Intratumor Heterogeneity Analyzed in Neuroblastoma
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 22 Dec 2021 |
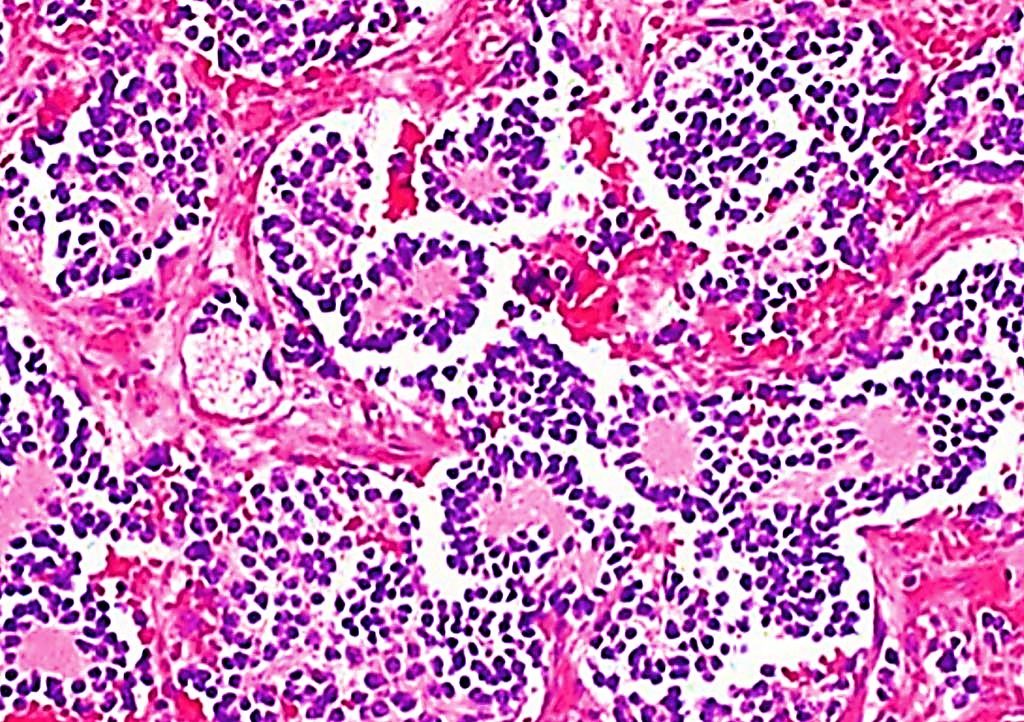
Image: Histopathology of a typical neuroblastoma with rosette formation (Photo courtesy of Dr. Mark Applebaum, MD)
Neuroblastoma is the most common solid pediatric tumour, accounting for 15% of cancer-related deaths in early childhood and especially for patients directly diagnosed with high-risk neuroblastoma have a poor prognosis.
Tumors are heterogeneous, which means that different parts of the same tumor can be genetically distinct. This phenomenon, known as intratumor heterogeneity, is steadily gaining in significance within the field of oncology. Cellular and molecular differences within the same tumor play an important role in many different cancers due to their implications for diagnosis and the use of targeted therapies.
A large team of pediatric oncologists at the Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin (Berlin, Germany) and their colleagues collected tumor samples from 10 patients who were enrolled in a study between 2014 and 2018. Samples were collected by open surgical biopsy either at diagnosis, at tumour resection after 4–6 cycles of chemotherapy or at diagnosis of relapse. Fresh samples were immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. Portions of tumour material were formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) in parallel for diagnostics and preservation in the pathology unit. The team analyzed a total of 140 neuroblastoma samples.
Peripheral blood collected from each patient was used as a matched germline control for tumor samples. DNA was prepared using the Qiagen DNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Venlo, the Netherlands). The SureSelect Human All Exon V6 kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to prepare libraries enriched with exonic sequences. The libraries were further prepared for sequencing using the Illumina TruSeq Exome Kit and sequenced on Illumina HiSeq 2500 and Illumina NextSeq sequencers (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). A list of genes potentially involved in neuroblastoma development was compiled by combining lists of potential cancer driver genes from several sources.
The investigators focused their analysis on the neuroblastoma-associated genes ALK, MYCN and FGFR1, which play an important role in both clinical course and treatment. According to their results, changes in the ALK and MYCN genes were not present continuously throughout the course of the disease, nor were they found in all tumor cells. Changes in the ALK and FGFR1 genes can offer useful treatment targets, particularly in relapsed patients. They found that, in some patients, ALK mutations which were present at the time of diagnosis had disappeared by the time the tumor was surgically removed. Changes in the FGFR1 gene were only found in distinct tumor regions. The scientists were also able to identify an instability in the number of gene copies present in neuroblastoma cells.
