Changes in Eye Tissue May Enable Early Detection of Brain Diseases
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 11 Oct 2016 |
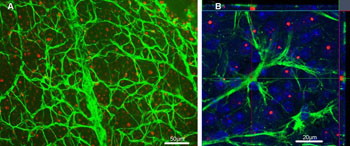
Image: An experiment examining retina tissue for mHtt deposition in GFAP-ir astrocytes in R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s Disease. Green: glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP); Red: mutant huntingtin protein (mHtt). (A) A low magnification picture illustrates GFAP-ir astrocytes and mHtt deposits from the retinal wholemount of 12-week-old R6/2 (Huntington’s disease model) mouse. Scale bar = 50 µm. (B) A detailed confocal analysis of GFAP positivity, mHtt immunoreactivity, and DAPI counterstain (blue) revealed no colocalization of GFAP and mHtt. Scale bar = 20 µm (Image courtesy of PLoS One).
Research with mouse models has shown that at least some diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) manifest as pathological changes in the retina of the eye and that these changes may be detected earlier than brain changes. The findings suggest that eye examination could be used for minimally invasive screening for these diseases.
Retina tissue can be considered an integral part of the central nervous system (CNS). During fetal development, it matures from part of the brain and its innervation closely resembles that of the brain. Retinal structure and function can be readily examined with noninvasive or minimally invasive methods, whereas direct brain examination has numerous limitations. If, at least for some brain diseases, the health status of the brain could be indirectly assessed through the eyes, diagnostic screening could become more efficient.
In his PhD project at the University of Eastern Finland at Kuopio (Kuopio, Finland), Dr. Henri Leinonen and colleagues investigated functional abnormalities of the retina using mouse models of human CNS diseases. Electroretinography (ERG) and visual evoked potentials (VEP) were chosen as research techniques, since similar methodology can be applied in both laboratory animals and humans. ERG can precisely track the function of retina using corneal or skin electrodes, whereas VEP measures the function of visual cortex.
These methods were used to test different attributes of vision in 3 distinct genetically engineered mouse models of human CNS diseases. Also, basic life science methods were used to test the correlation between functional abnormalities and the anatomical status of the retina.
Day and color vision -associated retinal dysfunction was found in a mouse model of Huntington´s disease (HD) while the mouse was presymptomatic. Retinal structure remained relatively normal, even in an advanced disease state, although aggregation of toxic mutated huntingtin-protein was widespread in the diseased mouse retina. Although the retinopathy in mice is exaggerated compared to human HD patients, the finding is partly in line with patient data showing impaired color vision but no clear-cut anatomical retinopathy.
In a mouse model of Alzheimer´s disease (AD), the researchers observed abnormality in night vision -associated retinal function. Specifically, rod-mediated inner retinal responses to dim light flashes were faster in diseased mice than in their wild-type controls. The observation may be explained by impaired cholinergic neurotransmission that is also partly causative for the deterioration of memory in AD.
In a mouse model of late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL), a pediatric neurological disease, the researchers described retinal degenerative changes that mimic the characteristic pathology of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). These included impaired function of retinal pigment epithelium and subsequent blindness due to photoreceptor atrophy and death. It has been postulated that the retinal degeneration in human patients progresses similarly.
Adding to the growing body of evidence, the results showed that functional changes of the retina occur in mouse models of three human CNS diseases whose phenotype, age of onset, and pathological mechanism clearly differ from each other. Visual impairment was the fastest progressive symptom in two models tested.
The findings support the idea of eye examinations as potential screening tools for CNS diseases. Development of efficient, safe, and economic screening is imperative since the diagnosis of these diseases is often obtained only in the advanced disease state, when as such satisfactory remedies are poorly effective. Since eye and vision research can be conducted noninvasively, advancement of trials from the preclinical to the clinical phase could be relatively fast.
Dr. Leinonen’s doctoral dissertation, entitled “Electrophysiology of visual pathways as a screening tool for neurodegenerative diseases: evidence from mouse disease models”, is available for download. The findings were published in PLoS One, the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, and most recently in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
Related Links:
University of Eastern Finland
Retina tissue can be considered an integral part of the central nervous system (CNS). During fetal development, it matures from part of the brain and its innervation closely resembles that of the brain. Retinal structure and function can be readily examined with noninvasive or minimally invasive methods, whereas direct brain examination has numerous limitations. If, at least for some brain diseases, the health status of the brain could be indirectly assessed through the eyes, diagnostic screening could become more efficient.
In his PhD project at the University of Eastern Finland at Kuopio (Kuopio, Finland), Dr. Henri Leinonen and colleagues investigated functional abnormalities of the retina using mouse models of human CNS diseases. Electroretinography (ERG) and visual evoked potentials (VEP) were chosen as research techniques, since similar methodology can be applied in both laboratory animals and humans. ERG can precisely track the function of retina using corneal or skin electrodes, whereas VEP measures the function of visual cortex.
These methods were used to test different attributes of vision in 3 distinct genetically engineered mouse models of human CNS diseases. Also, basic life science methods were used to test the correlation between functional abnormalities and the anatomical status of the retina.
Day and color vision -associated retinal dysfunction was found in a mouse model of Huntington´s disease (HD) while the mouse was presymptomatic. Retinal structure remained relatively normal, even in an advanced disease state, although aggregation of toxic mutated huntingtin-protein was widespread in the diseased mouse retina. Although the retinopathy in mice is exaggerated compared to human HD patients, the finding is partly in line with patient data showing impaired color vision but no clear-cut anatomical retinopathy.
