Personal Lab Offers Rapid Detection of Food Allergens
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 06 Nov 2017 |
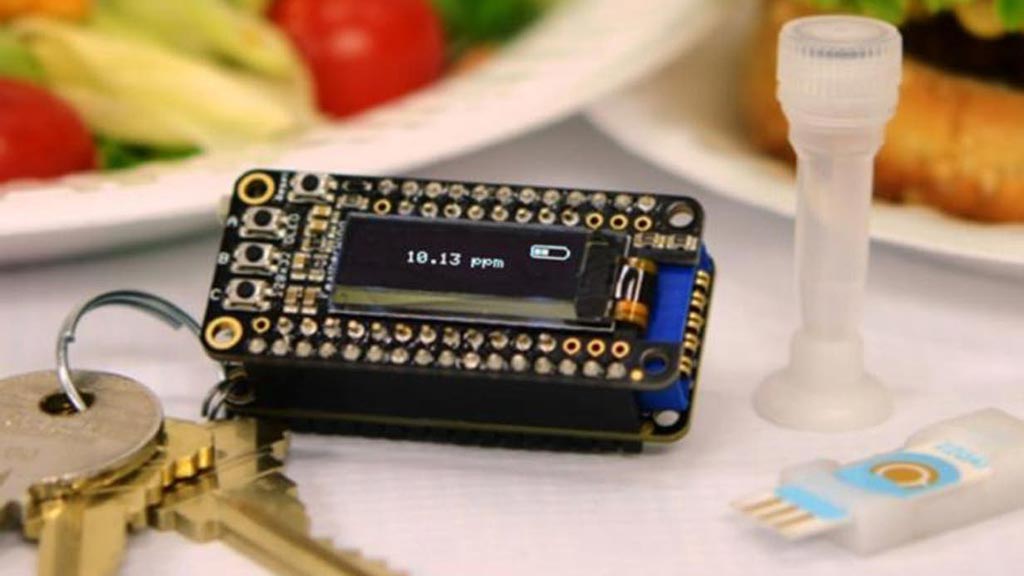
Image: The iEAT system for onsite antigen detection consists of a pocket-sized detector, an electrode chip, and a disposable kit for allergen extraction. The detector connects with a smartphone for system control and data upload to a cloud server (Photo courtesy of Lin, et al. ACS Nano, August 2017).
Researchers have developed a small, low cost device for individual use that can accurately detect food allergens in less than ten minutes.
Adverse food reactions, including food allergies, food sensitivities, and autoimmune reaction (e.g., celiac disease) affect 5-15% of the population of the USA and remain a considerable public health problem requiring stringent food avoidance and epinephrine availability for emergency events. Avoiding problematic foods is difficult in practical terms, given current reliance on prepared foods and out-of-home meals.
In response to the food allergy problem, investigators at Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA) developed a portable, point-of-use detection technology, that they called "integrated exogenous antigen testing" (iEAT).
The iEAT device consists of three components: (1) a small plastic test tube, (2) a small electronic detection module, and (3) the electronic keychain reader. To perform the test, the user dissolves a small sample of the food in the plastic test tube and then adds magnetic beads that capture the food allergen of interest. A bit of this mixture is loaded onto electrode strips attached to a small module that is then inserted into the electronic keychain reader. The keychain reader has a small display that indicates whether the allergen is present, and if so, in what concentration.
The prototype iEAT system was optimized to detect five major food antigens in peanuts, hazelnuts, wheat, milk, and eggs. Antigen extraction and detection with iEAT required less than 10 minutes and achieved high-detection sensitivities (e.g., 0.1 milligram per kilogram for gluten, 200 times lower than regulatory limits of 20 milligram per kilogram).
The investigators also developed a dedicated cell phone application, which allows the user to compile and store the data collected by testing different foods for various allergens at different restaurants or in packaged foods. The application is set up to share this information online with both time and location stamps indicating when, where, and in what food or dish an allergen reading was taken.
