New sPCR Technology Runs on Standard Devices
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 24 Apr 2017 |
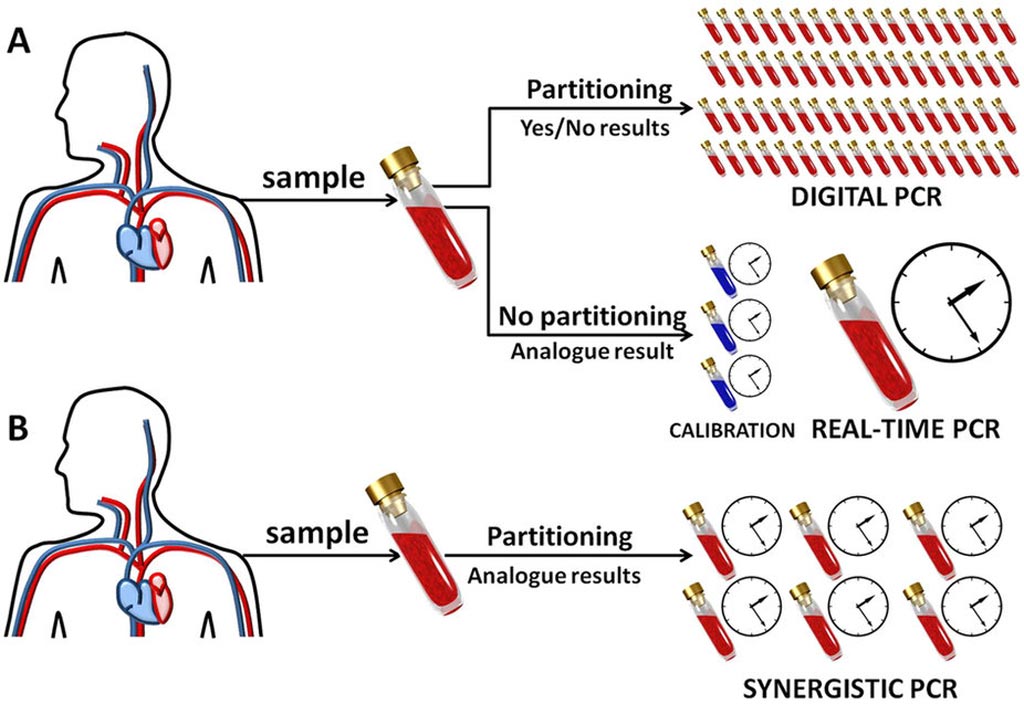
Image: A comparison of analytical PCR procedures (Photo courtesy of Scientific Reports).
Synergistic PCR (sPCR), a new method of DNA analysis developed for use on a new high-speed assay device, can also be carried out on widely available laboratory real-time PCR (qPCR) instruments and does not require calibration.
While developing a record high-speed genetic research tool, Curiosity Diagnostics (CD; Warsaw, Poland), a spinoff company of the Warsaw Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS) and part of the Scope Fluidics group, has developed the new sPCR method, which combines key advantages of the two currently most used methods.
"The DNA assay technique we propose was born during the development of the innovative PCR|ONE analytical instrument, which can be used to test the genetic code in only 7 minutes. This is more than 10-fold shorter time than is required in classic solutions," said Prof. Piotr Garstecki (IPC PAS, CD).
PCR is used both to detect specific DNA fragments and to estimate the original amount of genetic material. In quantitative PCR (qPCR) measurements are usually carried out using real-time PCR – an analogue technique. Due to the sensitivity of PCR to even single particles of impurities, qPCR requires careful, continuous calibration. Conversely, in digital PCR (dPCR) there is no need to calibrate the device, however, because of the need to conduct a large number of reactions in parallel, the testing equipment is expensive and is not as common in laboratories as the analogue apparatus.
sPCR combines the most important advantages of analogue and digital methods to obtain reliable measurements: it is sufficient to dilute a sample into only a dozen or at most several dozen partitions, and calibration is not required.
"A small number of partitions, characteristic of our technique, are of specific practical significance. It means that to perform the analysis all that is needed is the standard well plate format used in popular analogue PCR devices," said Pawel Debski, an IPC PAS PhD student who developed the sPCR method with Curiosity Diagnostics.
Also due to a small number of sample partitions, the sPCR technique is easier to perform and slightly faster than digital variants. Compared to analogue techniques, however, more reagents are required, and so it will not replace the analogue variant. Nevertheless, sPCR could be a valuable addition, as it requires no calibration and so will allow laboratory staff to independently and regularly check the correctness of analogue measurements.
sPCR was developed as an integral component of PCR|ONE, an innovative device designed for rapid DNA analysis. In standard PCR machines, relatively slow heat diffusion between the sample and an adjacent large block of alternately heated or cooled material is used to heat and cool the genetic material. In PCR|ONE, infrared radiation is used to heat the sample rapidly. The diffusion cooling mechanism has also been modified: the block used for this purpose is smaller than in conventional instruments and it is maintained at a constant, strictly controlled temperature. As a result of the technical and analytical improvements, the currently being tested prototypes of PCR|ONE are able to complete DNA assays in less than 15 minutes, and the PCR itself takes only 7 minutes. The first PCR|ONE devices are expected to be commercially available in 2-3 years.
