Microbiology

Flow Cytometry Employed in Diagnosing Male Urethritis
According to the established guidelines, diagnosis of non-gonococcal urethritis should be confirmed by demonstrating polymorphonuclear leukocytes from the anterior urethra using a Gram-stained (GSS) or methylene blue-stained urethral smear. More...17 Dec 2020
Lab-on-a-Chip Infection Test Provides Cheaper, Faster Portable Diagnostics
Rapid screening and low-cost diagnosis play a crucial role in choosing the correct course of intervention when dealing with highly infectious pathogens. This is especially important if the disease-causing agent has no effective treatment. More...15 Dec 2020
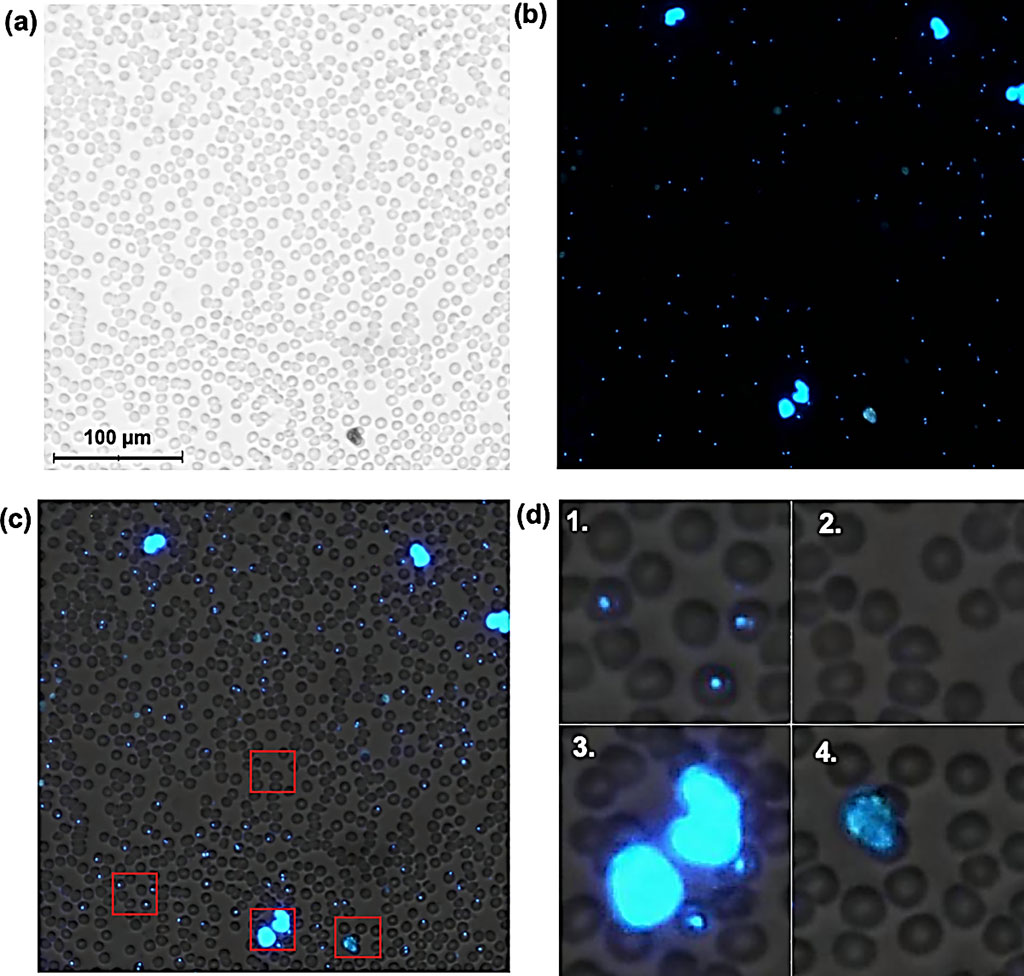
Deep Learning Digital Microscope Scanner Detects Malaria
Malaria remains a major global health problem with a need for improved field-usable diagnostic tests. Light microscopy assessment of blood smears to detect Plasmodium parasites remains the diagnostic gold standard and allows detection and quantification of Plasmodium species while also being more sensitive than rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs). More...09 Dec 2020
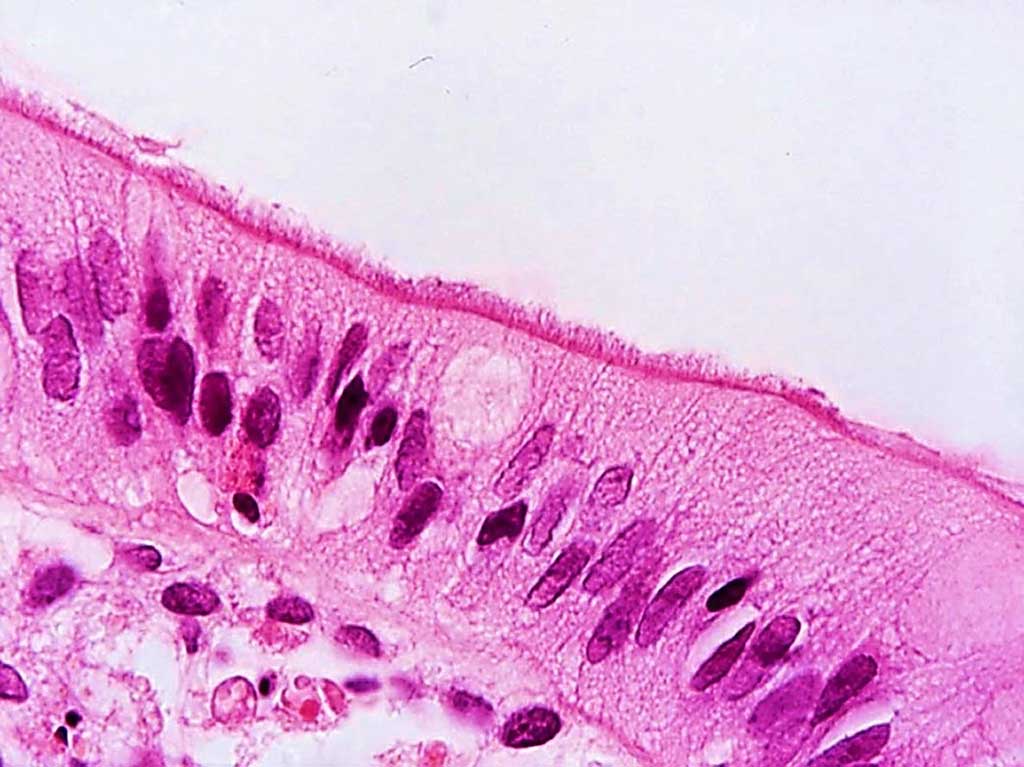
Specific Gut Bacterium Linked to Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The incidence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) steeply increases following a gastroenteritis episode, suggesting a possible causative role for microbial perturbation. Gut microbiota composition studies overwhelmingly rely on fecal material. More...08 Dec 2020