Angelika Eggert, MD, a Professor of Pediatric Oncology and a senior author of the study, said, “We are now in a better position to understand how neuroblastoma cells behave. This knowledge is essential in relation to patients who suffer a recurrence of their disease because their treatment often requires the use of personalized and targeted therapies. When a tumor presents as genetically heterogeneous, targeted molecular therapy may well capture a majority of the abnormal tissue but, crucially, will not capture all of the affected cells. The cancer will then be able to regrow from those remaining cells.”
The authors conclude that their in-depth analysis of neuroblastoma intratumor heterogeneity reveals that extensive genetic heterogeneity and subclonal diversification evolves under therapy and may have important implications for the clinical interpretation of molecular diagnostic results and for the selection of appropriate second-line treatment approaches. The study was published on November 23, 2021 in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Qiagen
Agilent Technologies
Illumina
Tumors are heterogeneous, which means that different parts of the same tumor can be genetically distinct. This phenomenon, known as intratumor heterogeneity, is steadily gaining in significance within the field of oncology. Cellular and molecular differences within the same tumor play an important role in many different cancers due to their implications for diagnosis and the use of targeted therapies.
A large team of pediatric oncologists at the Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin (Berlin, Germany) and their colleagues collected tumor samples from 10 patients who were enrolled in a study between 2014 and 2018. Samples were collected by open surgical biopsy either at diagnosis, at tumour resection after 4–6 cycles of chemotherapy or at diagnosis of relapse. Fresh samples were immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C. Portions of tumour material were formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) in parallel for diagnostics and preservation in the pathology unit. The team analyzed a total of 140 neuroblastoma samples.
Peripheral blood collected from each patient was used as a matched germline control for tumor samples. DNA was prepared using the Qiagen DNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Venlo, the Netherlands). The SureSelect Human All Exon V6 kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to prepare libraries enriched with exonic sequences. The libraries were further prepared for sequencing using the Illumina TruSeq Exome Kit and sequenced on Illumina HiSeq 2500 and Illumina NextSeq sequencers (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). A list of genes potentially involved in neuroblastoma development was compiled by combining lists of potential cancer driver genes from several sources.
The investigators focused their analysis on the neuroblastoma-associated genes ALK, MYCN and FGFR1, which play an important role in both clinical course and treatment. According to their results, changes in the ALK and MYCN genes were not present continuously throughout the course of the disease, nor were they found in all tumor cells. Changes in the ALK and FGFR1 genes can offer useful treatment targets, particularly in relapsed patients. They found that, in some patients, ALK mutations which were present at the time of diagnosis had disappeared by the time the tumor was surgically removed. Changes in the FGFR1 gene were only found in distinct tumor regions. The scientists were also able to identify an instability in the number of gene copies present in neuroblastoma cells.
Angelika Eggert, MD, a Professor of Pediatric Oncology and a senior author of the study, said, “We are now in a better position to understand how neuroblastoma cells behave. This knowledge is essential in relation to patients who suffer a recurrence of their disease because their treatment often requires the use of personalized and targeted therapies. When a tumor presents as genetically heterogeneous, targeted molecular therapy may well capture a majority of the abnormal tissue but, crucially, will not capture all of the affected cells. The cancer will then be able to regrow from those remaining cells.”
The authors conclude that their in-depth analysis of neuroblastoma intratumor heterogeneity reveals that extensive genetic heterogeneity and subclonal diversification evolves under therapy and may have important implications for the clinical interpretation of molecular diagnostic results and for the selection of appropriate second-line treatment approaches. The study was published on November 23, 2021 in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Qiagen
Agilent Technologies
Illumina
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- DNA Aptamers Offer New Tool for Easy Alzheimer's Blood Test
- AI-Based Liquid Biopsy Detects Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis and Chronic Disease Signals
- Blood Test Could Detect Pre-Eclampsia Before Symptoms Appear
- Jumping "DNA Parasites” Linked to Early Tumor Development
- AI-Powered Blood Test Flags Relapse Risk Earlier After Transplant
- AI-Powered Blood Test Detects Early Pancreatic Cancer with More Than 90% Accuracy
- World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
- Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
- Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
- Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Study Highlights Accuracy Gaps in Consumer Gut Microbiome Kits
Direct-to-consumer gut microbiome kits promise personalized insights by profiling fecal bacteria and generating health readouts, but their analytical accuracy remains uncertain. A new study shows that... Read more
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