"Our DNA testing technique has been patented. However, we want to emphasize the freedom of using it for non-commercial purposes," said Prof. Garstecki.
The study, by Debski PR et al, was published March 22, 2017, in the journal Scientific Reports.
While developing a record high-speed genetic research tool, Curiosity Diagnostics (CD; Warsaw, Poland), a spinoff company of the Warsaw Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences (IPC PAS) and part of the Scope Fluidics group, has developed the new sPCR method, which combines key advantages of the two currently most used methods.
"The DNA assay technique we propose was born during the development of the innovative PCR|ONE analytical instrument, which can be used to test the genetic code in only 7 minutes. This is more than 10-fold shorter time than is required in classic solutions," said Prof. Piotr Garstecki (IPC PAS, CD).
PCR is used both to detect specific DNA fragments and to estimate the original amount of genetic material. In quantitative PCR (qPCR) measurements are usually carried out using real-time PCR – an analogue technique. Due to the sensitivity of PCR to even single particles of impurities, qPCR requires careful, continuous calibration. Conversely, in digital PCR (dPCR) there is no need to calibrate the device, however, because of the need to conduct a large number of reactions in parallel, the testing equipment is expensive and is not as common in laboratories as the analogue apparatus.
sPCR combines the most important advantages of analogue and digital methods to obtain reliable measurements: it is sufficient to dilute a sample into only a dozen or at most several dozen partitions, and calibration is not required.
"A small number of partitions, characteristic of our technique, are of specific practical significance. It means that to perform the analysis all that is needed is the standard well plate format used in popular analogue PCR devices," said Pawel Debski, an IPC PAS PhD student who developed the sPCR method with Curiosity Diagnostics.
Also due to a small number of sample partitions, the sPCR technique is easier to perform and slightly faster than digital variants. Compared to analogue techniques, however, more reagents are required, and so it will not replace the analogue variant. Nevertheless, sPCR could be a valuable addition, as it requires no calibration and so will allow laboratory staff to independently and regularly check the correctness of analogue measurements.
sPCR was developed as an integral component of PCR|ONE, an innovative device designed for rapid DNA analysis. In standard PCR machines, relatively slow heat diffusion between the sample and an adjacent large block of alternately heated or cooled material is used to heat and cool the genetic material. In PCR|ONE, infrared radiation is used to heat the sample rapidly. The diffusion cooling mechanism has also been modified: the block used for this purpose is smaller than in conventional instruments and it is maintained at a constant, strictly controlled temperature. As a result of the technical and analytical improvements, the currently being tested prototypes of PCR|ONE are able to complete DNA assays in less than 15 minutes, and the PCR itself takes only 7 minutes. The first PCR|ONE devices are expected to be commercially available in 2-3 years.
"Our DNA testing technique has been patented. However, we want to emphasize the freedom of using it for non-commercial purposes," said Prof. Garstecki.
The study, by Debski PR et al, was published March 22, 2017, in the journal Scientific Reports.
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Swab Test Helps Transplant Patients Receive Right Anti-Rejection Medication Dose
- Blood Test Predicts Which Bladder Cancer Patients May Safely Skip Surgery
- Ultra-Sensitive DNA Test Identifies Relapse Risk in Aggressive Leukemia
- Blood Test Could Help Detect Gallbladder Cancer Earlier
- New Blood Test Score Detects Hidden Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- New Blood Test Predicts Who Will Most Likely Live Longer
- Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
- Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
- New Genome Sequencing Technique Measures Epstein-Barr Virus in Blood
- Blood Test Boosts Early Detection of Brain Cancer
- Molecular Monitoring Approach Helps Bladder Cancer Patients Avoid Surgery
- Genetic Tests to Speed Diagnosis of Lymphatic Disorders
- Changes In Lymphatic Vessels Can Aid Early Identification of Aggressive Oral Cancer
- New Extraction Kit Enables Consistent, Scalable cfDNA Isolation from Multiple Biofluids
- New CSF Liquid Biopsy Assay Reveals Genomic Insights for CNS Tumors
- AI-Powered Liquid Biopsy Classifies Pediatric Brain Tumors with High Accuracy
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read more
Hidden Gut Viruses Linked to Colorectal Cancer Risk
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality in many Western countries, and existing risk-stratification approaches leave substantial room for improvement. Although age, diet, and... Read morePathology
view channel
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read more
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more


















