Immunoassay Device Based on Acoustic Vortex Nanoparticle Enrichment
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 08 Feb 2017 |
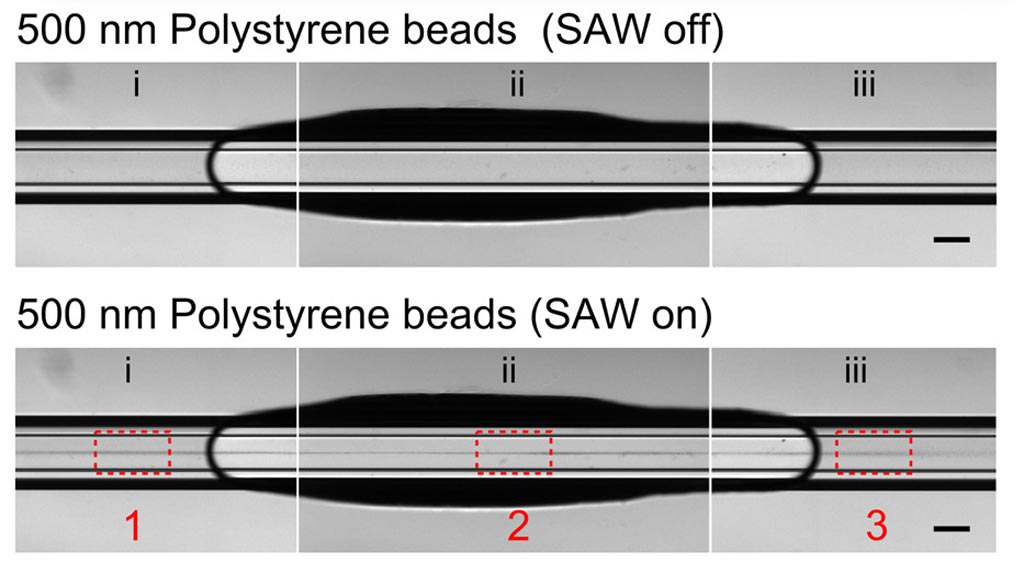
Image: A sample of 500 nanometer particles in solution. In the top image, the acoustic whirlpool device was turned off. The bottom image shows that when the device was turned on, the nanoparticles were concentrated to the point of becoming visible as a dark line down the center of the chamber (Photo courtesy of Duke University).
An inexpensive acoustic transducer is the key to a novel immunoassay that may eventually be combined with a smartphone camera to form a platform for the rapid detection of diagnostic proteins in blood, urine, or saliva samples.
Investigators at Duke University developed an acoustic-fluidic chip capable of generating single vortex acoustic streaming inside a glass capillary through using low-power acoustic waves (only five volts was required). The single vortex acoustic streaming that was generated, in conjunction with the acoustic radiation force, was able to enrich submicrometer- and nanometer-sized particles in a small volume. Numerical simulations were used to clarify the mechanism of the single vortex formation and were verified experimentally, demonstrating the focusing of silica and polystyrene particles ranging in diameter from 80 to 500 nanometers.
In a proof-of-principle study, the acoustic-fluidic chip was used to perform an immunoassay in which nanoparticles that captured fluorescently labeled biomarkers were concentrated in a long, thin glass vial to enhance the emitted signal.
“Diagnosis impacts about 70% of healthcare decisions,” said senior author Dr. Tony Huang, professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at Duke University. “If we can improve the quality of diagnostics while reducing its costs, then we can tremendously improve the entire healthcare system. My goal is to create a small diagnostic device about the size of a cell phone that can autonomously separate biomarkers from samples. With this vortex technology, the biomarkers could then be concentrated enough to see with a simple camera like the ones found in today’s cellular phones.”
Investigators at Duke University developed an acoustic-fluidic chip capable of generating single vortex acoustic streaming inside a glass capillary through using low-power acoustic waves (only five volts was required). The single vortex acoustic streaming that was generated, in conjunction with the acoustic radiation force, was able to enrich submicrometer- and nanometer-sized particles in a small volume. Numerical simulations were used to clarify the mechanism of the single vortex formation and were verified experimentally, demonstrating the focusing of silica and polystyrene particles ranging in diameter from 80 to 500 nanometers.
In a proof-of-principle study, the acoustic-fluidic chip was used to perform an immunoassay in which nanoparticles that captured fluorescently labeled biomarkers were concentrated in a long, thin glass vial to enhance the emitted signal.
“Diagnosis impacts about 70% of healthcare decisions,” said senior author Dr. Tony Huang, professor of mechanical engineering and materials science at Duke University. “If we can improve the quality of diagnostics while reducing its costs, then we can tremendously improve the entire healthcare system. My goal is to create a small diagnostic device about the size of a cell phone that can autonomously separate biomarkers from samples. With this vortex technology, the biomarkers could then be concentrated enough to see with a simple camera like the ones found in today’s cellular phones.”
Latest Technology News
- AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channelNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read more
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
New Blood Test Can Help Predict Testicular Cancer Recurrence
Stage 1 testicular germ cell tumor is typically treated with surgery followed by active surveillance. Although most patients experience strong long-term outcomes, about one in four will see their cancer... Read more
New Test Detects Alzheimer’s by Analyzing Altered Protein Shapes in Blood
Alzheimer’s disease begins developing years before memory loss or other symptoms become visible. Misfolded proteins gradually accumulate in the brain, disrupting normal cellular processes.... Read more
New Diagnostic Markers for Multiple Sclerosis Discovered in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects nearly three million people worldwide and can cause symptoms such as numbness, visual disturbances, fatigue, and neurological disability. Diagnosing the disease can be challenging... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read more
Blood-Based Viral Signature Identified in Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disorder affecting approximately 0.4% of the European population, with symptoms and progression that vary widely. Although viral components of the microbiome... Read morePathology
view channel
Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing became widely recognized during the COVID-19 pandemic as a powerful method for detecting viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. PCR belongs to a group of diagnostic methods... Read more
Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer and accounts for the vast majority of skin cancer-related deaths. Because early melanomas can closely resemble benign moles, clinicians often rely on visual... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more



















