Immunoassay Developed for Lassa Fever Virus
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 12 Apr 2018 |
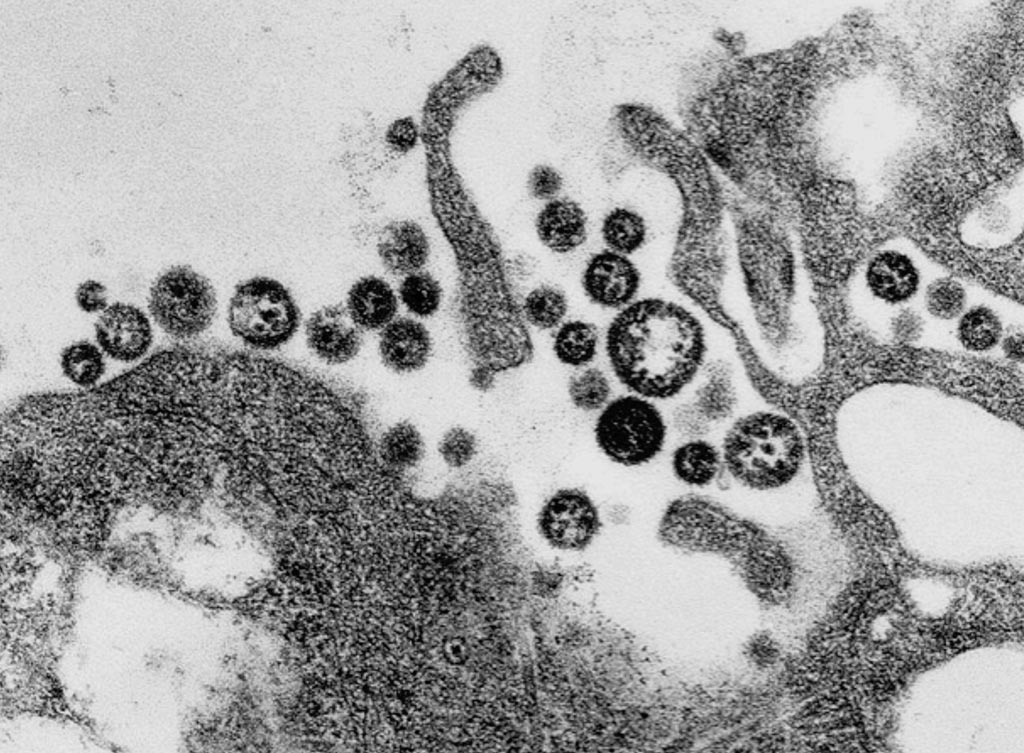
Image: A transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of a number of Lassa virus virions adjacent to some cell debris (Photo courtesy of C. S. Goldsmith/CDC).
Lassa fever is a type of viral hemorrhagic fever and is endemic in several West African countries. However, only few hospitals and laboratories in the region have the capacity to conduct molecular or serological Lassa fever diagnostics.
The classical method for detection of Lassa virus-specific antibodies is the immunofluorescence assay (IFA) using virus-infected cells as antigen. However, IFA requires laboratories of biosafety level 4 for assay production and an experienced investigator to interpret the fluorescence signals.
Scientists at the Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine (Hamburg, Germany) and their West African colleagues chose a total of 576 sera from the diagnostic service of the Institute of Lassa Fever Research and Control. Of those, 270 sera tested positive by Lassa virus real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) establishing the diagnosis of Lassa fever; 101 sera tested negative by Lassa virus RT-PCR; and 23 had no RT-PCR result. From 47 RT-PCR confirmed Lassa fever patients, 182 (1–9 per patient) follow-up sera were available. From Lassa fever non-endemic areas, 199 samples collected between 2008 and 2011 from patients with suspected viral hemorrhagic fever or viral hepatitis in Ghana, all of whom tested negative by Lassa virus RT-PCR. Another 105 diagnostic leftover samples from German patients with various unknown diseases were included in the study.
The developed immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IgM ELISA) was based on capturing IgM antibodies using anti-IgM, and the IgG ELISA is based on capturing IgG antibody–antigen complexes using rheumatoid factor or Fc gamma receptor CD32a. Analytical and clinical evaluation was performed with 880 sera from Lassa fever endemic (Nigeria) and non-endemic (Ghana and Germany) areas. The team used the IFA as the reference method, and observed 91.5% to 94.3% analytical accuracy of the ELISAs in detecting Lassa virus-specific antibodies. Evaluation of the ELISAs for diagnosis of Lassa fever on admission to hospital in an endemic area revealed a clinical sensitivity for the stand-alone IgM ELISA of 31% and for combined IgM/IgG detection of 26% compared to RT-PCR. In non-Lassa fever patients from non-endemic areas, the specificity of IgM and IgG ELISA was estimated at 96% and 100%, respectively.
