Elevated Levels of Two Protein Biomarkers Indicate Potential for Development of Pre-Eclampsia
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 16 Jul 2020 |
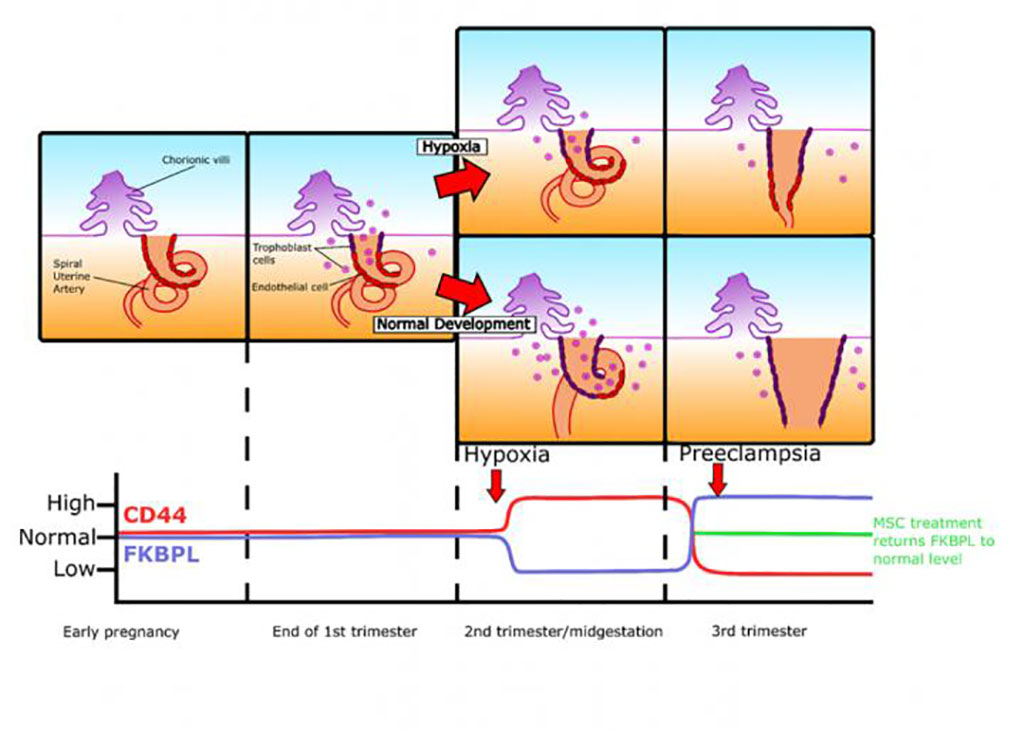
Image: Summary of changes FKBPL and CD44 changes throughout gestation in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia (Photo courtesy of Oxford Press)
A pair of novel protein biomarkers has been identified in the blood of asymptomatic pregnant women that can be used to predict the potential onset of pre-eclampsia.
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of poor outcomes for both the mother and the baby. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia. Ten to 15% of maternal mortality is associated with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
Development of effective prevention and treatment strategies for pre-eclampsia has been limited by the lack of accurate methods for identification of at-risk pregnancies.
In an effort to correct this lack, investigators at the University of Technology Sydney (Australia) evaluated the diagnostic and therapeutic potential for pre-eclampsia of the angiogenesis protein markers, FKBPL-CD44. FKBPL (FKBP prolyl isomerase like) has similarity to the immunophilin protein family, which play a role in immunoregulation and basic cellular processes involving protein folding and trafficking. CD44 is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion, and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis.
For the current study, the investigators analyzed 57 samples that were pre-diagnosis (15 and 20 weeks’ gestation) and 18 that were post-diagnosis (14 for plasma; four for placenta) of pre-eclampsia for determination of FKBPL and CD44 concentrations, compared to healthy controls.
Results revealed that the CD44/FKBPL ratio was reduced in placenta and plasma following clinical diagnosis of pre-eclampsia. At 20 weeks’ gestation, a high plasma CD44/FKBPL ratio was independently associated with the 2.5-fold increased risk of pre-eclampsia.
"There are two main types of pre-eclampsia: early-onset pre-eclampsia diagnosed before 34 weeks of a pregnancy and late-onset pre-eclampsia diagnosed from 34 weeks onwards," said senior author Dr. Lana McClements, lecturer in biotechnology at the University of Technology Sydney. "The vast majority of the current screening and monitoring strategies are focused on early-onset pre-eclampsia, which comprises only 10-15% of all pre-eclampsia cases, whereas late pre-eclampsia has been largely neglected."
"The biomarkers allow the prediction of irregular placenta or maternal vascular function, which are key underlying causes of pre-eclampsia," said Dr. McClements. "This could lead to the early diagnosis and prevention of severe pre-eclampsia and associated complications including death, therefore also giving insight into disease mechanisms and possible treatment targets."
The study was published in the July 3, 2020, online edition of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Related Links:
University of Technology Sydney
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of poor outcomes for both the mother and the baby. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia. Ten to 15% of maternal mortality is associated with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
Development of effective prevention and treatment strategies for pre-eclampsia has been limited by the lack of accurate methods for identification of at-risk pregnancies.
In an effort to correct this lack, investigators at the University of Technology Sydney (Australia) evaluated the diagnostic and therapeutic potential for pre-eclampsia of the angiogenesis protein markers, FKBPL-CD44. FKBPL (FKBP prolyl isomerase like) has similarity to the immunophilin protein family, which play a role in immunoregulation and basic cellular processes involving protein folding and trafficking. CD44 is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion, and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis.
For the current study, the investigators analyzed 57 samples that were pre-diagnosis (15 and 20 weeks’ gestation) and 18 that were post-diagnosis (14 for plasma; four for placenta) of pre-eclampsia for determination of FKBPL and CD44 concentrations, compared to healthy controls.
Results revealed that the CD44/FKBPL ratio was reduced in placenta and plasma following clinical diagnosis of pre-eclampsia. At 20 weeks’ gestation, a high plasma CD44/FKBPL ratio was independently associated with the 2.5-fold increased risk of pre-eclampsia.
"There are two main types of pre-eclampsia: early-onset pre-eclampsia diagnosed before 34 weeks of a pregnancy and late-onset pre-eclampsia diagnosed from 34 weeks onwards," said senior author Dr. Lana McClements, lecturer in biotechnology at the University of Technology Sydney. "The vast majority of the current screening and monitoring strategies are focused on early-onset pre-eclampsia, which comprises only 10-15% of all pre-eclampsia cases, whereas late pre-eclampsia has been largely neglected."
"The biomarkers allow the prediction of irregular placenta or maternal vascular function, which are key underlying causes of pre-eclampsia," said Dr. McClements. "This could lead to the early diagnosis and prevention of severe pre-eclampsia and associated complications including death, therefore also giving insight into disease mechanisms and possible treatment targets."
The study was published in the July 3, 2020, online edition of the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Related Links:
University of Technology Sydney
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- AI-Powered Blood Test Flags Relapse Risk Earlier After Transplant
- AI-Powered Blood Test Detects Early Pancreatic Cancer with More Than 90% Accuracy
- World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
- Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
- Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
- Blood Test Could Spot Common Post-Surgery Condition Early
- New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
- New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
- New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Cell-Free DNA Predicts Bloodstream Infections in Children with Leukemia
- Study Uses Blood Samples to Identify Diseases Years Before They Start
- MicroRNA-Based Method Predicts CKD and Cardiovascular Risk
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more





