In a mouse model of Alzheimer´s disease (AD), the researchers observed abnormality in night vision -associated retinal function. Specifically, rod-mediated inner retinal responses to dim light flashes were faster in diseased mice than in their wild-type controls. The observation may be explained by impaired cholinergic neurotransmission that is also partly causative for the deterioration of memory in AD.
In a mouse model of late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL), a pediatric neurological disease, the researchers described retinal degenerative changes that mimic the characteristic pathology of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). These included impaired function of retinal pigment epithelium and subsequent blindness due to photoreceptor atrophy and death. It has been postulated that the retinal degeneration in human patients progresses similarly.
Adding to the growing body of evidence, the results showed that functional changes of the retina occur in mouse models of three human CNS diseases whose phenotype, age of onset, and pathological mechanism clearly differ from each other. Visual impairment was the fastest progressive symptom in two models tested.
The findings support the idea of eye examinations as potential screening tools for CNS diseases. Development of efficient, safe, and economic screening is imperative since the diagnosis of these diseases is often obtained only in the advanced disease state, when as such satisfactory remedies are poorly effective. Since eye and vision research can be conducted noninvasively, advancement of trials from the preclinical to the clinical phase could be relatively fast.
Dr. Leinonen’s doctoral dissertation, entitled “Electrophysiology of visual pathways as a screening tool for neurodegenerative diseases: evidence from mouse disease models”, is available for download. The findings were published in PLoS One, the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, and most recently in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
Related Links:
University of Eastern Finland
Latest Pathology News
- Sex Differences in Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Linked to Faster Cognitive Decline
- World’s First Optical Microneedle Device to Enable Blood-Sampling-Free Clinical Testing
- Novel mcPCR Technology to Transform Testing of Clinical Samples
- Pathogen-Agnostic Testing Reveals Hidden Respiratory Threats in Negative Samples
- Molecular Imaging to Reduce Need for Melanoma Biopsies
- Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
- AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
- Single Sample Classifier Predicts Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subtypes in Patient Samples
- New AI-Driven Platform Standardizes Tuberculosis Smear Microscopy Workflow
- AI Tool Uses Blood Biomarkers to Predict Transplant Complications Before Symptoms Appear
- High-Resolution Cancer Virus Imaging Uncovers Potential Therapeutic Targets
- Research Consortium Harnesses AI and Spatial Biology to Advance Cancer Discovery
- AI Tool Helps See How Cells Work Together Inside Diseased Tissue
- AI-Powered Microscope Diagnoses Malaria in Blood Smears Within Minutes
- Engineered Yeast Cells Enable Rapid Testing of Cancer Immunotherapy
- First-Of-Its-Kind Test Identifies Autism Risk at Birth
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
AI Sensor Detects Neurological Disorders Using Single Saliva Drop
Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease often develop gradually and present subtle symptoms in their early stages. Because early signs are frequently vague or atypical,... Read moreNew Blood Test Index Offers Earlier Detection of Liver Scarring
Metabolic fatty liver disease is highly prevalent and often silent, yet it can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. Current first-line blood test scores frequently return indeterminate results,... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Simple One-Hour Saliva Test Detects Common Cancers
Early detection is critical for improving cancer outcomes, yet many diagnostic tests rely on invasive procedures such as blood draws or biopsies. Researchers are exploring simpler approaches that could... Read more
Blood Test Could Help Guide Treatment Decisions in Germ Cell Tumors
Chemotherapy is often highly effective for germ cell tumors, but in a subset of patients, the disease does not respond well to standard treatment. For these individuals, doctors may consider high-dose... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Cancer Mutation ‘Fingerprints’ to Improve Prediction of Immunotherapy Response
Cancer cells accumulate thousands of genetic mutations, but not all mutations affect tumors in the same way. Some make cancer cells more visible to the immune system, while others allow tumors to evade... Read more
Immune Signature Identified in Treatment-Resistant Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a rare autoimmune disorder in which immune attack at the neuromuscular junction causes fluctuating weakness that can impair vision, movement, speech, swallowing, and breathing.... Read more
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Help Predict Dangerous Gut Infection
Clostridioides difficile infections affect roughly half a million people in the United States each year and are a leading cause of infectious diarrhea in healthcare settings. The bacterium can trigger... Read more
Rapid Sequencing Could Transform Tuberculosis Care
Tuberculosis remains the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, responsible for more than one million deaths each year. Diagnosing and monitoring the disease can be slow because... Read moreTechnology
view channel
AI Model Outperforms Clinicians in Rare Disease Detection
Rare diseases affect an estimated 300 million people worldwide, yet diagnosis is often protracted and error-prone. Many conditions present with heterogeneous signs that overlap with common disorders, leading... Read more
AI-Driven Diagnostic Demonstrates High Accuracy in Detecting Periprosthetic Joint Infection
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a rare but serious complication affecting 1% to 2% of primary joint replacement surgeries. The condition occurs when bacteria or fungi infect tissues around an implanted... Read moreIndustry
view channel
Cepheid Joins CDC Initiative to Strengthen U.S. Pandemic Testing Preparednesss
Cepheid (Sunnyvale, CA, USA) has been selected by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as one of four national collaborators in a federal initiative to speed rapid diagnostic technologies... Read more
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more




