Distinct Inflammatory Profiles Distinguish COVID-19 From Influenza
Acute respiratory failure occurs in a subset of COVID-19 patients. Understanding the etiology of respiratory failure in COVID-19 patients is critical for determining the best management strategies and pharmacologic targets for treatment. More...30 Nov 2020
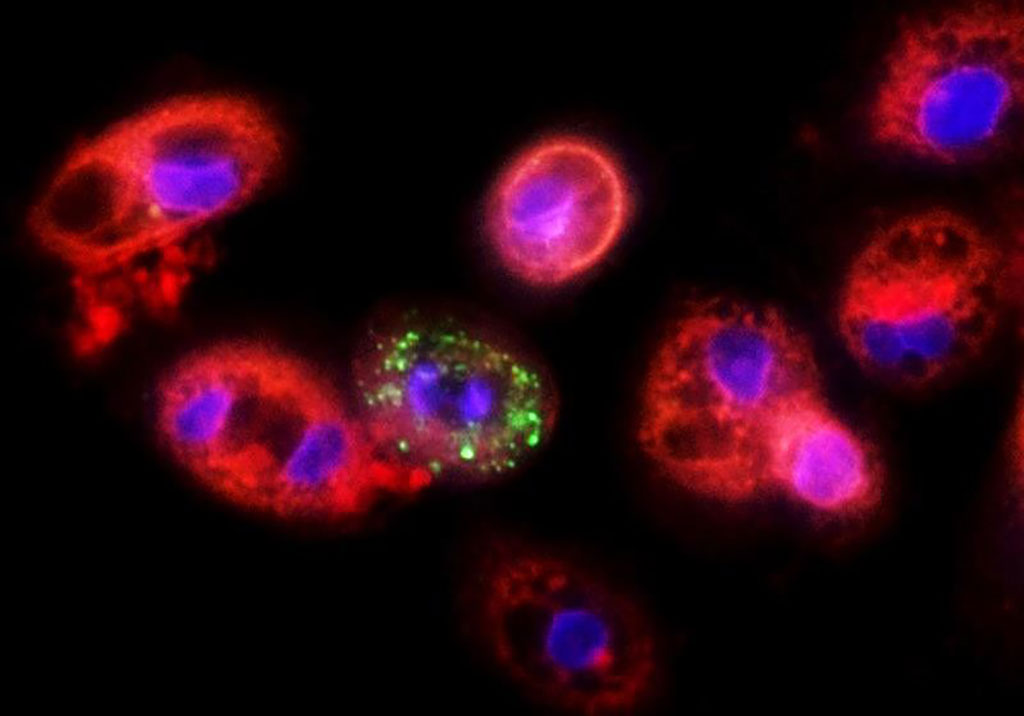
SARS-CoV-2 RNA Test Assessed Among Recovered COVID-19 Patients
Some patients who have recovered from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with documented negative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) results at the time of recovery have had subsequent positive RT-PCR test results for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). More...25 Nov 2020

Metagenomic Sequencing Quickly Identifies Pathogens in Body Fluids
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) is a shotgun sequencing approach in which all of the nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) in a clinical sample is sequenced at a very high depth, 10-20 million sequences per sample. More...23 Nov 2020
In Other News
COVID-19 Lung Damage Caused by Persistence of Abnormal Cells
Rapid Tests Evaluated in the Management of Dengue Fever
Serum-IgG Responses in Patients with Mild and Severe COVID-19
Antibodies Against Rabies Detected in Human Dried Blood Spots
Single-Molecule Tethering Detects Nucleic Acids and Microorganisms
