Smart Fibers Could Allow T-Shirts to Analyze Electrolytes and Metabolites in Sweat
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 23 Jan 2023 |
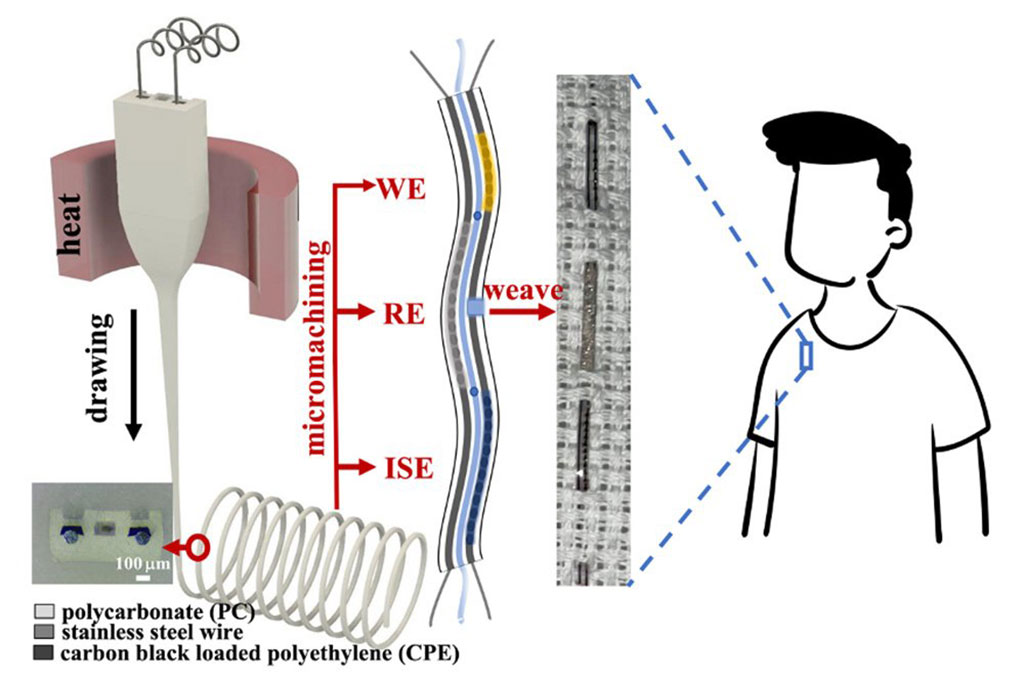
Fibers and fabrics have become an integral part of our daily lives, although much remains unchanged for them despite centuries of human progression. Nevertheless, recent advancements in the multi-material fiber drawing process have led to the development of new multifunctional, fiber-based smart fabrics. Smart fabrics make it possible to seamlessly integrate electronics, optics, biosensors, and mechanics into a thin strand of fiber that is intrinsically flexible and as thin as the human hair. Such fabrics can then be used for monitoring the vital physiological signals related to human mental and physical health.
Now, a team of researchers at Tohoku University (Sendai, Japan) has developed a microelectronic fiber with microscopic parameters that is capable of analyzing electrolytes and metabolites in sweat. The micrometer scale of the microelectronic fiber enables it to be woven into clothes for healthcare applications. The researchers developed the microelectronic fiber by leveraging the versatile thermal drawing process, in which heat is applied to draw out micro-structured fiber from its macroscopic preform. The researchers also patterned on two sensing electrodes for sodium and uric acid on the longitudinal surface of the fiber.
Mainstream photolithography and printing technology have made wearable electronics possible, although this generally requires the attachment of fairly rigid electronic patches to the existing fabrics or directly on the skin, resulting in just a small area of the body being covered. The new microelectronic fiber could pave the way for fiber-based smart clothes that offer more versatility in terms of functions, larger sensing areas, and greater comfort. The new smart fabric could revolutionize the textile and healthcare industries, according to the researchers, benefiting the overall society.
"Our breakthrough is the first successful attempt at using thermally drawn fiber in wearable bioelectronics for monitoring biochemical signatures," said Dr. Yuanyuan Guo, assistant professor at Tohoku University's Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences, who led the research team.
