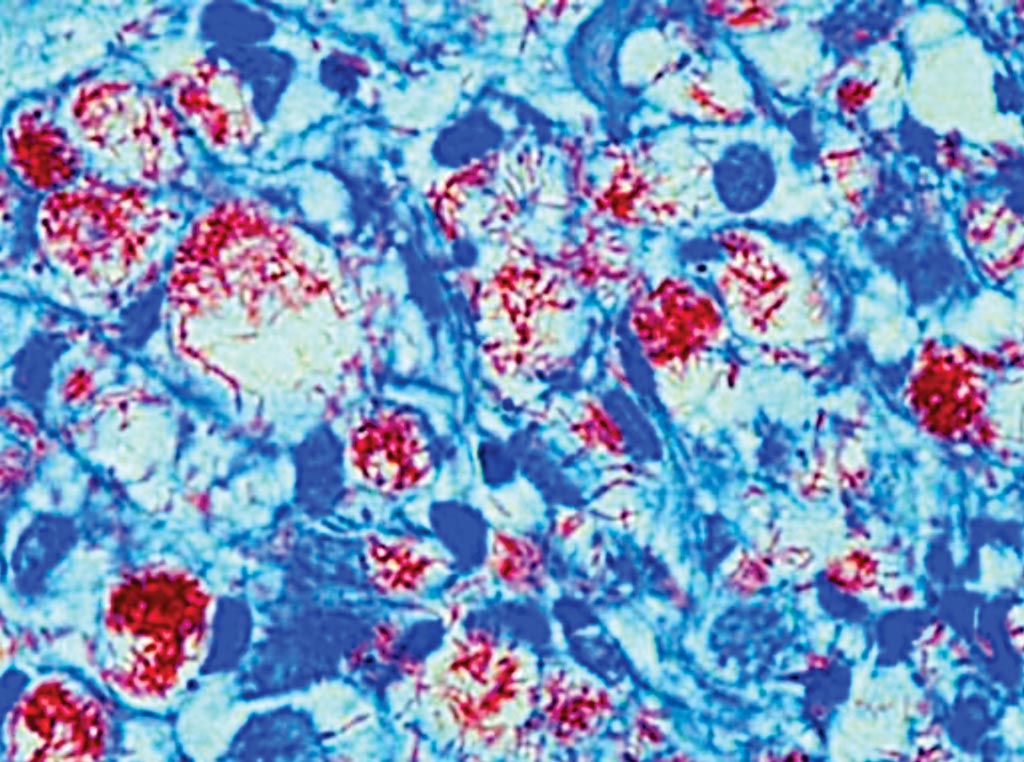
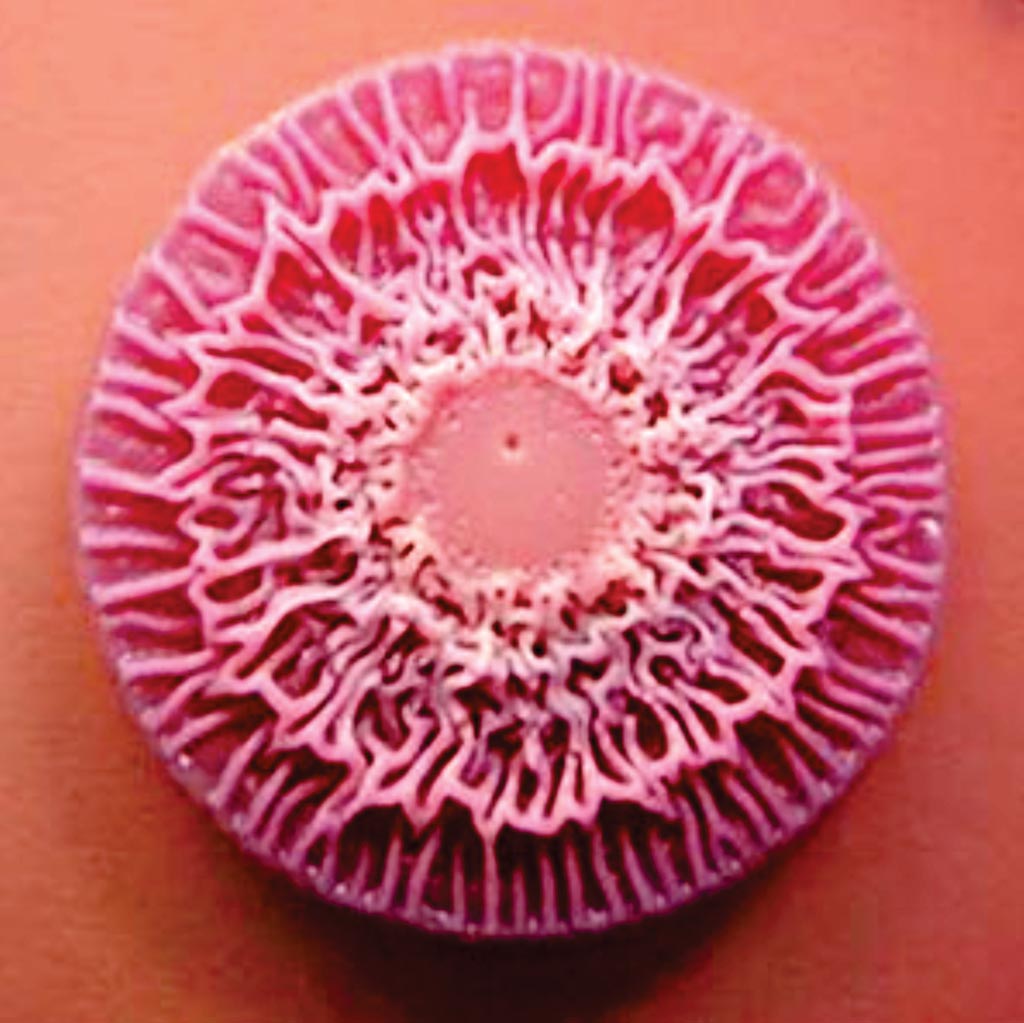
Antigenic Targets Compared for Melioidosis Serodiagnosis
Melioidosis, caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, is a life-threatening infection endemic in tropical countries and definitive diagnosis of the disease relies upon bacterial culture, which requires suitable laboratory facilities and reliable antibody testing. More...13 Apr 2017
Lymphocyte Subtyping Proves Useful in Predicting Pneumonia
Pneumocystis jirovecii is an opportunistic fungus that can cause interstitial pneumonia in the immunocompromised host and is associated with a high mortality rate. Antimicrobial prophylaxis reduces the occurrence of P. jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) considerably in susceptible patients. More...13 Apr 2017
