Mutation Found Determines Nature of Host Response to MRSA Infection
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 22 Sep 2019 |
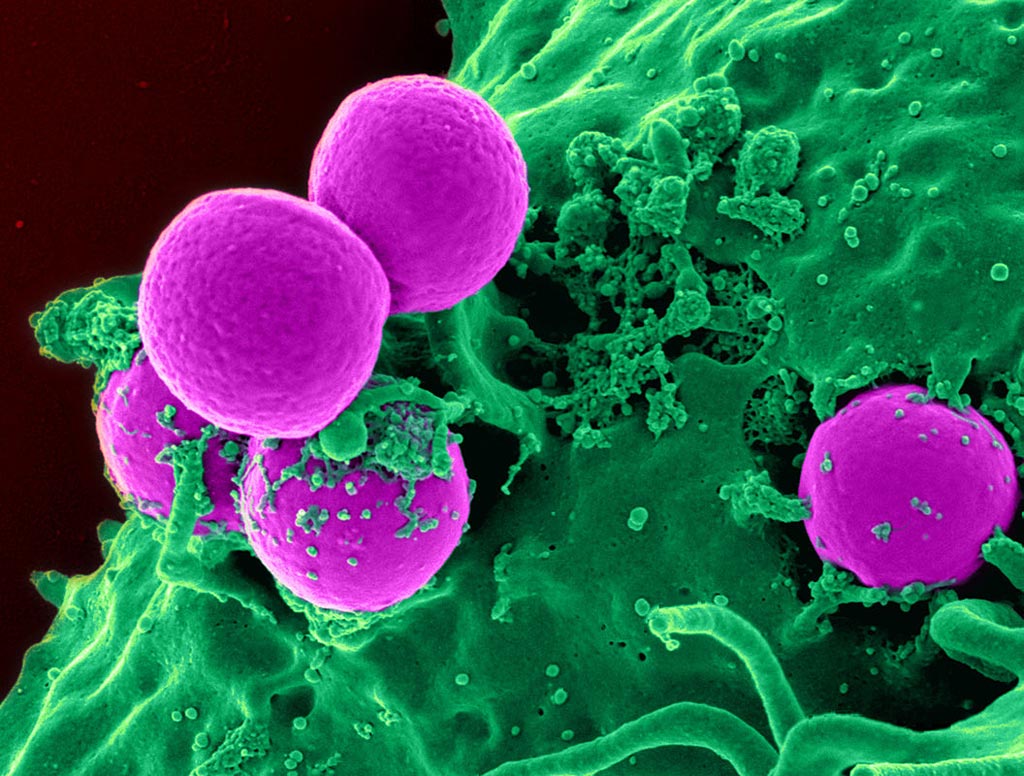
Image: A scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of a human neutrophil ingesting MRSA (Photo courtesy of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases).
A recent paper described the genetic factors that determine why some individuals develop chronic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections while others develop infections that resolve relatively quickly.
The severity and duration of MRSA infection varies widely between individuals. Host factors predisposing to persistent MRSA infection are poorly understood, although genetic association studies are beginning to identify potentially influential variants.
Investigators at Duke University (Durham, NC, USA) searched for such host factors by analyzing two sets of patients who had been closely matched by age, sex, health conditions, and other risk factors for MRSA bloodstream infections. Sixty-eight patients were included in the study; half with a persistent MRSA infection and half who had been able to clear the infection from their bloodstream. Whole-exome sequencing was used to pinpoint genomic differences between the two sets of patients.
Results revealed that a mutation located in the DNA of the DNMT3A region of chromosome 2p was expressed in about 62% of the patients who cleared their MRSA infection, while it was expressed in only 9% in those who had persistent infections.
In a further series of experiments, the investigators demonstrated that DNMT3A variants could alter host response to infection through increased methylation of key regulatory genes, which resulted in reduced interleukin-10 production and in turn, allowed for a more protective immune response that cleared infection.
"The increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistant staph infections has created an urgent need to better understand who is most susceptible to these difficult-to-treat S. aureus infections and why," said senior author Dr. Vance Fowler, professor of medicine, molecular genetics, and microbiology at Duke University. "Our study identifies a particular DNMT3A mutation that contributes to an increased ability to resolve MRSA infections. The mechanism for this appears to be increased methylation of gene regulatory regions, and reduced levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10."
The MRSA paper was published in the September 16, 2019, online edition of the journal Proceedings of the [U.S.] National Academy of Sciences.
Related Links:
Duke University
The severity and duration of MRSA infection varies widely between individuals. Host factors predisposing to persistent MRSA infection are poorly understood, although genetic association studies are beginning to identify potentially influential variants.
Investigators at Duke University (Durham, NC, USA) searched for such host factors by analyzing two sets of patients who had been closely matched by age, sex, health conditions, and other risk factors for MRSA bloodstream infections. Sixty-eight patients were included in the study; half with a persistent MRSA infection and half who had been able to clear the infection from their bloodstream. Whole-exome sequencing was used to pinpoint genomic differences between the two sets of patients.
Results revealed that a mutation located in the DNA of the DNMT3A region of chromosome 2p was expressed in about 62% of the patients who cleared their MRSA infection, while it was expressed in only 9% in those who had persistent infections.
In a further series of experiments, the investigators demonstrated that DNMT3A variants could alter host response to infection through increased methylation of key regulatory genes, which resulted in reduced interleukin-10 production and in turn, allowed for a more protective immune response that cleared infection.
"The increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistant staph infections has created an urgent need to better understand who is most susceptible to these difficult-to-treat S. aureus infections and why," said senior author Dr. Vance Fowler, professor of medicine, molecular genetics, and microbiology at Duke University. "Our study identifies a particular DNMT3A mutation that contributes to an increased ability to resolve MRSA infections. The mechanism for this appears to be increased methylation of gene regulatory regions, and reduced levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10."
The MRSA paper was published in the September 16, 2019, online edition of the journal Proceedings of the [U.S.] National Academy of Sciences.
Related Links:
Duke University
Latest Microbiology News
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
- Rapid POC Tuberculosis Test Provides Results Within 15 Minutes
- Rapid Assay Identifies Bloodstream Infection Pathogens Directly from Patient Samples
- Blood-Based Molecular Signatures to Enable Rapid EPTB Diagnosis
- 15-Minute Blood Test Diagnoses Life-Threatening Infections in Children
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a rare but aggressive blood cancer in which relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplant remains a major clinical challenge, particularly for patients with NPM1-mutated disease.... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
Gallbladder cancer is one of the deadliest gastrointestinal cancers because it is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. Early symptoms are minimal, and current screening... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















