New Infectious Disease Test Promises Quick Diagnosis
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 05 Jan 2016 |
Image: Colored Transmission electron micrograph of Clostridium difficile forming an endospore (red) (Photo courtesy of Dr. J. Thomas Lamont).
Early detection of specific pathogens has long been recognized as a vital strategy in the control of infectious diseases because it can lead to timely care of patients and prevent potential outbreaks.
The detection of specific bacteria represents a significant challenge because of the presence of many different species of bacteria in biological samples. Furthermore, for any given species of bacterium, only virulent strains are infectious while other strains of the same species may be harmless or even beneficial to human health.
A team of scientists led by those at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada) found a way to make DNAzymes, or single-stranded catalytic DNA molecules from a simple test tube technique that allows for isolation of rare DNA sequences with special functions. The team's first success was the development of a molecular probe that precisely recognizes the strain which caused the outbreak of Clostridium difficile infection in Hamilton, Ontario in 2011. This strain was very infectious, resistant to antibiotics and even fatal to some patients. Instead of having to do several different tests to narrow down to a positive identification of the specific strain, the scientists can now quickly pinpoint this superbug using their new molecular probe.
The team obtained an RNA-cleaving fluorogenic DNAzyme (RFD) that can recognize an infectious strain of C. difficile. This DNAzyme not only exhibits no cross-reactivity to other bacterial species, but also is highly strain-selective for C. difficile. The special DNAzyme (catalytic DNA), RFD-CD1, showed exquisite specificity for a pathogenic strain of C. difficile. RFD-CD1 was derived by an in vitro selection approach where a random-sequence DNA library was allowed to react with an unpurified molecular mixture derived from this strain of C. difficile, coupled with a subtractive selection strategy to eliminate cross-reactivities to unintended C. difficile strains and other bacteria species.
Bruno J. Salena, MD, an associate professor of medicine and coauthor of the study, said, “This technology can be extended to the further discovery of other superbug strain-specific pathogens. For example, such technology would prove useful in the identification of hypervirulent or resistant strains, implementation of the most appropriate strain-specific treatments and tracking of outbreaks.” The study was published on December 16, 2015, in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Related Links:
McMaster University
The detection of specific bacteria represents a significant challenge because of the presence of many different species of bacteria in biological samples. Furthermore, for any given species of bacterium, only virulent strains are infectious while other strains of the same species may be harmless or even beneficial to human health.
A team of scientists led by those at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada) found a way to make DNAzymes, or single-stranded catalytic DNA molecules from a simple test tube technique that allows for isolation of rare DNA sequences with special functions. The team's first success was the development of a molecular probe that precisely recognizes the strain which caused the outbreak of Clostridium difficile infection in Hamilton, Ontario in 2011. This strain was very infectious, resistant to antibiotics and even fatal to some patients. Instead of having to do several different tests to narrow down to a positive identification of the specific strain, the scientists can now quickly pinpoint this superbug using their new molecular probe.
The team obtained an RNA-cleaving fluorogenic DNAzyme (RFD) that can recognize an infectious strain of C. difficile. This DNAzyme not only exhibits no cross-reactivity to other bacterial species, but also is highly strain-selective for C. difficile. The special DNAzyme (catalytic DNA), RFD-CD1, showed exquisite specificity for a pathogenic strain of C. difficile. RFD-CD1 was derived by an in vitro selection approach where a random-sequence DNA library was allowed to react with an unpurified molecular mixture derived from this strain of C. difficile, coupled with a subtractive selection strategy to eliminate cross-reactivities to unintended C. difficile strains and other bacteria species.
Bruno J. Salena, MD, an associate professor of medicine and coauthor of the study, said, “This technology can be extended to the further discovery of other superbug strain-specific pathogens. For example, such technology would prove useful in the identification of hypervirulent or resistant strains, implementation of the most appropriate strain-specific treatments and tracking of outbreaks.” The study was published on December 16, 2015, in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Related Links:
McMaster University
Latest Technology News
- Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
- AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
- Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
- ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
- Aptamer Biosensor Technology to Transform Virus Detection