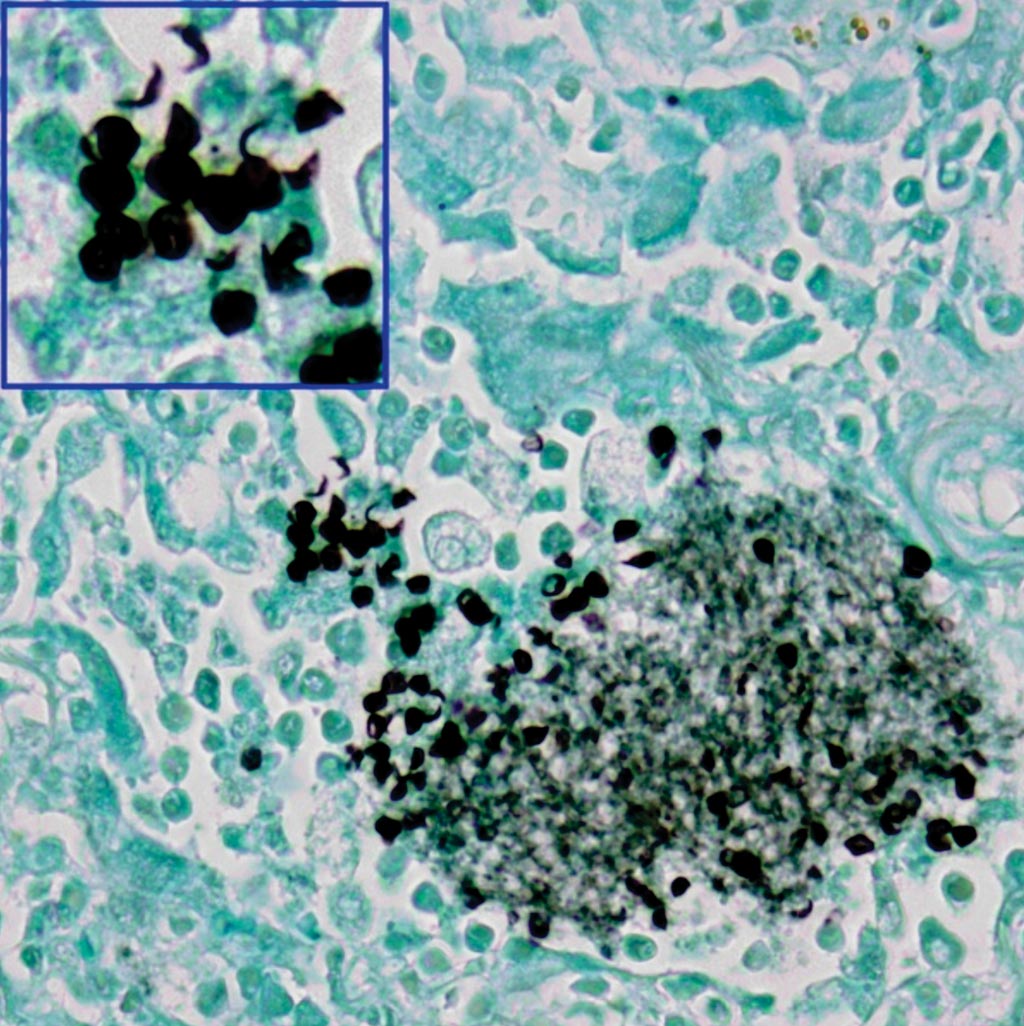
Circulating TB Antigens Allows Rapid Diagnosis of Active Disease
A rapid and quantitative blood-based assay with high sensitivity and specificity for active Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infections has been developed that can be used to monitor responses to anti-mycobacterial therapy. More...13 Apr 2017
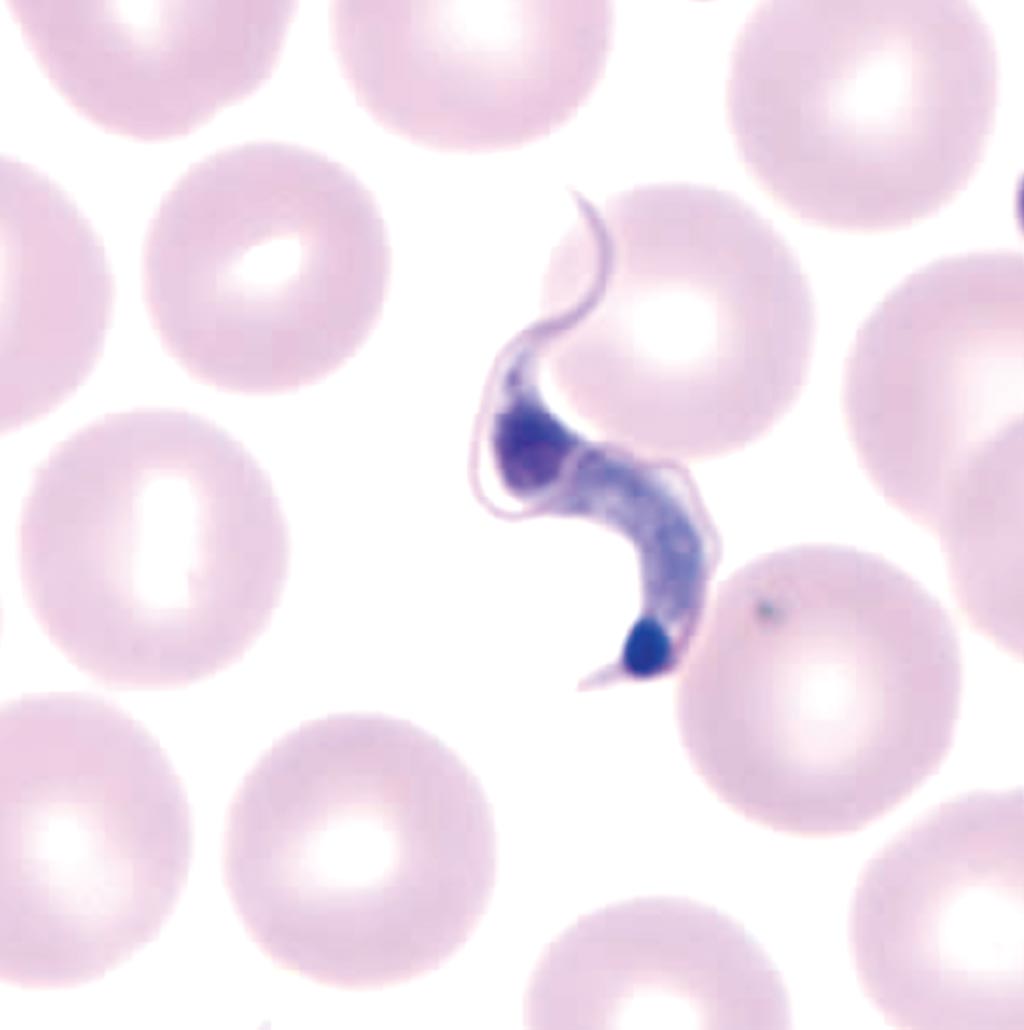
Performance of Chagas Disease Genotyping Assay Evaluated
Chagas disease remains a significant public health issue infecting six to seven million people worldwide. The factors influencing the clinical heterogeneity of Chagas disease have not been elucidated, although it has been suggested that different clinical outcome may be associated with the genetic diversity of Trypanosoma cruzi isolates. More...07 Apr 2017