New Diagnostic Tests for Rotavirus and Norovirus Infections Evaluated
MAIT Cell Activation Dynamics Associated with COVID-19 Disease Severity
Bacterium and Viral Coinfection Contributes to Postinfectious Hydrocephalus
Elevated Clotting Factor V Found with Severe COVID-19
Blood-Based Test Accurately Identifies Viral Infection Before Symptoms Develop
RBC Distribution Width Associated with COVID-19 Mortality Risk
Performance Compared for Three Ebola Rapid Diagnostic Tests
Hypokalemia Is Associated With COVID-19 Severity
Rapid One-Step Assay for Field-Based Detection of Asymptomatic Malaria
Mannose-Binding Lectin Associated with Coagulopathy in Severe COVID-19
Ammonia Predicts Prognosis in Hepatitis B Virus‐Related Liver Failure
Gut Microbiome Data Helps Routine Screening of Cardiovascular Disease
Unconventional T Cells in COVID-19 Patients Predicts Disease Outcome
Proteomics-Based Diagnostic Test Predicts Risk of Dying from Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
Six Biomarkers Predict Severity of COVID-19
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Kit Detects Chagas Disease
Rapid CRISPR/Cas Assay for Diagnosis of Viral Fevers in Low-Tech Environments
Lymphocyte Count Correlated to Comorbid Diabetes and COVID-19
The LabMedica Microbiology channel provides the latest news in the fields of epidemiology, bacteriology, virology, and parasitology, all viewed from the unique perspective of Laboratory Medicine.