- AI Models Could Predict Pre-Eclampsia and Anemia Earlier Using Routine Blood Tests
- AI-Generated Sensors Open New Paths for Early Cancer Detection
- Pioneering Blood Test Detects Lung Cancer Using Infrared Imaging
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
Electronic Nose Smells Early Signs of Ovarian Cancer in Blood
Ovarian cancer is often diagnosed at a late stage because its symptoms are vague and resemble those of more common conditions. Unlike breast cancer, there is currently no reliable screening method, and... Read more
Simple Blood Test Offers New Path to Alzheimer’s Assessment in Primary Care
Timely evaluation of cognitive symptoms in primary care is often limited by restricted access to specialized diagnostics and invasive confirmatory procedures. Clinicians need accessible tools to determine... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel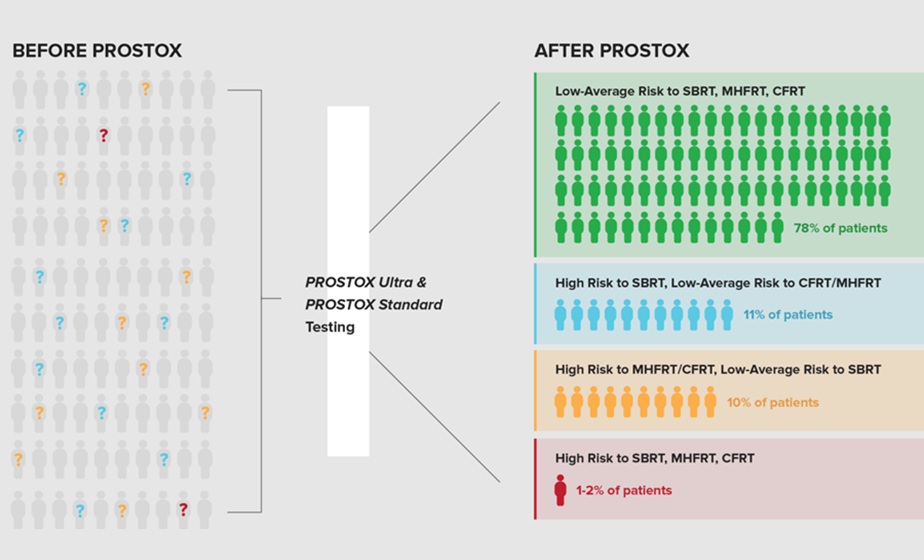
Genetic Test Predicts Radiation Therapy Risk for Prostate Cancer Patients
External beam radiation therapy is widely used to treat localized prostate cancer, which has a five-year survival rate exceeding 99%. However, more than 20% of patients develop persistent urinary side... Read more
Genetic Test Aids Early Detection and Improved Treatment for Cancers
Lynch syndrome is a hereditary genetic condition that significantly increases the risk of several cancers, including those of the bowel and urinary tract. Urinary tract cancers—affecting the kidney, bladder,... Read moreHematology
view channel
Rapid Cartridge-Based Test Aims to Expand Access to Hemoglobin Disorder Diagnosis
Sickle cell disease and beta thalassemia are hemoglobin disorders that often require referral to specialized laboratories for definitive diagnosis, delaying results for patients and clinicians.... Read more
New Guidelines Aim to Improve AL Amyloidosis Diagnosis
Light chain (AL) amyloidosis is a rare, life-threatening bone marrow disorder in which abnormal amyloid proteins accumulate in organs. Approximately 3,260 people in the United States are diagnosed... Read moreImmunology
view channel
New Biomarker Predicts Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer is an aggressive form of breast cancer in which patients often show widely varying responses to chemotherapy. Predicting who will benefit from treatment remains challenging,... Read moreBlood Test Identifies Lung Cancer Patients Who Can Benefit from Immunotherapy Drug
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive disease with limited treatment options, and even newly approved immunotherapies do not benefit all patients. While immunotherapy can extend survival for some,... Read more
Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach Identifies Cancer Patients Benefitting From PARP-Inhibitor Treatment
Targeted cancer therapies such as PARP inhibitors can be highly effective, but only for patients whose tumors carry specific DNA repair defects. Identifying these patients accurately remains challenging,... Read more
Ultrasensitive Liquid Biopsy Demonstrates Efficacy in Predicting Immunotherapy Response
Immunotherapy has transformed cancer treatment, but only a small proportion of patients experience lasting benefit, with response rates often remaining between 10% and 20%. Clinicians currently lack reliable... Read morePathology
view channel
Urine Specimen Collection System Improves Diagnostic Accuracy and Efficiency
Urine testing is a critical, non-invasive diagnostic tool used to detect conditions such as pregnancy, urinary tract infections, metabolic disorders, cancer, and kidney disease. However, contaminated or... Read more
AI-Powered 3D Scanning System Speeds Cancer Screening
Cytology remains a cornerstone of cancer detection, requiring specialists to examine bodily fluids and cells under a microscope. This labor-intensive process involves inspecting up to one million cells... Read moreTechnology
view channel
Blood Test “Clocks” Predict Start of Alzheimer’s Symptoms
More than 7 million Americans live with Alzheimer’s disease, and related health and long-term care costs are projected to reach nearly USD 400 billion in 2025. The disease has no cure, and symptoms often... Read more
AI-Powered Biomarker Predicts Liver Cancer Risk
Liver cancer, or hepatocellular carcinoma, causes more than 800,000 deaths worldwide each year and often goes undetected until late stages. Even after treatment, recurrence rates reach 70% to 80%, contributing... Read more
Robotic Technology Unveiled for Automated Diagnostic Blood Draws
Routine diagnostic blood collection is a high‑volume task that can strain staffing and introduce human‑dependent variability, with downstream implications for sample quality and patient experience.... Read more
ADLM Launches First-of-Its-Kind Data Science Program for Laboratory Medicine Professionals
Clinical laboratories generate billions of test results each year, creating a treasure trove of data with the potential to support more personalized testing, improve operational efficiency, and enhance patient care.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
QuidelOrtho Collaborates with Lifotronic to Expand Global Immunoassay Portfolio
QuidelOrtho (San Diego, CA, USA) has entered a long-term strategic supply agreement with Lifotronic Technology (Shenzhen, China) to expand its global immunoassay portfolio and accelerate customer access... Read more