In Other News
Microarray PCR System Detects STI Pathogens
Transplanted Microbes Alter Gut Function and Behavior
Portable Device Being Developed to Detect Zika at POC
Evidence Shows Nosocomial Infections Linked to Hospital Sink Bacteria
Proteomic Assay Pinpoints Cause of Upper Respiratory Disease
Nodding Syndrome Linked to Worm Protein
Listeria May Pose Serious Threat Early in Pregnancy
Rapid Method Developed to Identify Bacteria in Blood Samples
Rapid Test Specifically Detects Mobile Colistin Resistance in Isolates
POC Test for Chagas Disease Available in US
Cerebrospinal Fluid Lens-Free Microscopy Used to Diagnose Meningitis
Premature Birth Risk Linked to Bacteria in Cervicovaginal Space
Faster Way of Detecting Bacteria Developed
Real-Time PCR Assay Developed for Detection of Candida
Direct Blood Dry LAMP System Detects Malaria Species
Pathogenic Antibodies to Dengue Virus Linked to Disease Severity
Enterovirus Infections Linked with Autoimmunity Leading to Diabetes
Nanoparticles and Faraday Rotation Allow Faster Diagnoses
Seropositivity Thresholds Defined for Use in Trachoma Elimination Studies
Thromboelastometry Analysis Assessed for Thrombocytopenic Dengue Patients
New Immunoassay Developed for Zika Virus Detection
Gene Panel Differentiates Survival Outcomes in Humans Infected with Ebola
Serological Test Differentiates Zika from Dengue Infections
The LabMedica Microbiology channel provides the latest news in the fields of epidemiology, bacteriology, virology, and parasitology, all viewed from the unique perspective of Laboratory Medicine.