Related Links:
Tohoku University
Latest Clinical Chem. News
- Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
- New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
- Extracellular Vesicles Linked to Heart Failure Risk in CKD Patients
- Study Compares Analytical Performance of Quantitative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Assays
- Blood Test Could Predict and Identify Early Relapses in Myeloma Patients
- Compact Raman Imaging System Detects Subtle Tumor Signals
- Noninvasive Blood-Glucose Monitoring to Replace Finger Pricks for Diabetics
- POC Breath Diagnostic System to Detect Pneumonia-Causing Pathogens
- Online Tool Detects Drug Exposure Directly from Patient Samples
- Chemical Imaging Probe Could Track and Treat Prostate Cancer
- Mismatch Between Two Common Kidney Function Tests Indicates Serious Health Problems
- VOCs Show Promise for Early Multi-Cancer Detection
- Portable Raman Spectroscopy Offers Cost-Effective Kidney Disease Diagnosis at POC
- Gold Nanoparticles to Improve Accuracy of Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
- Simultaneous Cell Isolation Technology Improves Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Simple Non-Invasive Hair-Based Test Could Speed ALS Diagnosis
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Rapid Blood Testing Method Aids Safer Decision-Making in Drug-Related Emergencies
Acute recreational drug toxicity is a frequent reason for emergency department visits, yet clinicians rarely have access to confirmatory toxicology results in real time. Instead, treatment decisions are... Read more
New PSA-Based Prognostic Model Improves Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer death among American men, and about one in eight will be diagnosed in their lifetime. Screening relies on blood levels of prostate-specific antigen... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Group A Strep Molecular Test Delivers Definitive Results at POC in 15 Minutes
Strep throat is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It is a leading bacterial cause of acute pharyngitis, particularly in children and adolescents, and one of the most common reasons... Read more
Rapid Molecular Test Identifies Sepsis Patients Most Likely to Have Positive Blood Cultures
Sepsis is caused by a patient’s overwhelming immune response to an infection. If undetected or left untreated, sepsis leads to tissue damage, organ failure, permanent disability, and often death.... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channelBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance has accelerated into a global health crisis, with projections estimating more than 10 million deaths per year by 2050 as drug-resistant “superbugs” continue to spread.... Read more
Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease affects approximately 6.7 million people in the United States and nearly 50 million worldwide, yet early cognitive decline remains difficult to characterize. Increasing evidence suggests... Read morePathology
view channel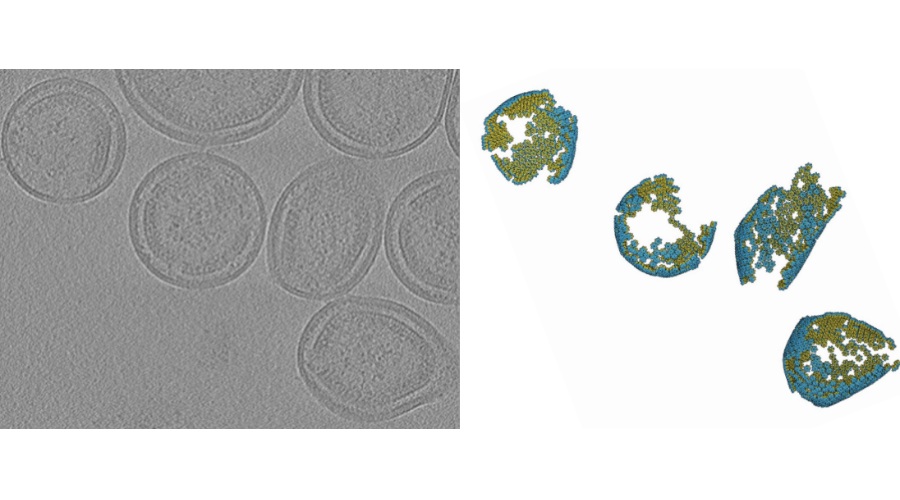
High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) is a retrovirus that causes adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma, a serious blood cancer with no approved treatment. Although related to HIV, HTLV remains less understood at... Read more
AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
Microscopes have long been central to diagnosing disease by allowing doctors to examine stained tissue samples. However, modern medical research now generates vast amounts of additional data, including... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more