Blood Platelet Score Detects Previously Unmeasured Risk of Heart Attack and Stroke
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 22 Aug 2024 |
Platelets, which are cell fragments circulating in the blood, play a critical role in clot formation to stop bleeding. However, in some individuals, platelets can become "hyperreactive," leading to excessive clotting and causing heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease, affecting millions worldwide. Until now, assessing platelet reactivity in patients has been challenging due to inconsistencies in the conventional test, platelet aggregometry, which often shows varied results across different laboratories. To overcome this issue, researchers have now accurately identified patients with hyperreactive platelets and conducted a study revealing significant genetic variations among those with hyperreactive platelets compared to others. Using bioinformatics, they developed a new metric called the Platelet Reactivity ExpresSion Score (PRESS), which effectively identifies those at risk of heart attacks and spots those who might not yet know their risk.
Researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine (New York, NY, USA) designed PRESS by switching to a low-dose epinephrine aggregometry technique, which is more indicative of hyperreactivity than previous high-dose tests. This method determined hyperreactive platelets based on their reaction to a minimal stimulus. To move beyond the confines of specialized laboratory techniques, the team developed PRESS as a standardizable, genetic-based score to predict cardiovascular risk. This tool was designed to be broadly applicable, avoiding the variability of direct platelet testing.
The researchers validated the clinical relevance of PRESS in a study tracking major adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing procedures to clear blocked arteries. Upon comparing PRESS to traditional aggregometry results and examining its diagnostic ability in various patient populations, they found that higher PRESS scores correlated with increased cardiovascular events. The findings, published online on August 20 in Nature Communications, found that those identified as having hyperreactive platelets faced a significantly higher risk of serious cardiovascular events shortly after surgery, providing a new tool for early identification and management of patients at risk due to platelet hyperreactivity.
"Our results demonstrate that our new platelet-centric scoring system can, for the first time and across populations, circumvent aggregometry to reliably predict platelet hyperreactivity and the related risk of cardiovascular events," said corresponding study author Jeffrey Berger, MD, director of the Center for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
"In current practice, anti-platelet therapy is not routinely recommended for the prevention of a first heart attack or stroke, but a platelet-based test would help to identify patients at highest risk, and those who would benefit most from anti-platelet therapy to prevent a cardiovascular event," added study author Tessa Barrett, PhD, assistant professor in the departments of Medicine and Pathology at NYU Langone. "Our score has the potential to further personalize cardiovascular disease risk prevention."
Related Links:
NYU Grossman School of Medicine
Latest Hematology News
- New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
- Automated Hemostasis System Helps Labs of All Sizes Optimize Workflow
- Fast and Easy Test Could Revolutionize Blood Transfusions
- High-Sensitivity Blood Test Improves Assessment of Clotting Risk in Heart Disease Patients
- AI Algorithm Effectively Distinguishes Alpha Thalassemia Subtypes
- MRD Tests Could Predict Survival in Leukemia Patients
- Platelet Activity Blood Test in Middle Age Could Identify Early Alzheimer’s Risk
- Microvesicles Measurement Could Detect Vascular Injury in Sickle Cell Disease Patients
- ADLM’s New Coagulation Testing Guidance to Improve Care for Patients on Blood Thinners
- Viscoelastic Testing Could Improve Treatment of Maternal Hemorrhage
- Pioneering Model Measures Radiation Exposure in Blood for Precise Cancer Treatments
- Platelets Could Improve Early and Minimally Invasive Detection of Cancer