“High accuracy built into a compact system was the key goals of the project,” said contributing author Dr. Ralph Weissleder, professor of radiology and systems biology at Harvard Medical School. “Users can be confident that even if they are sensitive to very low levels, iEAT will be able to give them exact concentrations. Armed with accurate concentration levels they will not have to completely avoid potentially problematic foods, but will know whether an allergen is at a dangerous level for them or a concentration that is safe for them to eat.”
The iEAT device was described in the August 2017 issue of the journal ACS Nano.
Related Links:
Harvard Medical School
Adverse food reactions, including food allergies, food sensitivities, and autoimmune reaction (e.g., celiac disease) affect 5-15% of the population of the USA and remain a considerable public health problem requiring stringent food avoidance and epinephrine availability for emergency events. Avoiding problematic foods is difficult in practical terms, given current reliance on prepared foods and out-of-home meals.
In response to the food allergy problem, investigators at Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA) developed a portable, point-of-use detection technology, that they called "integrated exogenous antigen testing" (iEAT).
The iEAT device consists of three components: (1) a small plastic test tube, (2) a small electronic detection module, and (3) the electronic keychain reader. To perform the test, the user dissolves a small sample of the food in the plastic test tube and then adds magnetic beads that capture the food allergen of interest. A bit of this mixture is loaded onto electrode strips attached to a small module that is then inserted into the electronic keychain reader. The keychain reader has a small display that indicates whether the allergen is present, and if so, in what concentration.
The prototype iEAT system was optimized to detect five major food antigens in peanuts, hazelnuts, wheat, milk, and eggs. Antigen extraction and detection with iEAT required less than 10 minutes and achieved high-detection sensitivities (e.g., 0.1 milligram per kilogram for gluten, 200 times lower than regulatory limits of 20 milligram per kilogram).
The investigators also developed a dedicated cell phone application, which allows the user to compile and store the data collected by testing different foods for various allergens at different restaurants or in packaged foods. The application is set up to share this information online with both time and location stamps indicating when, where, and in what food or dish an allergen reading was taken.
“High accuracy built into a compact system was the key goals of the project,” said contributing author Dr. Ralph Weissleder, professor of radiology and systems biology at Harvard Medical School. “Users can be confident that even if they are sensitive to very low levels, iEAT will be able to give them exact concentrations. Armed with accurate concentration levels they will not have to completely avoid potentially problematic foods, but will know whether an allergen is at a dangerous level for them or a concentration that is safe for them to eat.”
The iEAT device was described in the August 2017 issue of the journal ACS Nano.
Related Links:
Harvard Medical School
Latest Technology News
- AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Blood Test Tracks Transplant Health Using Donor DNA
Organ transplantation offers life-saving treatment for patients with end-stage disease, but complications such as rejection remain a constant risk. Monitoring transplanted organs typically relies on invasive... Read more
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Study Highlights Accuracy Gaps in Consumer Gut Microbiome Kits
Direct-to-consumer gut microbiome kits promise personalized insights by profiling fecal bacteria and generating health readouts, but their analytical accuracy remains uncertain. A new study shows that... Read more
WHO Recommends Near POC Tests, Tongue Swabs and Sputum Pooling for TB Diagnosis
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s leading infectious disease killers, yet millions of cases go undiagnosed or are detected too late. Barriers such as reliance on sputum samples, limited laboratory... Read morePathology
view channel
Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
DNA methylation is an important biological marker used in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases, including cancer. These chemical modifications to DNA influence gene activity and can reveal early... Read more
Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease present ongoing diagnostic challenges, with women often experiencing a disproportionate disease burden even when preclinical amyloid-beta levels are similar to men.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Agilent Technologies Acquires Pathology Diagnostics Company Biocare Medical
Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, USA) has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Biocare Medical (Pacheco, CA, USA), expanding its pathology portfolio through the addition of highly complementary... Read more
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more



