The authors concluded that the ELISAs are not equivalent to RT-PCR for early diagnosis of Lassa fever; however, they are of value in diagnosing patients at later stage. The IgG ELISA may be useful for epidemiological studies and clinical trials due its high specificity, and the higher throughput rate and easier operation compared to IFA. The established assays do not require expensive equipment; ELISA readers are available in many diagnostic laboratories in West Africa. The study was published on March 29, 2018, in the journal PloS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine
The classical method for detection of Lassa virus-specific antibodies is the immunofluorescence assay (IFA) using virus-infected cells as antigen. However, IFA requires laboratories of biosafety level 4 for assay production and an experienced investigator to interpret the fluorescence signals.
Scientists at the Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine (Hamburg, Germany) and their West African colleagues chose a total of 576 sera from the diagnostic service of the Institute of Lassa Fever Research and Control. Of those, 270 sera tested positive by Lassa virus real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) establishing the diagnosis of Lassa fever; 101 sera tested negative by Lassa virus RT-PCR; and 23 had no RT-PCR result. From 47 RT-PCR confirmed Lassa fever patients, 182 (1–9 per patient) follow-up sera were available. From Lassa fever non-endemic areas, 199 samples collected between 2008 and 2011 from patients with suspected viral hemorrhagic fever or viral hepatitis in Ghana, all of whom tested negative by Lassa virus RT-PCR. Another 105 diagnostic leftover samples from German patients with various unknown diseases were included in the study.
The developed immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IgM ELISA) was based on capturing IgM antibodies using anti-IgM, and the IgG ELISA is based on capturing IgG antibody–antigen complexes using rheumatoid factor or Fc gamma receptor CD32a. Analytical and clinical evaluation was performed with 880 sera from Lassa fever endemic (Nigeria) and non-endemic (Ghana and Germany) areas. The team used the IFA as the reference method, and observed 91.5% to 94.3% analytical accuracy of the ELISAs in detecting Lassa virus-specific antibodies. Evaluation of the ELISAs for diagnosis of Lassa fever on admission to hospital in an endemic area revealed a clinical sensitivity for the stand-alone IgM ELISA of 31% and for combined IgM/IgG detection of 26% compared to RT-PCR. In non-Lassa fever patients from non-endemic areas, the specificity of IgM and IgG ELISA was estimated at 96% and 100%, respectively.
The authors concluded that the ELISAs are not equivalent to RT-PCR for early diagnosis of Lassa fever; however, they are of value in diagnosing patients at later stage. The IgG ELISA may be useful for epidemiological studies and clinical trials due its high specificity, and the higher throughput rate and easier operation compared to IFA. The established assays do not require expensive equipment; ELISA readers are available in many diagnostic laboratories in West Africa. The study was published on March 29, 2018, in the journal PloS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine
Latest Microbiology News
- WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
- New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
- Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
- Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
- Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
- Three-Test Panel Launched for Detection of Liver Fluke Infections
- Rapid Test Promises Faster Answers for Drug-Resistant Infections
- CRISPR-Based Technology Neutralizes Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria
- Comprehensive Review Identifies Gut Microbiome Signatures Associated With Alzheimer’s Disease
- AI-Powered Platform Enables Rapid Detection of Drug-Resistant C. Auris Pathogens
- New Test Measures How Effectively Antibiotics Kill Bacteria
- New Antimicrobial Stewardship Standards for TB Care to Optimize Diagnostics
- New UTI Diagnosis Method Delivers Antibiotic Resistance Results 24 Hours Earlier
- Breakthroughs in Microbial Analysis to Enhance Disease Prediction
- Blood-Based Diagnostic Method Could Identify Pediatric LRTIs
- Rapid Diagnostic Test Matches Gold Standard for Sepsis Detection
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
AI-Powered Blood Test Detects Early Pancreatic Cancer with More Than 90% Accuracy
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal cancers, often referred to as the “King of Cancers” because symptoms usually appear only at advanced stages. As a result, most patients are diagnosed late, and... Read more
AI-Powered Blood Test Flags Relapse Risk Earlier After Transplant
Relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant is a major cause of mortality in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), and standard monitoring can miss early warning signals.... Read more
World’s First Portable POC Test Simultaneously Detects Four Common STIs in One Hour
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with similar symptoms, making accurate diagnosis challenging without laboratory testing. Delays in identifying the exact infection can lead to inappropriate... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more










 (3) (1).png)