- Portable and Disposable Device Obtains Platelet-Rich Plasma Without Complex Equipment
- Disposable Cartridge-Based Test Delivers Rapid and Accurate CBC Results
- First Point-of-Care Heparin Monitoring Test Provides Results in Under 15 Minutes

- New Scoring System Predicts Risk of Developing Cancer from Common Blood Disorder
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read more
Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects more than 1 in 7 Americans and is strongly associated with cardiovascular complications, which account for more than half of deaths among people with CKD.... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Diagnostic Device Predicts Treatment Response for Brain Tumors Via Blood Test
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest forms of brain cancer, largely because doctors have no reliable way to determine whether treatments are working in real time. Assessing therapeutic response currently... Read more
Blood Test Detects Early-Stage Cancers by Measuring Epigenetic Instability
Early-stage cancers are notoriously difficult to detect because molecular changes are subtle and often missed by existing screening tools. Many liquid biopsies rely on measuring absolute DNA methylation... Read more
“Lab-On-A-Disc” Device Paves Way for More Automated Liquid Biopsies
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny particles released by cells into the bloodstream that carry molecular information about a cell’s condition, including whether it is cancerous. However, EVs are highly... Read more
Blood Test Identifies Inflammatory Breast Cancer Patients at Increased Risk of Brain Metastasis
Brain metastasis is a frequent and devastating complication in patients with inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive subtype with limited treatment options. Despite its high incidence, the biological... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read moreAI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
Infections caused by the pathogenic yeast Candida auris pose a significant threat to hospitalized patients, particularly those with weakened immune systems or those who have invasive medical devices.... Read morePathology
view channel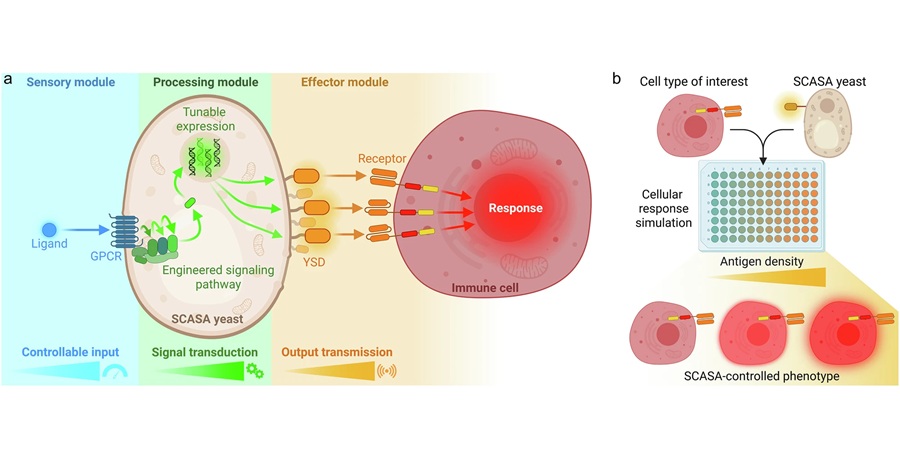
Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
Developing new cancer immunotherapies is a slow, costly, and high-risk process, particularly for CAR T cell treatments that must precisely recognize cancer-specific antigens. Small differences in tumor... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Autism spectrum disorder is treatable, and extensive research shows that early intervention can significantly improve cognitive, social, and behavioral outcomes. Yet in the United States, the average age... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreAptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
Rapid and reliable virus detection is essential for controlling outbreaks, from seasonal influenza to global pandemics such as COVID-19. Conventional diagnostic methods, including cell culture, antigen... Read more
AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
Pre-eclampsia and anemia are major contributors to maternal and child mortality worldwide, together accounting for more than half a million deaths each year and leaving millions with long-term health complications.... Read moreIndustry
view channelNew Collaboration Brings Automated Mass Spectrometry to Routine Laboratory Testing
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that identifies and quantifies molecules based on their mass and electrical charge. Its high selectivity, sensitivity, and accuracy make it indispensable... Read more
AI-Powered Cervical Cancer Test Set for Major Rollout in Latin America
Noul Co., a Korean company specializing in AI-based blood and cancer diagnostics, announced it will supply its intelligence (AI)-based miLab CER cervical cancer diagnostic solution to Mexico under a multi‑year... Read more
Diasorin and Fisher Scientific Enter into US Distribution Agreement for Molecular POC Platform
Diasorin (Saluggia, Italy) has entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Fisher Scientific, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), for the LIAISON NES molecular point-of-care... Read more